Quickstart: Use Azure Cache for Redis with an ASP.NET Core web app
In this quickstart, you incorporate Azure Cache for Redis into an ASP.NET Core web application that connects to Azure Cache for Redis to store and retrieve data from the cache.
There are also caching providers in .NET core. To quickly start using Redis with minimal changes to your existing code, see:
- ASP.NET core Output Cache provider
- ASP.NET core Distributed Caching provider
- ASP.NET core Redis session provider
Skip to the code on GitHub
Clone the repo https://github.com/Azure-Samples/azure-cache-redis-samples/tree/main/quickstart/aspnet-core on GitHub.
As a next step, you can see a real-world scenario eShop application demonstrating the ASP.NET core caching providers: ASP.NET core eShop using Redis caching providers.
Features included:
- Redis Distributed Caching
- Redis session state provider
Deployment instructions are in the README.md.
Prerequisites
- Azure subscription - create one for free
- .NET Core SDK
Create a cache
To create a cache, sign in to the Azure portal and select Create a resource.

On the Get Started page, type Azure Cache for Redis in the search box. Then, select Create.

On the New Redis Cache page, configure the settings for your cache.
Setting Choose a value Description Subscription Drop down and select your subscription. The subscription under which to create this new Azure Cache for Redis instance. Resource group Drop down and select a resource group, or select Create new and enter a new resource group name. Name for the resource group in which to create your cache and other resources. By putting all your app resources in one resource group, you can easily manage or delete them together. DNS name Enter a unique name. The cache name must be a string between 1 and 63 characters that contain only numbers, letters, or hyphens. The name must start and end with a number or letter, and can't contain consecutive hyphens. Your cache instance's host name is <DNS name>.redis.cache.windows.net. Location Drop down and select a location. Select a region near other services that use your cache. Cache SKU Drop down and select a SKU. The SKU determines the size, performance, and features parameters that are available for the cache. For more information, see Azure Cache for Redis Overview. Cache size Drop down and select a size of your cache For more information, see Azure Cache for Redis Overview. Select the Networking tab or select the Networking button at the bottom of the page.
In the Networking tab, select your connectivity method.
Select the Next: Advanced tab or select the Next: Advanced button on the bottom of the page to see the Advanced tab.
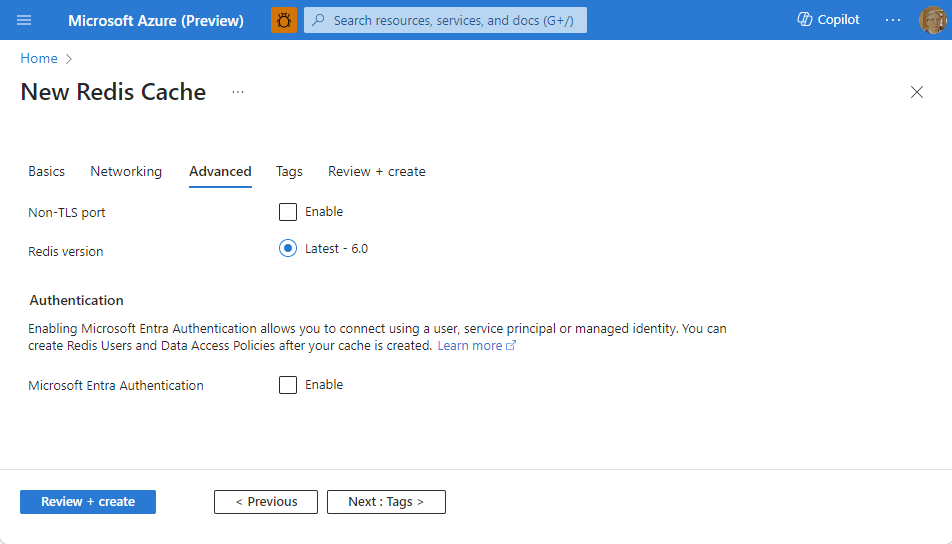
- For Basic or Standard caches, toggle the selection for a non-TLS port. You can also select if you want to enable Microsoft Entra Authentication.
- For a Premium cache, configure the settings for non-TLS port, clustering, managed identity, and data persistence. You can also select if you want to enable Microsoft Entra Authentication.
