Monitor metrics on Azure Database for PostgreSQL - Flexible Server
APPLIES TO:  Azure Database for PostgreSQL - Flexible Server
Azure Database for PostgreSQL - Flexible Server
Monitoring data about your servers helps you troubleshoot and optimize for your workload. Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server provides various monitoring options to provide insight into how your server is performing.
Metrics
Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server provides various metrics that give insight into the behavior of the resources that support the Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server instance. Each metric is emitted at a 1-minute interval and has up to 93 days of history. You can configure alerts on the metrics. Other options include setting up automated actions, performing advanced analytics, and archiving the history. For more information, see the Azure Metrics overview.
Note
While metrics are stored for 93 days, you can only query (in the Metrics tile) for a maximum of 30 days' worth of data on any single chart. If you see a blank chart or your chart displays only part of metric data, verify that the difference between start and end dates in the time picker doesn't exceed the 30-day interval. After you've selected a 30-day interval, you can pan the chart to view the full retention window.
Default Metrics
The following metrics are available for an Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server instance:
| Display name | Metric ID | Unit | Description | Default enabled |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Active Connections | active_connections |
Count | Total number of connections to the database server, including all connection states such as active, idle, and others, as seen in pg_stat_activity view. This figure represents the overall sum of connections across all states, without distinguishing between specific states. For an in-depth analysis on a specific state, such as active connections, refer to the 'Sessions By State' metric. |
Yes |
| Backup Storage Used | backup_storage_used |
Bytes | Amount of backup storage used. This metric represents the sum of storage that's consumed by all the full backups, differential backups, and log backups that are retained based on the backup retention period that's set for the server. The frequency of the backups is service managed. For geo-redundant storage, backup storage usage is twice the usage for locally redundant storage. | Yes |
| Failed Connections | connections_failed |
Count | Number of failed connections. | Yes |
| Succeeded Connections | connections_succeeded |
Count | Number of succeeded connections. | Yes |
| CPU Credits Consumed | cpu_credits_consumed |
Count | Number of credits used by the flexible server. Applies to the Burstable tier. | Yes |
| CPU Credits Remaining | cpu_credits_remaining |
Count | Number of credits available to burst. Applies to the Burstable tier. | Yes |
| CPU percent | cpu_percent |
Percent | Percentage of CPU in use. | Yes |
| Database Size (preview) | database_size_bytes |
Bytes | Database size in bytes. | Yes |
| Disk Queue Depth | disk_queue_depth |
Count | Number of outstanding I/O operations to the data disk. | Yes |
| IOPS | iops |
Count | Number of I/O operations to disk per second. | Yes |
| Maximum Used Transaction IDs | maximum_used_transactionIDs |
Count | Maximum number of transaction IDs in use. | Yes |
| Memory percent | memory_percent |
Percent | Percentage of memory in use. | Yes |
| Network Out | network_bytes_egress |
Bytes | Amount of outgoing network traffic. | Yes |
| Network In | network_bytes_ingress |
Bytes | Amount of incoming network traffic. | Yes |
| Read IOPS | read_iops |
Count | Number of data disk I/O read operations per second. | Yes |
| Read Throughput | read_throughput |
Bytes | Bytes read per second from disk. | Yes |
| Storage Free | storage_free |
Bytes | Amount of storage space that's available. | Yes |
| Storage percent | storage_percent |
Percentage | Percent of storage space that's used. The storage that's used by the service can include database files, transaction logs, and server logs. | Yes |
| Storage Used | storage_used |
Bytes | Amount of storage space that's used. The storage that's used by the service can include the database files, transaction logs, and the server logs. | Yes |
| Transaction Log Storage Used | txlogs_storage_used |
Bytes | Amount of storage space that's used by the transaction logs. | Yes |
| Write Throughput | write_throughput |
Bytes | Bytes written to disk per second. | Yes |
| Write IOPS | write_iops |
Count | Number of data disk I/O write operations per second. | Yes |
Enhanced metrics
You can use enhanced metrics for Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server to get fine-grained monitoring and alerting on databases. You can configure alerts on the metrics. Some enhanced metrics include a Dimension parameter that you can use to split and filter metrics data by using a dimension like database name or state.
Enabling enhanced metrics
- Most of these new metrics are disabled by default. There are a few exceptions though, which are enabled by default. Rightmost column in the following tables indicates whether each metric is enabled by default or not.
- To enable those metrics which are not enabled by default, set the server parameter
metrics.collector_database_activitytoON. This parameter is dynamic and doesn't require an instance restart.
