Artifact cache in Azure Container Registry
Artifact cache feature allows users to cache container images in a private container registry. Artifact cache is available in Basic, Standard, and Premium service tiers.
Artifact cache enhances container image management by providing a caching solution for both public and private repositories.
Artifact cache offers faster and more reliable pull operations through Azure Container Registry (ACR), utilizing features like Geo-Replication and Availability Zone support for higher availability and speed image pulls.
Artifact cache allows cached registries to be accessible over private networks for users to align with firewall configurations and compliance standards seamlessly.
Artifact cache addresses the challenge of anonymous pull limits imposed by public registries like Docker Hub. By allowing users to pull images from the local ACR, it circumvents these limits, ensuring uninterrupted content delivery from upstream sources and eliminating the concern of hitting pull limits.
Terminology
Cache Rule - A Cache Rule is a rule you can create to pull artifacts from a supported repository into your cache.
A cache rule contains four parts:
Rule Name - The name of your cache rule. For example,
Hello-World-Cache.Source - The name of the Source Registry.
Repository Path - The source path of the repository to find and retrieve artifacts you want to cache. For example,
docker.io/library/hello-world.New ACR Repository Namespace - The name of the new repository path to store artifacts. For example,
hello-world. The Repository can't already exist inside the ACR instance.
Credentials
Credentials are a set of username and password for the source registry. You require Credentials to authenticate with a public or private repository. Credentials contain four parts
Credentials - The name of your credentials.
Source registry Login Server - The login server of your source registry.
Source Authentication - The key vault locations to store credentials.
Username and Password secrets- The secrets containing the username and password.
Limitations
Cache will only occur after at least one image pull is complete on the available container image. For every new image available, a new image pull must be complete. Artifact cache doesn't automatically pull new tags of images when a new tag is available. It is on the roadmap but not supported in this release.
Artifact cache only supports 1,000 cache rules.
Upstream support
Artifact cache currently supports the following upstream registries:
| Upstream Registries | Support | Availability |
|---|---|---|
| Docker Hub | Supports both authenticated and unauthenticated pulls. | Azure CLI, Azure portal |
| Microsoft Artifact Registry | Supports unauthenticated pulls only. | Azure CLI, Azure portal |
| AWS Elastic Container Registry (ECR) Public Gallery | Supports unauthenticated pulls only. | Azure CLI, Azure portal |
| GitHub Container Registry | Supports both authenticated and unauthenticated pulls. | Azure CLI, Azure portal |
| Nvidia | Supports both authenticated and unauthenticated pulls. | Azure CLI |
| Quay | Supports both authenticated and unauthenticated pulls. | Azure CLI, Azure portal |
| registry.k8s.io | Supports both authenticated and unauthenticated pulls. | Azure CLI |
| Google Container Registry | Supports both authenticated and unauthenticated pulls. | Azure CLI |
Wildcards
Wildcard use asterisks (*) to match multiple paths within the container image registry. Artifact cache currently supports the following wildcards:
Note
The cache rules map from Target Repository => Source Repository.
Registry Level Wildcard
The registry level wildcard allows you to cache all repositories from an upstream registry.
| Cache Rule | Mapping | Example |
|---|---|---|
| contoso.azurecr.io/* => mcr.microsoft.com/* | Mapping for all images under ACR to MCR. | contoso.azurecr.io/myapp/image1 => mcr.microsoft.com/myapp/image1 contoso.azurecr.io/myapp/image2 => mcr.microsoft.com/myapp/image2 |
Repository Level Wildcard
The repository level wildcard allows you to cache all repositories from an upstream registry mapping to the repository prefix.