Select the Next: Tags tab or select the Next: Tags button at the bottom of the page.
Optionally, in the Tags tab, enter the name and value if you wish to categorize the resource.
Select Review + create. You're taken to the Review + create tab where Azure validates your configuration.
After the green Validation passed message appears, select Create.
It takes a while for a cache to create. You can monitor progress on the Azure Cache for Redis Overview page. When Status shows as Running, the cache is ready to use.
Retrieve host name, ports, and access keys from the Azure portal
To connect your Azure Cache for Redis server, the cache client needs the host name, ports, and a key for the cache. Some clients might refer to these items by slightly different names. You can get the host name, ports, and keys from the Azure portal.
To get the access keys, select Authentication from the Resource menu. Then, select the Access keys tab.

To get the host name and ports for your cache, select Overview from the Resource menu. The host name is of the form <DNS name>.redis.cache.windows.net.
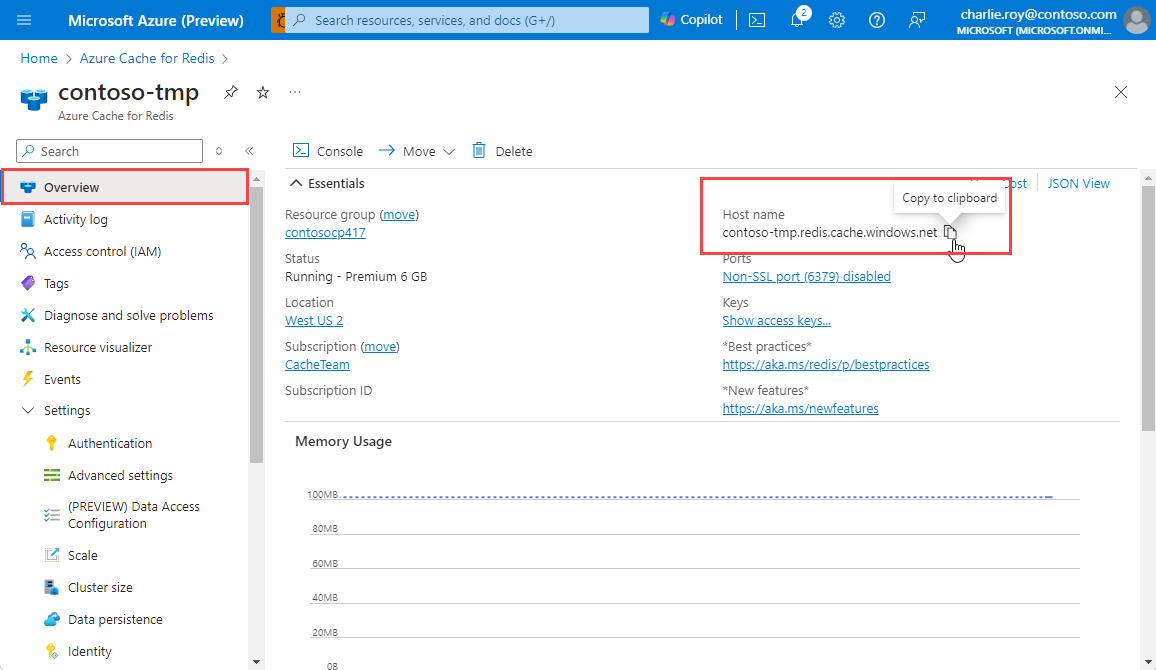
Make a note of the HOST NAME and the Primary access key. You use these values later to construct the CacheConnection secret.
Add a local secret for the connection string
In your command window, execute the following command to store a new secret named CacheConnection, after replacing the placeholders, including angle brackets, for your cache name and primary access key:
dotnet user-secrets set CacheConnection "<cache name>.redis.cache.windows.net,abortConnect=false,ssl=true,allowAdmin=true,password=<primary-access-key>"
Connect to the cache with RedisConnection
The RedisConnection class manages the connection to your cache. The connection is made in this statement in HomeController.cs in the Controllers folder:
_redisConnection = await _redisConnectionFactory;
In RedisConnection.cs, you see the StackExchange.Redis namespace is added to the code. This is needed for the RedisConnection class.
using StackExchange.Redis;
The RedisConnection code ensures that there's always a healthy connection to the cache by managing the ConnectionMultiplexer instance from StackExchange.Redis. The RedisConnection class recreates the connection when a connection is lost and unable to reconnect automatically.
