Creator for indoor maps
This article introduces concepts and tools that apply to Azure Maps Creator. We recommend that you read this article before you begin to use the Azure Maps Creator API and SDK.
You can use Creator to develop applications with map features that are based on indoor map data. This article describes the process of uploading, converting, creating, and using your map data. Typically, the workflow is completed by two different personas with distinct areas of expertise and responsibility:
- Map maker: responsible for curating and preparing the map data.
- Creator map data user: uses customer map data in applications.
The following diagram illustrates the entire workflow.
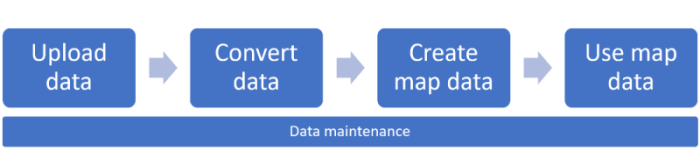
Create Azure Maps Creator
To use Creator services, an Azure Maps Creator resource must be created and associated to an Azure Maps account with the Gen 2 pricing tier. For information about how to create an Azure Maps Creator resource in Azure, see Manage Azure Maps Creator.
Tip
For pricing information see the Creator section in Azure Maps pricing.
Creator authentication
Creator inherits Azure Maps Access Control (IAM) settings. All API calls for data access must be sent with authentication and authorization rules.
Creator usage data is incorporated in your Azure Maps usage charts and activity log. For more information, see Manage authentication in Azure Maps.
Important
We recommend using:
Microsoft Entra ID in all solutions that are built with an Azure Maps account using Creator services. For more information about Microsoft Entra ID, see Microsoft Entra authentication.
Role-based access control settings. Using these settings, map makers can act as the Azure Maps Data Contributor role, and Creator map data users can act as the Azure Maps Data Reader role. For more information, see Authorization with role-based access control.
Creator data item types
Creator services create, store, and use various data types that are defined and discussed in the following sections. A creator data item can be of the following types:
- Converted data
- Dataset
- Tileset
- style
- Map configuration
- Feature stateset
- Routeset
Upload a drawing package
Creator collects indoor map data by converting an uploaded drawing package. The drawing package represents a constructed or remodeled facility. For information about drawing package requirements, see Drawing package requirements.
Follow the steps outlined in the How to create data registry article to upload the drawing package into your Azure storage account then register it in your Azure Maps account.
Important
Make sure to make a note of the unique identifier (udid) value, you will need it. The udid is required to convert the uploaded package into indoor map data.
Convert a drawing package
The Conversion service converts an uploaded drawing package into indoor map data. The Conversion service also validates the package. Validation issues are classified into two types:
- Errors: If any errors are detected, the conversion process fails. When an error occurs, the Conversion service provides a link to the Azure Maps Drawing Error Visualizer stand-alone web application. You can use the Drawing Error Visualizer to inspect Drawing package warnings and errors that occurred during the conversion process. After you fix the errors, you can attempt to upload and convert the package.
- Warnings: If any warnings are detected, the conversion succeeds. However, we recommend that you review and resolve all warnings. A warning means that part of the conversion was ignored or automatically fixed. Failing to resolve the warnings could result in errors in later processes. For more information, see Drawing package warnings and errors.
Create indoor map data
Azure Maps Creator provides the following services that support map creation:
- Dataset service.
- Tileset service. Use the Tileset service to create a vector-based representation of a dataset. Applications can use a tileset to present a visual tile-based view of the dataset.
- Custom styling service. Use the style service or visual style editor to customize the visual elements of an indoor map.
- Feature State service. Use the Feature State service to support dynamic map styling. Applications can use dynamic map styling to reflect real-time events on spaces provided by the IoT system.
- Wayfinding service. Use the wayfinding API to generate a path between two points within a facility. Use the routeset API to create the data that the wayfinding service needs to generate paths.
Datasets
A dataset is a collection of indoor map features. The indoor map features represent facilities that are defined in a converted drawing package. After you create a dataset with the Dataset service, you can create any number of tilesets or feature statesets.
At any time, developers can use the Dataset service to add or remove facilities to an existing dataset. For more information about how to update an existing dataset using the API, see the append options in Dataset service. For an example of how to update a dataset, see Data maintenance.
Tilesets
A tileset is a collection of vector data that represents a set of uniform grid tiles. Developers can use the Tileset service to create tilesets from a dataset.