List of enhanced metrics
You can choose from the following categories of enhanced metrics:
- Activity
- Database
- Logical replication
- Replication
- Saturation
- Traffic
Activity
| Display name | Metric ID | Unit | Description | Dimension | Default enabled |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sessions By State | sessions_by_state |
Count | Sessions by state as shown in pg_stat_activity view. It categorizes client backends into various states, such as active or idle. |
State | No |
| Sessions By WaitEventType | sessions_by_wait_event_type |
Count | Sessions by the type of event for which the client backend is waiting. | Wait Event Type | No |
| Oldest Backend | oldest_backend_time_sec |
Seconds | Age in seconds of the oldest backend (irrespective of the state). | Doesn't apply | No |
| Oldest Query | longest_query_time_sec |
Seconds | Age in seconds of the longest query that's currently running. | Doesn't apply | No |
| Oldest Transaction | longest_transaction_time_sec |
Seconds | Age in seconds of the longest transaction (including idle transactions). | Doesn't apply | No |
| Oldest xmin | oldest_backend_xmin |
Count | The actual value of the oldest xmin. If xmin isn't increasing, it indicates that there are some long-running transactions that can potentially hold dead tuples from being removed. |
Doesn't apply | No |
| Oldest xmin Age | oldest_backend_xmin_age |
Count | Age in units of the oldest xmin. Indicates how many transactions passed since the oldest xmin. |
Doesn't apply | No |
Database
| Display name | Metric ID | Unit | Description | Dimension | Default enabled |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Backends | numbackends |
Count | Number of backends that are connected to this database. | DatabaseName | No |
| Deadlocks | deadlocks |
Count | Number of deadlocks that are detected in this database. | DatabaseName | No |
| Disk Blocks Hit | blks_hit |
Count | Number of times disk blocks were found already in the buffer cache, so that a read wasn't necessary. | DatabaseName | No |
| Disk Blocks Read | blks_read |
Count | Number of disk blocks that were read in this database. | DatabaseName | No |
| Temporary Files | temp_files |
Count | Number of temporary files that were created by queries in this database. | DatabaseName | No |
| Temporary Files Size | temp_bytes |
Bytes | Total amount of data that's written to temporary files by queries in this database. | DatabaseName | No |
| Total Transactions | xact_total |
Count | Number of total transactions that executed in this database. | DatabaseName | No |
| Transactions Committed | xact_commit |
Count | Number of transactions in this database that have been committed. | DatabaseName | No |
| Transactions per second (Preview) | tps |
Count | Number of transactions executed within a second. | DatabaseName | No |
| Transactions Rolled back | xact_rollback |
Count | Number of transactions in this database that have been rolled back. | DatabaseName | No |
| Tuples Deleted | tup_deleted |
Count | Number of rows that were deleted by queries in this database. | DatabaseName | No |
| Tuples Fetched | tup_fetched |
Count | Number of rows that were fetched by queries in this database. | DatabaseName | No |
| Tuples Inserted | tup_inserted |
Count | Number of rows that were inserted by queries in this database. | DatabaseName | No |
| Tuples Returned | tup_returned |
Count | Number of rows that were returned by queries in this database. | DatabaseName | No |
| Tuples Updated | tup_updated |
Count | Number of rows that were updated by queries in this database. | DatabaseName | No |
Logical replication
| Display name | Metric ID | Unit | Description | Dimension | Default enabled |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max Logical Replication Lag | logical_replication_delay_in_bytes |
Bytes | Maximum lag across all logical replication slots. | Doesn't apply | Yes |
Replication
| Display name | Metric ID | Unit | Description | Dimension | Default enabled |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max Physical Replication Lag | physical_replication_delay_in_bytes |
Bytes | Maximum lag across all asynchronous physical replication slots. | Doesn't apply | Yes |
| Read Replica Lag | physical_replication_delay_in_seconds |
Seconds | Read replica lag in seconds. | Doesn't apply | Yes |
Saturation
| Display name | Metric ID | Unit | Description | Dimension | Default enabled |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Disk Bandwidth Consumed Percentage | disk_bandwidth_consumed_percentage |
Percent | Percentage of data disk bandwidth consumed per minute. | Doesn't apply | Yes |
| Disk IOPS Consumed Percentage | disk_iops_consumed_percentage |
Percent | Percentage of data disk I/Os consumed per minute. | Doesn't apply | Yes |
Traffic
| Display name | Metric ID | Unit | Description | Dimension | Default enabled |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max Connections ^ | max_connections |
Count | Number of maximum connections. | Doesn't apply | Yes |
^ Max Connections represents the configured value for the max_connections server parameter. This metric is polled every 30 minutes.