For more information, see StackExchange.Redis and the code in a GitHub repo.
Layout views in the sample
The home page layout for this sample is stored in the _Layout.cshtml file. From this page, you start the actual cache testing by clicking the Azure Cache for Redis Test from this page.
Open Views\Shared\_Layout.cshtml.
You should see in
<div class="navbar-header">:<a class="navbar-brand" asp-area="" asp-controller="Home" asp-action="RedisCache">Azure Cache for Redis Test</a>
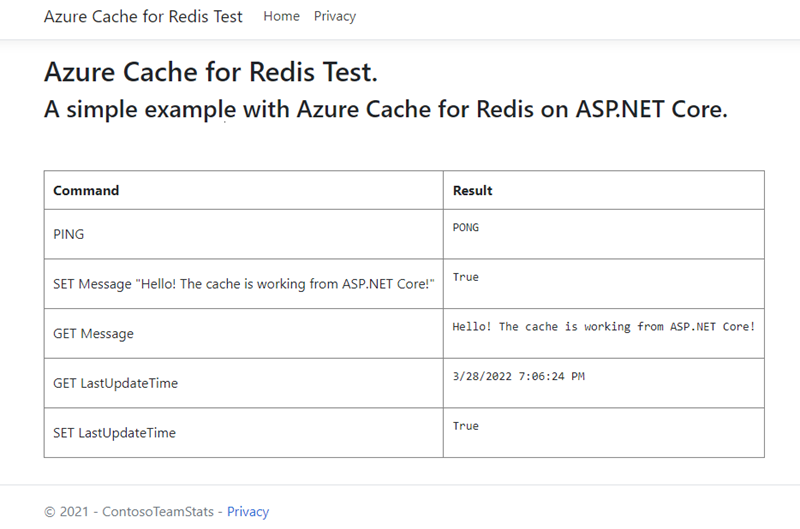
Showing data from the cache
From the home page, you select Azure Cache for Redis Test to see the sample output.
In Solution Explorer, expand the Views folder, and then right-click the Home folder.
You should see this code in the RedisCache.cshtml file.
@{ ViewBag.Title = "Azure Cache for Redis Test"; } <h2>@ViewBag.Title.</h2> <h3>@ViewBag.Message</h3> <br /><br /> <table border="1" cellpadding="10"> <tr> <th>Command</th> <th>Result</th> </tr> <tr> <td>@ViewBag.command1</td> <td><pre>@ViewBag.command1Result</pre></td> </tr> <tr> <td>@ViewBag.command2</td> <td><pre>@ViewBag.command2Result</pre></td> </tr> <tr> <td>@ViewBag.command3</td> <td><pre>@ViewBag.command3Result</pre></td> </tr> <tr> <td>@ViewBag.command4</td> <td><pre>@ViewBag.command4Result</pre></td> </tr> <tr> <td>@ViewBag.command5</td> <td><pre>@ViewBag.command5Result</pre></td> </tr> </table>
Run the app locally
Execute the following command in your command window to build the app:
dotnet buildThen run the app with the following command:
dotnet runBrowse to
https://localhost:5001in your web browser.Select Azure Cache for Redis Test in the navigation bar of the web page to test cache access.
Clean up resources
If you want to continue to use the resources you created in this article, keep the resource group.
Otherwise, if you're finished with the resources, you can delete the Azure resource group that you created to avoid charges.
Important
Deleting a resource group is irreversible. When you delete a resource group, all the resources in it are permanently deleted. Make sure that you do not accidentally delete the wrong resource group or resources. If you created the resources inside an existing resource group that contains resources you want to keep, you can delete each resource individually instead of deleting the resource group.
To delete a resource group
Sign in to the Azure portal, and then select Resource groups.
Select the resource group you want to delete.
If there are many resource groups, use the Filter for any field... box, type the name of your resource group you created for this article. Select the resource group in the results list.
Select Delete resource group.
You're asked to confirm the deletion of the resource group. Type the name of your resource group to confirm, and then select Delete.

After a few moments, the resource group and all of its resources are deleted.
Related content
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for