| Cache Rule | Mapping | Example |
|---|---|---|
| contoso.azurecr.io/dotnet/* => mcr.microsoft.com/dotnet/* | Mapping specific repositories under ACR to corresponding repositories in MCR. | contoso.azurecr.io/dotnet/sdk => mcr.microsoft.com/dotnet/sdk contoso.azurecr.io/dotnet/runtime => mcr.microsoft.com/dotnet/runtime |
| contoso.azurecr.io/library/dotnet/* => mcr.microsoft.com/dotnet/* contoso.azurecr.io/library/python/* => docker.io/library/python/* |
Mapping specific repositories under ACR to repositories from different upstream registries. | contoso.azurecr.io/library/dotnet/app1 => mcr.microsoft.com/dotnet/app1 contoso.azurecr.io/library/python/app3 => docker.io/library/python/app3 |
Limitations for Wildcard based cache rules
Wildcard cache rules use asterisks (*) to match multiple paths within the container image registry. These rules can't overlap with other wildcard cache rules. In other words, if you have a wildcard cache rule for a certain registry path, you cannot add another wildcard rule that overlaps with it.
Here are some examples of overlapping rules:
Example 1:
Existing cache rule: contoso.azurecr.io/* => mcr.microsoft.com/*
New cache being added: contoso.azurecr.io/library/* => docker.io/library/*
The addition of the new cache rule is blocked because the target repository path contoso.azurecr.io/library/* overlaps with the existing wildcard rule contoso.azurecr.io/*.
Example 2:
Existing cache rule: contoso.azurecr.io/library/* => mcr.microsoft.com/library/*
New cache being added: contoso.azurecr.io/library/dotnet/* => docker.io/library/dotnet/*
The addition of the new cache rule is blocked because the target repository path contoso.azurecr.io/library/dotnet/* overlaps with the existing wildcard rule contoso.azurecr.io/library/*.
Limitations for Static/fixed cache rules
Static or fixed cache rules are more specific and do not use wildcards. They can overlap with wildcard-based cache rules. If a cache rule specifies a fixed repository path, then it allows overlapping with a wildcard-based cache rule.
Example 1:
Existing cache rule: contoso.azurecr.io/* => mcr.microsoft.com/*
New cache being added: contoso.azurecr.io/library/dotnet => docker.io/library/dotnet
The addition of the new cache rule is allowed because contoso.azurecr.io/library/dotnet is a static path and can overlap with the wildcard cache rule contoso.azurecr.io/*.
Enable Artifact cache - Azure CLI
You can enable Artifact cache in your Azure Container Registry with or without authentication using Azure CLI by following the steps.
Prerequisites
- You can use the Azure Cloud Shell or a local installation of the Azure CLI to run the command examples in this article. If you'd like to use it locally, version 2.46.0 or later is required. Run
az --versionfor finding the version. If you need to install or upgrade, see Install Azure CLI. - You have an existing Key Vault to store the credentials. Learn more about creating and storing credentials in a Key Vault.
- You can set and retrieve secrets from your Key Vault. Learn more about set and retrieve a secret from Key Vault.
Configure and create a Cache rule without the Credentials.
Run az acr Cache create command to create a Cache rule.
- For example, to create a Cache rule without the credentials for a given
MyRegistryAzure Container Registry.
az acr Cache create -r MyRegistry -n MyRule -s docker.io/library/ubuntu -t ubuntu-- For example, to create a Cache rule without the credentials for a given
Run az acr Cache show command to show a Cache rule.
- For example, to show a Cache rule for a given
MyRegistryAzure Container Registry.
az acr Cache show -r MyRegistry -n MyRule- For example, to show a Cache rule for a given
Create the credentials
Before configuring the Credentials, you have to create and store secrets in the Azure KeyVault and retrieve the secrets from the Key Vault. Learn more about creating and storing credentials in a Key Vault. And to set and retrieve a secret from Key Vault..
Run az acr credential set create command to create the credentials.
- For example, To create the credentials for a given
MyRegistryAzure Container Registry.
az acr credential-set create -r MyRegistry \ -n MyRule \ -l docker.io \ -u https://MyKeyvault.vault.azure.net/secrets/usernamesecret \ -p https://MyKeyvault.vault.azure.net/secrets/passwordsecret- For example, To create the credentials for a given
Run az acr credential set update to update the username or password KV secret ID on a credential set.