Considerations for using enhanced metrics
- Enhanced metrics that use the DatabaseName dimension have a 50-database limit.
- On the Burstable SKU, the limit is 10 databases for metrics that use the DatabaseName dimension.
- The DatabaseName dimension limit is applied on the database identifier (datid) column of the pg_stat_database system view, which reflects the order of creation for the database.
- The
DatabaseNamein the metrics dimension is case insensitive. That means that after queryingpg_stat_databaseview, filtering out rows in whichdatnameis eithertemplate1ortemplate0, ordering bydatid, and limiting the returned rows to the first 50 (or 10 in the case of Burstable SKU), the metrics for database names in that result set, that are the same except for case (for example,contoso_databaseandContoso_database) will be merged and might not show accurate data.
Autovacuum metrics
Autovacuum metrics can be used to monitor and tune autovacuum performance for Azure Database for PostgreSQL - Flexible Server. Each metric is emitted at a 30-minute interval and has up to 93 days of retention. You can create alerts for specific metrics, and you can split and filter metrics data by using the DatabaseName dimension.
How to enable autovacuum metrics
- Autovacuum metrics are disabled by default.
- To enable these metrics, set the server parameter
metrics.autovacuum_diagnosticstoON. - This parameter is dynamic, so an instance restart isn't required.
List of autovacuum metrics
| Display name | Metric ID | Unit | Description | Dimension | Default enabled |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Analyze Counter User Tables | analyze_count_user_tables |
Count | Number of times user-only tables have been manually analyzed in this database. | DatabaseName | No |
| AutoAnalyze Counter User Tables | autoanalyze_count_user_tables |
Count | Number of times user-only tables have been analyzed by the autovacuum daemon in this database. | DatabaseName | No |
| AutoVacuum Counter User Tables | autovacuum_count_user_tables |
Count | Number of times user-only tables have been vacuumed by the autovacuum daemon in this database. | DatabaseName | No |
| Bloat Percent (Preview) | bloat_percent |
Percent | Estimated bloat percentage for user only tables. | DatabaseName | No |
| Estimated Dead Rows User Tables | n_dead_tup_user_tables |
Count | Estimated number of dead rows for user-only tables in this database. | DatabaseName | No |
| Estimated Live Rows User Tables | n_live_tup_user_tables |
Count | Estimated number of live rows for user-only tables in this database. | DatabaseName | No |
| Estimated Modifications User Tables | n_mod_since_analyze_user_tables |
Count | Estimated number of rows that were modified since user-only tables were last analyzed. | DatabaseName | No |
| User Tables Analyzed | tables_analyzed_user_tables |
Count | Number of user-only tables that have been analyzed in this database. | DatabaseName | No |
| User Tables AutoAnalyzed | tables_autoanalyzed_user_tables |
Count | Number of user-only tables that have been analyzed by the autovacuum daemon in this database. | DatabaseName | No |
| User Tables AutoVacuumed | tables_autovacuumed_user_tables |
Count | Number of user-only tables that have been vacuumed by the autovacuum daemon in this database. | DatabaseName | No |
| User Tables Counter | tables_counter_user_tables |
Count | Number of user-only tables in this database. | DatabaseName | No |
| User Tables Vacuumed | tables_vacuumed_user_tables |
Count | Number of user-only tables that have been vacuumed in this database. | DatabaseName | No |
| Vacuum Counter User Tables | vacuum_count_user_tables |
Count | Number of times user-only tables have been manually vacuumed in this database (not counting VACUUM FULL). |
DatabaseName | No |
Considerations for using autovacuum metrics
- Autovacuum metrics that use the DatabaseName dimension have a 30-database limit.
- On the Burstable SKU, the limit is 10 databases for metrics that use the DatabaseName dimension.
- The DatabaseName dimension limit is applied on the OID column, which reflects the order of creation for the database.
PgBouncer metrics
You can use PgBouncer metrics to monitor the performance of the PgBouncer process, including details for active connections, idle connections, total pooled connections, and the number of connection pools. Each metric is emitted at a 1-minute interval and has up to 93 days of history. Customers can configure alerts on the metrics and also access the new metrics dimensions to split and filter metrics data by database name.
