Quickstart: Configure an Azure VM to connect to Azure SQL Managed Instance
Applies to:
Azure SQL Managed Instance
This quickstart shows you how to configure an Azure virtual machine to connect to Azure SQL Managed Instance using SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS).
For a quickstart showing how to connect from an on-premises client computer using a point-to-site connection instead, see Configure a point-to-site connection.
Prerequisites
This quickstart uses the resources created in Create a managed instance as its starting point.
Sign in to the Azure portal
Sign in to the Azure portal.
Create a new subnet VNet
The following steps create a new subnet in the SQL Managed Instance VNet so an Azure virtual machine can connect to the managed instance. The SQL Managed Instance subnet is dedicated to managed instances. You can't create any other resources, like Azure virtual machines, in that subnet.
Open the resource group for the managed instance that you created in the Create a managed instance quickstart. Select the virtual network for your managed instance.
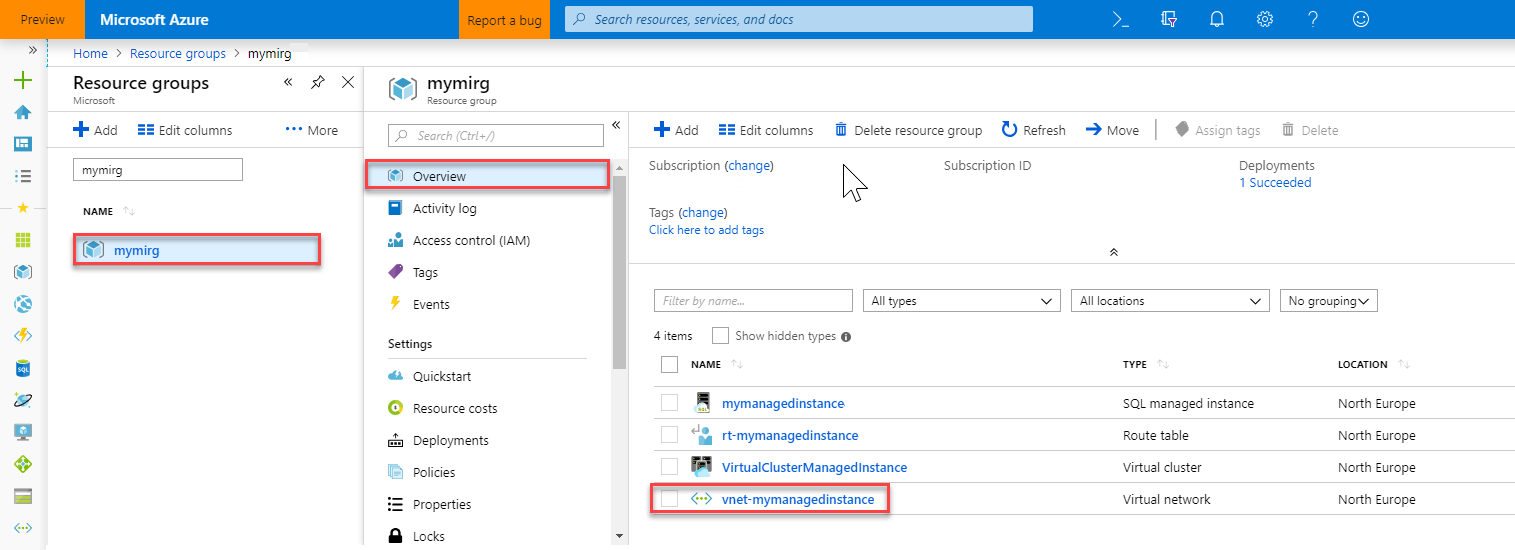
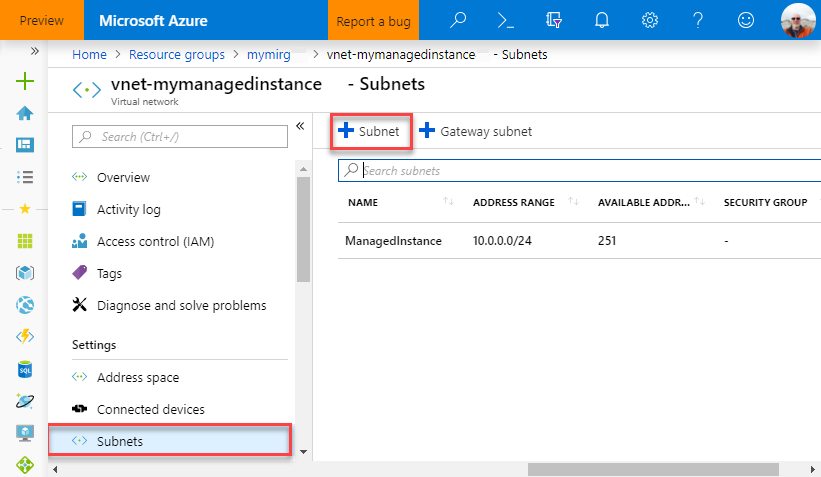
Select Subnets and then select + Subnet to create a new subnet.