- For example, to update the username or password KV secret ID on the credentials for a given
MyRegistryAzure Container Registry.
az acr credential-set update -r MyRegistry -n MyRule -p https://MyKeyvault.vault.azure.net/secrets/newsecretname- For example, to update the username or password KV secret ID on the credentials for a given
Run az-acr-credential-set-show to show the credentials.
- For example, to show the credentials for a given
MyRegistryAzure Container Registry.
az acr credential-set show -r MyRegistry -n MyCredSet- For example, to show the credentials for a given
Configure and create a cache rule with the credentials
Run az acr cache create command to create a cache rule.
- For example, to create a cache rule with the credentials for a given
MyRegistryAzure Container Registry.
az acr cache create -r MyRegistry -n MyRule -s docker.io/library/ubuntu -t ubuntu -c MyCredSet- For example, to create a cache rule with the credentials for a given
Run az acr cache update command to update the credentials on a cache rule.
- For example, to update the credentials on a cache rule for a given
MyRegistryAzure Container Registry.
az acr cache update -r MyRegistry -n MyRule -c NewCredSet- For example, to remove the credentials from an existing cache rule for a given
MyRegistryAzure Container Registry.
az acr cache update -r MyRegistry -n MyRule --remove-cred-set- For example, to update the credentials on a cache rule for a given
Run az acr cache show command to show a cache rule.
- For example, to show a cache rule for a given
MyRegistryAzure Container Registry.
az acr cache show -r MyRegistry -n MyRule- For example, to show a cache rule for a given
Assign permissions to Key Vault
Get the principal ID of system identity in use to access Key Vault.
PRINCIPAL_ID=$(az acr credential-set show -n MyCredSet \ -r MyRegistry \ --query 'identity.principalId' \ -o tsv)Run the az keyvault set-policy command to assign access to the Key Vault, before pulling the image.
- For example, to assign permissions for the credentials access the KeyVault secret
az keyvault set-policy --name MyKeyVault \ --object-id $PRINCIPAL_ID \ --secret-permissions get
Pull your image
Pull the image from your cache using the Docker command by the registry login server name, repository name, and its desired tag.
- For example, to pull the image from the repository
hello-worldwith its desired taglatestfor a given registry login servermyregistry.azurecr.io.
docker pull myregistry.azurecr.io/hello-world:latest- For example, to pull the image from the repository
Clean up the resources
Run az acr cache list command to list the cache rules in the Azure Container Registry.
- For example, to list the cache rules for a given
MyRegistryAzure Container Registry.
az acr cache list -r MyRegistry- For example, to list the cache rules for a given
Run az acr cache delete command to delete a cache rule.
- For example, to delete a cache rule for a given
MyRegistryAzure Container Registry.
az acr cache delete -r MyRegistry -n MyRule- For example, to delete a cache rule for a given
Runaz acr credential set list to list the credential in an Azure Container Registry.
- For example, to list the credentials for a given
MyRegistryAzure Container Registry.
az acr credential-set list -r MyRegistry- For example, to list the credentials for a given
Run az-acr-credential-set-delete to delete the credentials.
- For example, to delete the credentials for a given
MyRegistryAzure Container Registry.
az acr credential-set delete -r MyRegistry -n MyCredSet- For example, to delete the credentials for a given
Enable Artifact cache - Azure portal
You can enable Artifact cache in your Azure Container Registry with or without authentication using Azure portal by following the steps.
Prerequisites
- Sign in to the Azure portal
- You have an existing Key Vault to store credentials. Learn more about creating and storing credentials in a Key Vault.
- You have the existing Key vaults without the Role based access(RBAC) controls.
Configure Artifact cache without credentials
Follow the steps to create cache rule in the Azure portal.
Navigate to your Azure Container Registry.
In the side Menu, under the Services, select Cache.
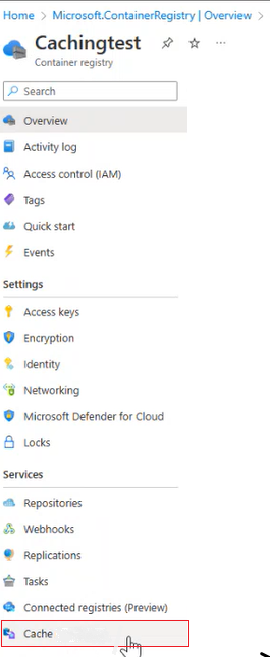
Select Create Rule.