How to enable PgBouncer metrics
- To monitor PgBouncer metrics, ensure that the pgbouncer feature is enabled via the server parameter
pgbouncer.enabledand metrics parametermetrics.pgbouncer_diagnosticsis enabled. - These parameters are dynamic and don't require an instance restart.
- PgBouncer metrics are disabled by default.
List of PgBouncer metrics
| Display name | Metric ID | Unit | Description | Dimension | Default enabled |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Active client connections | client_connections_active |
Count | Connections from clients that are associated with an Azure Database for PostgreSQL - Flexible Server connection. | DatabaseName | No |
| Waiting client connections | client_connections_waiting |
Count | Connections from clients that are waiting for an Azure Database for PostgreSQL - Flexible Server connection to service them. | DatabaseName | No |
| Active server connections | server_connections_active |
Count | Connections to Azure Database for PostgreSQL - Flexible Server that are in use by a client connection. | DatabaseName | No |
| Idle server connections | server_connections_idle |
Count | Connections to Azure Database for PostgreSQL - Flexible Server that are idle and ready to service a new client connection. | DatabaseName | No |
| Total pooled connections | total_pooled_connections |
Count | Current number of pooled connections. | DatabaseName | No |
| Number of connection pools | num_pools |
Count | Total number of connection pools. | DatabaseName | No |
Considerations for using the PgBouncer metrics
- PgBouncer metrics that use the DatabaseName dimension have a 30-database limit.
- On the Burstable SKU, the limit is 10 databases that have the DatabaseName dimension.
- The DatabaseName dimension limit is applied to the OID column, which reflects the order of creation for the database.
Database availability metric
Is-db-alive is a database server availability metric for Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server that returns [1 for available] and [0 for not-available]. Each metric is emitted at a 1 minute frequency, and has up to 93 days of retention. Customers can configure alerts on the metric.
| Display Name | Metric ID | Unit | Description | Dimension | Default enabled |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Database Is Alive | is_db_alive |
Count | Indicates if the database is up or not. | N/a | Yes |
Considerations when using the Database availability metrics
- Aggregating this metric with
MAX()will allow customers to determine whether the server has been up or down in the last minute. - Customers have option to further aggregate these metrics with any desired frequency (5m, 10m, 30m etc.) to suit their alerting requirements and avoid any false positive.
- Other possible aggregations are
AVG()andMIN().
Filter and split on dimension metrics
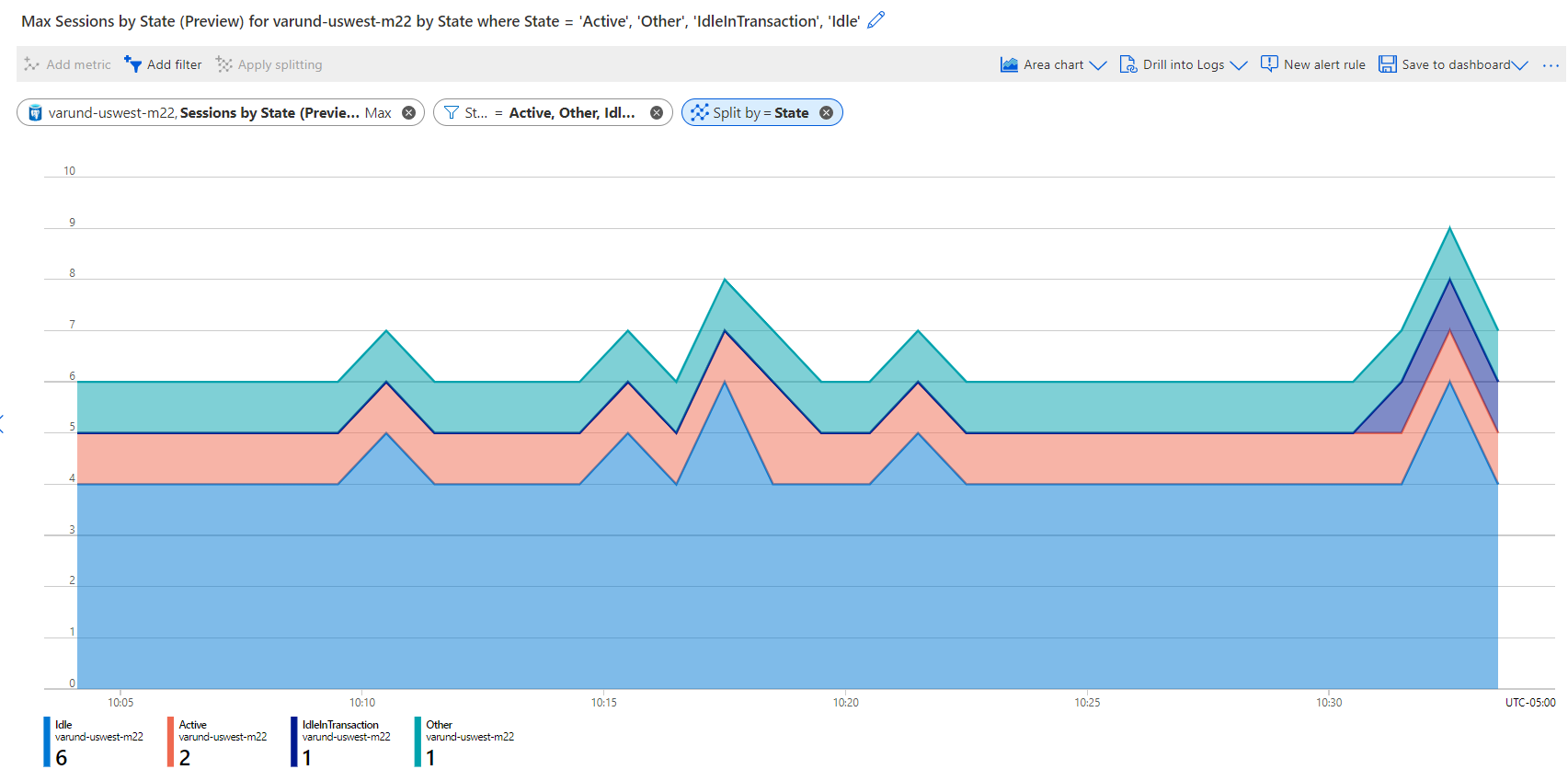
In the preceding tables, some metrics have dimensions like DatabaseName or State. You can use filtering and splitting for the metrics that have dimensions. These features show how various metric segments (or dimension values) affect the overall value of the metric. You can use them to identify possible outliers.