Fill out the form using the information in this table:
Setting Suggested value Description Name Any valid name For valid names, see Naming rules and restrictions. Address range (CIDR block) A valid range The default value is good for this quickstart. Network security group None The default value is good for this quickstart. Route table None The default value is good for this quickstart. Service endpoints 0 selected The default value is good for this quickstart. Subnet delegation None The default value is good for this quickstart. 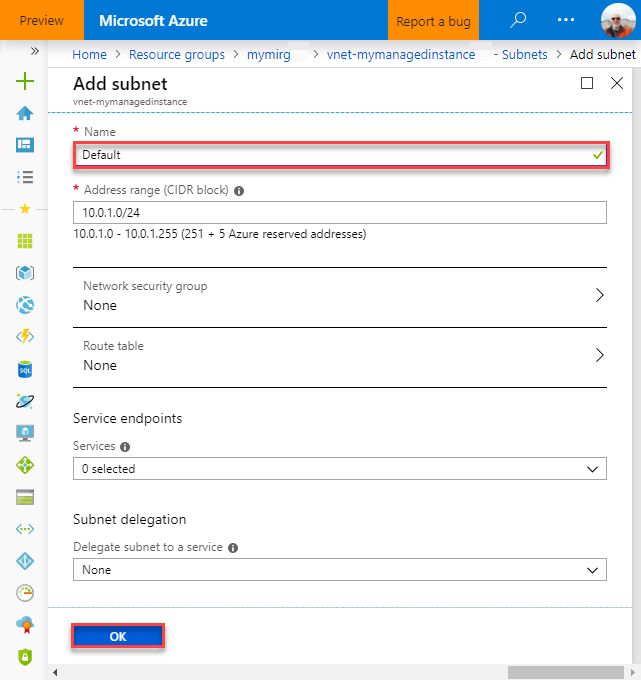
Select OK to create this additional subnet in the SQL Managed Instance VNet.
Create a VM in the new subnet
The following steps show you how to create a virtual machine in the new subnet to connect to SQL Managed Instance.
Prepare the Azure virtual machine
Since SQL Managed Instance is placed in your private virtual network, you need to create an Azure VM with an installed SQL client tool, like SQL Server Management Studio or Azure Data Studio. This tool lets you connect to SQL Managed Instance and execute queries. This quickstart uses SQL Server Management Studio.
The easiest way to create a client virtual machine with all necessary tools is to use the Azure Resource Manager templates.
Make sure that you're signed in to the Azure portal in another browser tab. Then, select the following button to create a client virtual machine and install SQL Server Management Studio:
Fill out the form using the information in the following table:
Setting Suggested value Description Subscription A valid subscription Must be a subscription in which you have permission to create new resources. Resource Group The resource group that you specified in the Create SQL Managed Instance quickstart This resource group must be the one in which the VNet exists. Location The location for the resource group This value is populated based on the resource group selected. Virtual machine name Any valid name For valid names, see Naming rules and restrictions. Admin Username Any valid username For valid names, see Naming rules and restrictions. Don't use "serveradmin" as that is a reserved server-level role.
You use this username any time you connect to the VM.Password Any valid password The password must be at least 12 characters long and meet the defined complexity requirements.