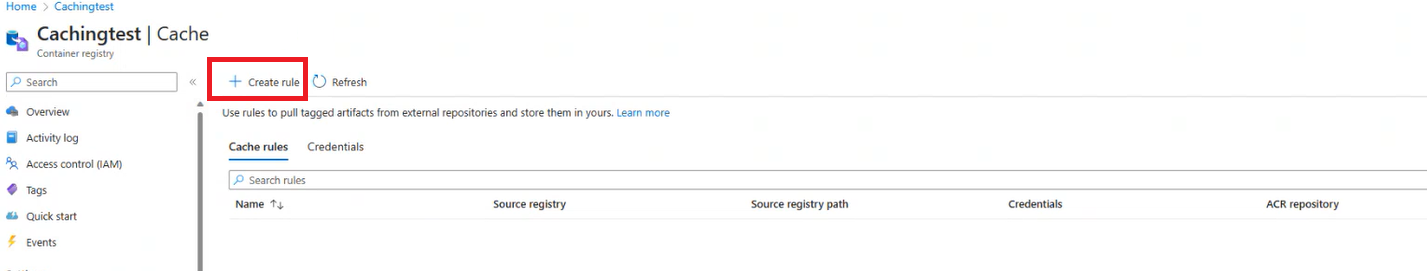
A window for New cache rule appears.
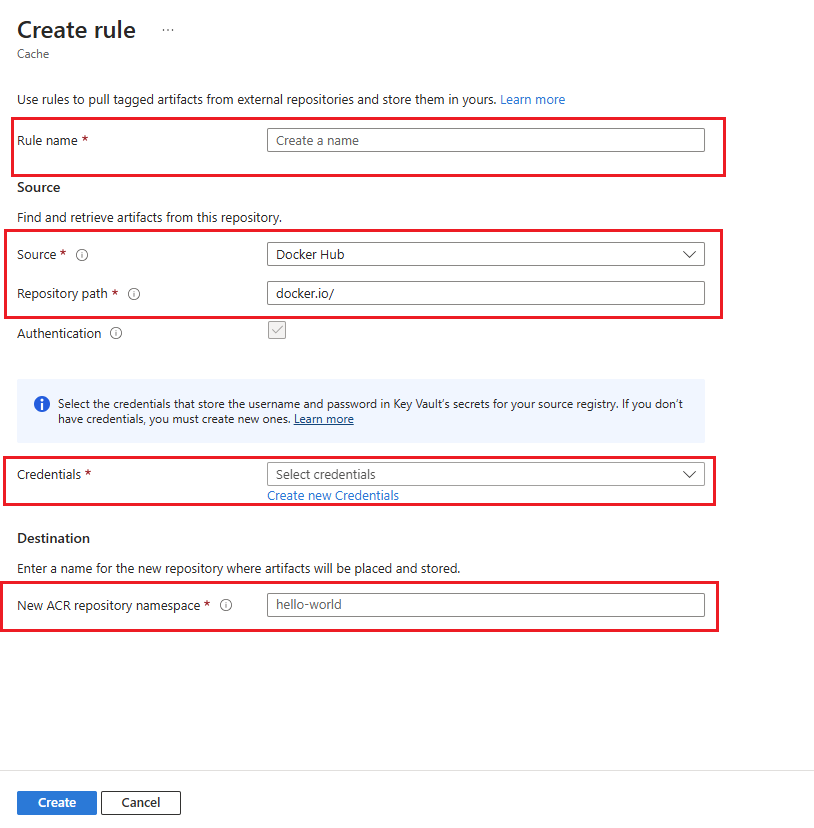
Enter the Rule name.
Select Source Registry from the dropdown menu.
Enter the Repository Path to the artifacts you want to cache.