- Filtering: Use filtering to choose which dimension values are included in the chart. For example, you might want to show idle connections when you chart the
Sessions-by-Statemetric. You set the filter for Idle in the State dimension. - Splitting: Use splitting to control whether the chart displays separate lines for each value of a dimension or if it aggregates the values in a single line. For example, you can see one line for a
Sessions-by-Statemetric across all sessions. You can see separate lines for each session grouped by State value. Apply splitting on the State dimension to see separate lines.
The following example demonstrates splitting by the State dimension and filtering on specific State values:
For more information about setting up charts for dimensional metrics, see Metric chart examples.
Metrics visualization
There are several options to visualize Azure Monitor metrics.
| Component | Description | Required training and/or configuration |
|---|---|---|
| Overview page | Most Azure services have an Overview page in the Azure portal that includes a Monitor section with charts that show recent critical metrics. This information is intended for owners of individual services to quickly assess the performance of the resource. | This page is based on platform metrics that are collected automatically. No configuration is required. |
| Metrics Explorer | You can use Metrics Explorer to interactively work with metric data and create metric alerts. You need minimal training to use Metrics Explorer, but you must be familiar with the metrics you want to analyze. | - Once data collection is configured, no other configuration is required. - Platform metrics for Azure resources are automatically available. - Guest metrics for virtual machines are available after an Azure Monitor agent is deployed to the virtual machine. - Application metrics are available after Application Insights is configured. |
| Grafana | You can use Grafana for visualizing and alerting on metrics. All versions of Grafana include the Azure Monitor datasource plug-in to visualize your Azure Monitor metrics and logs. | To become familiar with Grafana dashboards, some training is required. However, you can simplify the process by downloading a prebuilt Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server grafana monitoring dashboard, which allows for easy monitoring of all Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server instances within your organization. |
Logs
In addition to the metrics, you can use Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server to configure and access Azure Database for PostgreSQL standard logs. For more information, see Logging concepts.
Logs visualization
| Component | Description | Required training and/or configuration |
|---|---|---|
| Log Analytics | With Log Analytics, you can create log queries to interactively work with log data and create log query alerts. | Some training is required for you to become familiar with the query language, although you can use prebuilt queries for common requirements. |
Next steps
- Learn more about how to configure and access logs.
- Learn more about Azure Monitor pricing.
- Learn more about audit logs.
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for