You use this password any time you connect to the VM.Virtual Machine Size Any valid size The default in this template of Standard_B2s is sufficient for this quickstart. Location [resourceGroup().location]. Don't change this value. Virtual Network Name The virtual network in which you created the managed instance Subnet name The name of the subnet that you created in the previous procedure Don't choose the subnet in which you created the managed instance. artifacts Location [deployment().properties.templateLink.uri] Don't change this value. artifacts Location Sas token Leave blank Don't change this value. 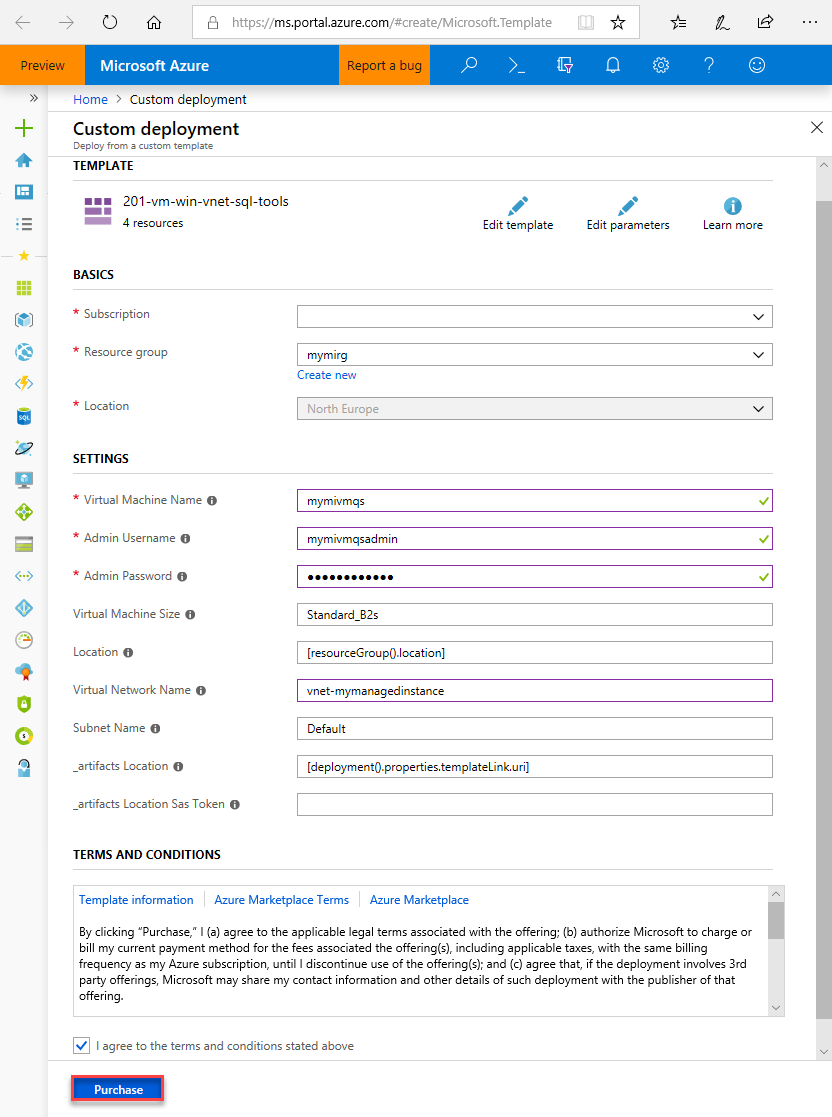
If you used the suggested VNet name and the default subnet in creating your SQL Managed Instance, you don't need to change last two parameters. Otherwise you should change these values to the values that you entered when you set up the network environment.
Select the I agree to the terms and conditions stated above checkbox.
Select Purchase to deploy the Azure VM in your network.
Select the Notifications icon to view the status of deployment.
Important
Do not continue until approximately 15 minutes after the virtual machine is created to give time for the post-creation scripts to install SQL Server Management Studio.
Connect to the virtual machine
The following steps show you how to connect to your newly created virtual machine using a Remote Desktop connection.
After deployment completes, go to the virtual machine resource.
