What is Azure Chaos Studio?
Azure Chaos Studio is a managed service that uses chaos engineering to help you measure, understand, and improve your cloud application and service resilience. Chaos engineering is a methodology by which you inject real-world faults into your application to run controlled fault injection experiments.
Resilience is the capability of a system to handle and recover from disruptions. Application disruptions can cause errors and failures that can adversely affect your business or mission. Whether you're developing, migrating, or operating Azure applications, it's important to validate and improve your application's resilience.
Chaos Studio helps you avoid negative consequences by validating that your application responds effectively to disruptions and failures. You can use Chaos Studio to test resilience against real-world incidents, like outages or high CPU utilization on virtual machines (VMs).
The following video provides more background about Chaos Studio:
Chaos Studio scenarios
You can use chaos engineering for various resilience validation scenarios that span the service development and operations lifecycle. There are two types of scenarios:
- Shift right: These scenarios use a production or preproduction environment. Usually, you do shift-right scenarios with real customer traffic or simulated load.
- Shift left: These scenarios can use a development or shared test environment. You can do shift-left scenarios without any real customer traffic.
You can use Chaos Studio for the following common chaos engineering scenarios:
- Reproduce an incident that affected your application to better understand the failure. Ensure that post-incident repairs prevent the incident from recurring.
- Prepare for a major event or season with "game day" load, scale, performance, and resilience validation.
- Do business continuity and disaster recovery drills to ensure that your application can recover quickly and preserve critical data in a disaster.
- Run high-availability drills to test application resilience against region outages, network configuration errors, high-stress events, or noisy neighbor issues.
- Develop application performance benchmarks.
- Plan capacity needs for production environments.
- Run stress tests or load tests.
- Ensure that services migrated from an on-premises or other cloud environment remain resilient to known failures.
- Build confidence in services built on cloud-native architectures.
- Validate that live site tooling, observability data, and on-call processes still work in unexpected conditions.
For many of these scenarios, you first build resilience by using ad-hoc chaos experiments. Then, you continuously validate that new deployments won't regress resilience. To check, you run chaos experiments as deployment gates in your continuous integration/continuous deployment pipelines.
How Chaos Studio works
With Chaos Studio, you can orchestrate safe, controlled fault injection on your Azure resources. Chaos experiments are the core of Chaos Studio. A chaos experiment describes the faults to run and the resources to run against. You can organize faults to run in parallel or sequence, depending on your needs.
Chaos Studio supports two types of faults:
- Service-direct: These faults run directly against an Azure resource, without any installation or instrumentation. Examples include rebooting an Azure Cache for Redis cluster or adding network latency to Azure Kubernetes Service pods.
- Agent-based: These faults run in VMs or virtual machine scale sets to do in-guest failures. Examples include applying virtual memory pressure or killing a process.
Each fault has specific parameters you can configure, like which process to kill or how much memory pressure to generate.
When you build a chaos experiment, you define one or more steps that execute sequentially. Each step contains one or more branches that run in parallel within the step. Each branch contains one or more actions, such as injecting a fault or waiting for a certain duration.
You organize resource targets to run faults against into groups called selectors so that you can easily reference a group of resources in each action.
The following diagram shows the layout of a chaos experiment in Chaos Studio:
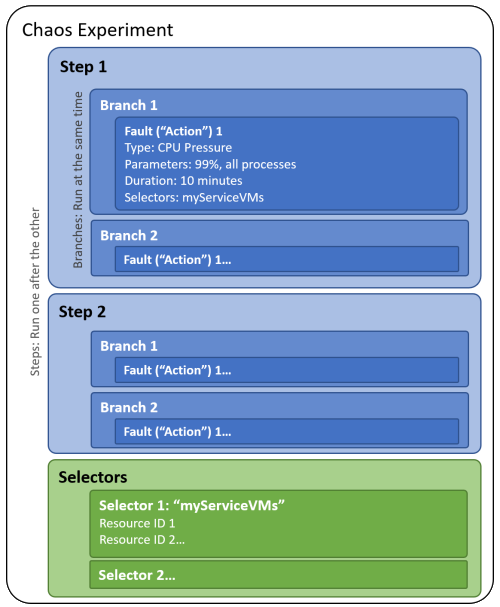
A chaos experiment is an Azure resource in a subscription and resource group. You can use the Azure portal or the Chaos Studio REST API to create, update, start, cancel, and view the status of experiments.
Next steps
Now that you understand how to use chaos engineering, you're ready to:
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for