You can skip Authentication, if you aren't accessing a private repository or performing an authenticated pull.
Under the Destination, Enter the name of the New ACR Repository Namespace to store cached artifacts.
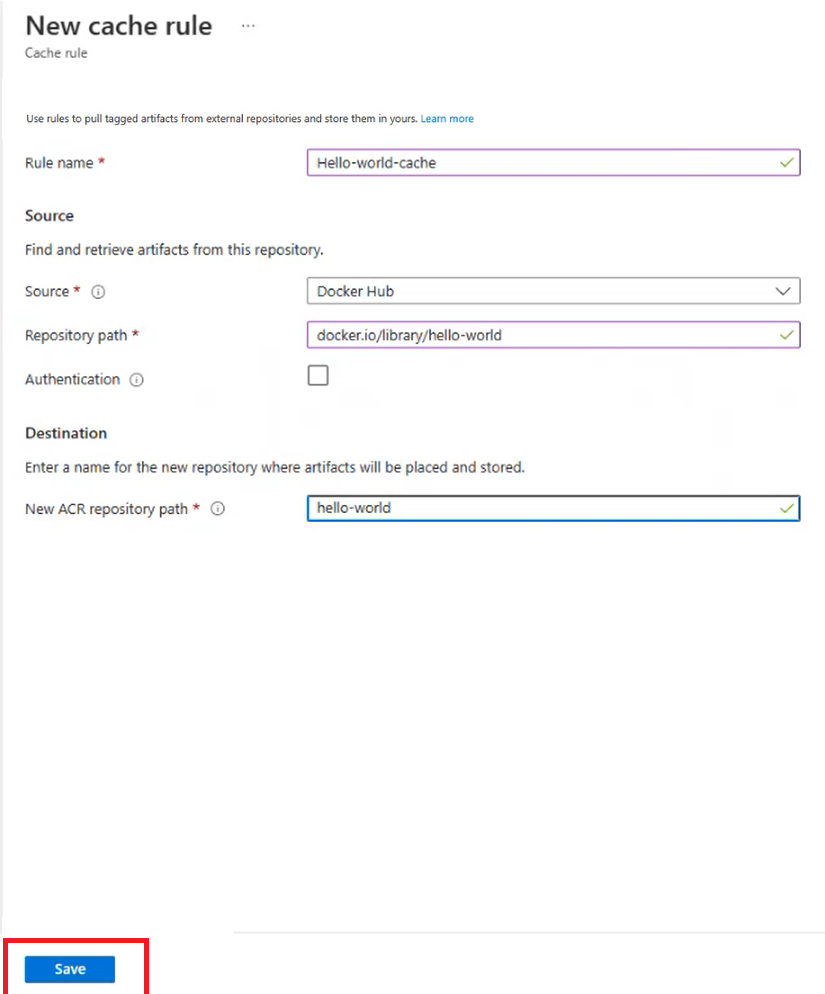
Select on Save.
Pull the image from your cache using the Docker command by the registry login server name, repository name, and its desired tag.
- For example, to pull the image from the repository
hello-worldwith its desired taglatestfor a given registry login servermyregistry.azurecr.io.
docker pull myregistry.azurecr.io/hello-world:latest- For example, to pull the image from the repository
Configure Artifact cache with authentication
Follow the steps to create cache rule in the Azure portal.
Navigate to your Azure Container Registry.
In the side Menu, under the Services, select Cache.

Select Create Rule.

A window for New cache rule appears.