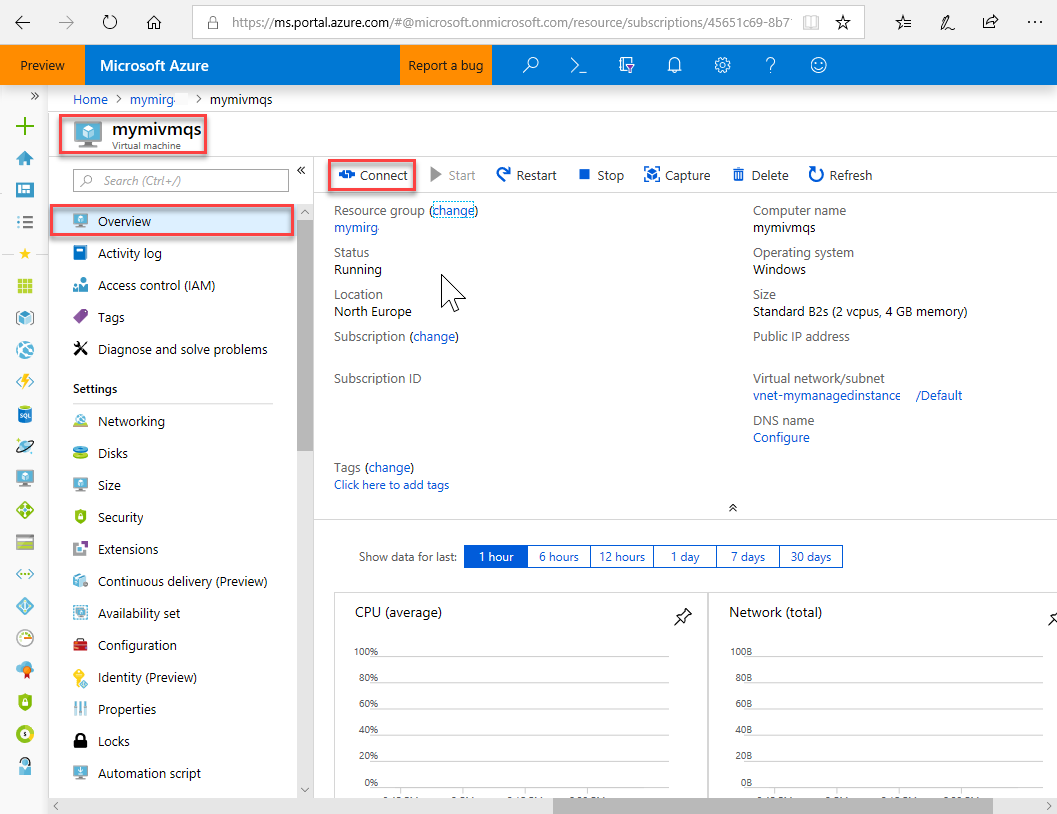
Select Connect.
A Remote Desktop Protocol file (.rdp file) form appears with the public IP address and port number for the virtual machine.
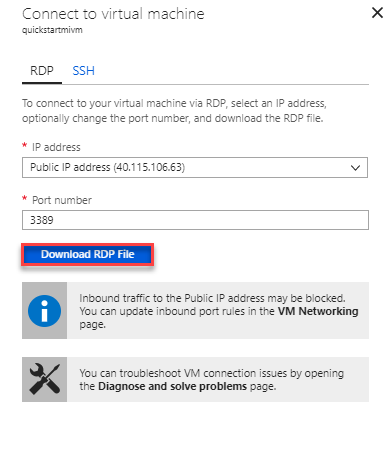
Select Download RDP File.
Note
You can also use SSH to connect to your VM.
Close the Connect to virtual machine form.
To connect to your VM, open the downloaded RDP file.
When prompted, select Connect. On a Mac, you need an RDP client such as this Remote Desktop Client from the Mac App Store.
Enter the username and password you specified when creating the virtual machine, and then choose OK.
You might receive a certificate warning during the sign-in process. Choose Yes or Continue to proceed with the connection.
You're connected to your virtual machine in the Server Manager dashboard.
Connect to SQL Managed Instance
In the virtual machine, open SQL Server Management Studio.
It takes a few moments to open, as it needs to complete its configuration since this is the first time SSMS has been started.
In the Connect to Server dialog box, enter the fully qualified host name for your managed instance in the Server name box. Select SQL Server Authentication, provide your username and password, and then select Connect.
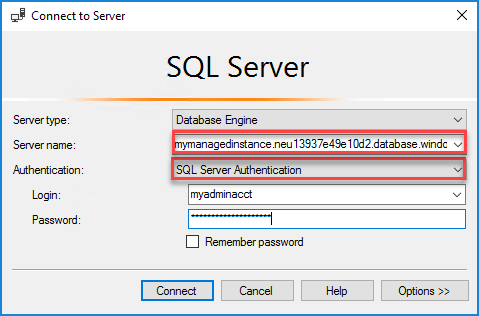
After you connect, you can view your system and user databases in the Databases node, and various objects in the Security, Server Objects, Replication, Management, SQL Server Agent, and XEvent Profiler nodes.
Next steps
- For a quickstart showing how to connect from an on-premises client computer using a point-to-site connection, see Configure a point-to-site connection.
- For an overview of the connection options for applications, see Connect your applications to SQL Managed Instance.
- To restore an existing SQL Server database from on-premises to a managed instance, you can use Azure Database Migration Service for migration or the T-SQL RESTORE command to restore from a database backup file.
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for