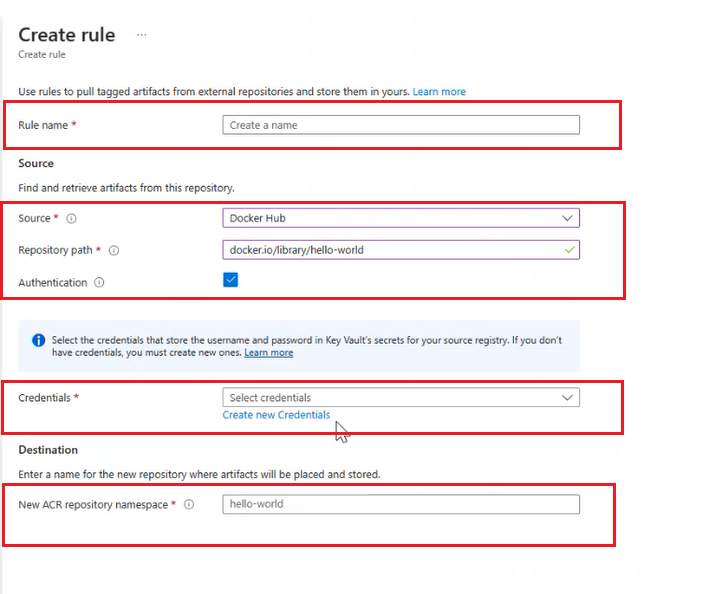
Enter the Rule name.
Select Source Registry from the dropdown menu.
Enter the Repository Path to the artifacts you want to cache.
For adding authentication to the repository, check the Authentication box.
Choose Create new credentials to create a new set of credentials to store the username and password for your source registry. Learn how to create new credentials.
If you have the credentials ready, Select credentials from the drop-down menu.
Under the Destination, Enter the name of the New ACR Repository Namespace to store cached artifacts.

Select on Save.
Pull the image from your cache using the Docker command by the registry login server name, repository name, and its desired tag.
- For example, to pull the image from the repository
hello-worldwith its desired taglatestfor a given registry login servermyregistry.azurecr.io.
docker pull myregistry.azurecr.io/hello-world:latest- For example, to pull the image from the repository
Create new credentials
Before configuring the Credentials, you require to create and store secrets in the Azure KeyVault and retrieve the secrets from the Key Vault. Learn more about creating and storing credentials in a Key Vault. And to set and retrieve a secret from Key Vault..
Navigate to Credentials > Create credentials.
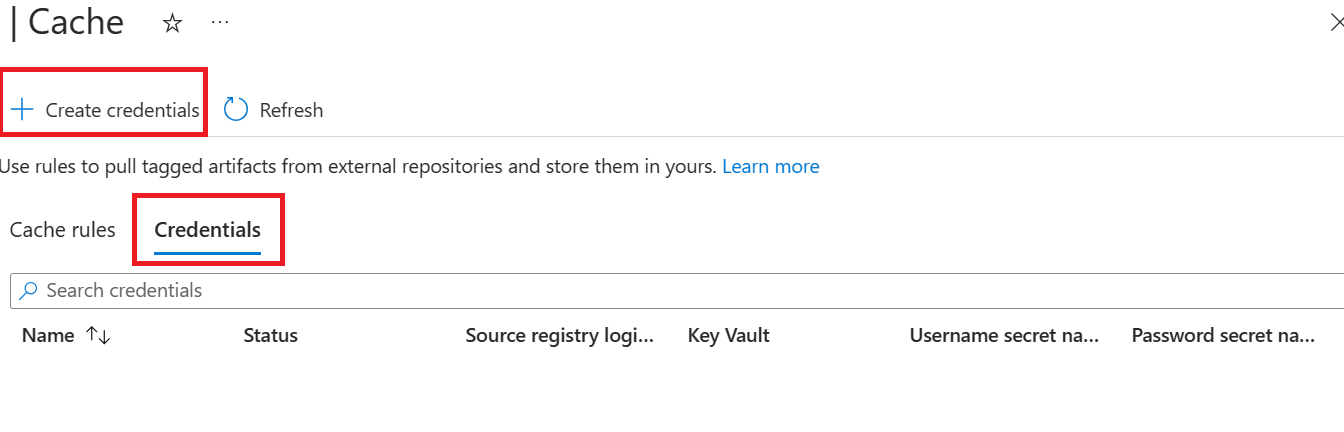
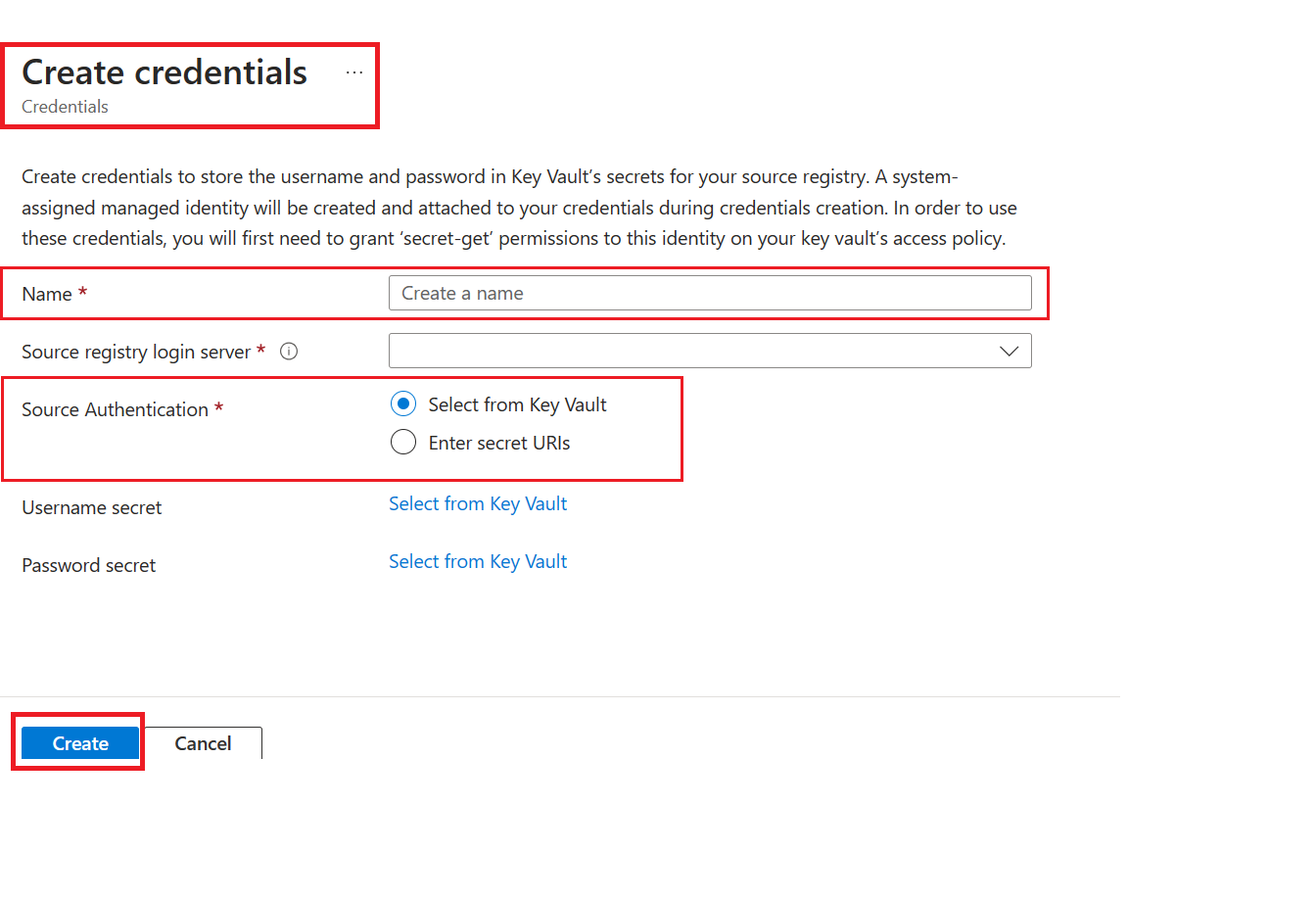
Enter Name for the new credentials for your source registry.
Select a Source Authentication. Artifact cache currently supports Select from Key Vault and Enter secret URI's.
For the Select from Key Vault option, Learn more about creating credentials using key vault.
Select on Create.
Next steps
- Advance to the next article to walk through the troubleshoot guide for Registry Cache.
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for