To reflect different content stages, you can create multiple tilesets from the same dataset. For example, you can make one tileset with furniture and equipment, and another tileset without furniture and equipment. You might choose to generate one tileset with the most recent data updates, and another tileset without the most recent data updates.
In addition to the vector data, the tileset provides metadata for map rendering optimization. For example, tileset metadata contains a minimum and maximum zoom level for the tileset. The metadata also provides a bounding box that defines the geographic extent of the tileset. An application can use a bounding box to programmatically set the correct center point. For more information about tileset metadata, see Tileset List.
After a tileset is created, it's retrieved using the Render service.
If a tileset becomes outdated and is no longer useful, you can delete the tileset. For information about how to delete tilesets, see Data maintenance.
Note
A tileset is independent of the dataset from which it was created. If you create tilesets from a dataset, and then subsequently update that dataset, the tilesets isn't updated.
To reflect changes in a dataset, you must create new tilesets. Similarly, if you delete a tileset, the dataset isn't affected.
Custom styling (preview)
A style defines the visual appearance of a map. It defines what data to draw, the order to draw it in, and how to style the data when drawing it. Azure Maps Creator styles support the MapLibre standard for style layers and sprites.
When you convert a drawing package after uploading it to your Azure Maps account, default styles are applied to the elements of your map. The custom styling service enables you to customize the visual appearance of your map. You can do this by manually editing the style JSON and importing it into your Azure Maps account using the Style - Create HTTP request, however the recommended approach is to use the visual style editor. For more information, see Create custom styles for indoor maps.
Example layer in the style.json file:
{
"id": "indoor_unit_gym_label",
"type": "symbol",
"filter": ["all", ["has","floor0"], ["any", ["==", "categoryName", "room.gym"]]],
"layout": {
"visibility": "none",
"icon-image": "gym",
"icon-size": {"stops": [[17.5, 0.7], [21, 1.1]]},
"symbol-avoid-edges": true,
"symbol-placement": "point",
"text-anchor": "top",
"text-field": "{name}",
"text-font": ["SegoeFrutigerHelveticaMYingHei-Medium"],
"text-keep-upright": true,
"text-letter-spacing": 0.1,
"text-offset": [0, 1.05],
"text-size": {"stops": [[18, 5], [18.5, 6.5], [19, 8], [19.5, 9.5], [20, 11]]}
},
"metadata": {"microsoft.maps:layerGroup": "labels_indoor"},
"minzoom": 17.5,
"paint": {
"text-color": "rgba(0, 0, 0, 1)",
"text-halo-blur": 0.5,
"text-halo-color": "rgba(255, 255, 255, 1)",
"text-halo-width": 1,
"text-opacity": ["step", ["zoom"], 0, 18, 1]
},
"source-layer": "Indoor unit"
},
| Layer Properties | Description |
|---|---|
| id | The name of the layer |
| type | The rendering type for this layer. Some of the more common types include: fill: A filled polygon with an optional stroked border. Line: A stroked line. Symbol: An icon or a text label. fill-extrusion: An extruded (3D) polygon. |
| filter | Only features that match the filter criteria are displayed. |
| layout | Layout properties for the layer. |
| minzoom | A number between 0 and 24 that represents the minimum zoom level for the layer. At zoom levels less than the minzoom, the layer is hidden. |
| paint | Default paint properties for this layer. |
| source-layer | A source supplies the data, from a vector tile source, displayed on a map. Required for vector tile sources; prohibited for all other source types, including GeoJSON sources. |
Map configuration
The map configuration is an array of configurations. Each configuration consists of a basemap and one or more layers, each layer consisting of a style + tileset tuple.
The map configuration is used when you Instantiate the Indoor Manager of a Map object when developing applications in Azure Maps. It's referenced using the mapConfigurationId or alias. Map configurations are immutable. When making changes to an existing map configuration, a new map configuration is created, resulting in a different mapConfingurationId. Anytime you create a map configuration using an alias already used by an existing map configuration, it points to the new map configuration.
The following JSON is an example of a default map configuration. See the following table for a description of each element of the file:
{
"version": 1.0,
"description": "This is the default Azure Maps map configuration for facility ontology tilesets.",
"defaultConfiguration": "indoor_light",
"configurations": [
{
"name": "indoor_light",
"displayName": "Indoor light",
"description": "A base style for Azure Maps.",
"thumbnail": "indoor_2022-01-01.png",
"baseMap": "microsoft_light",
"layers": [
{
"tilesetId": "fa37d225-924e-3f32-8441-6128d9e5519a",
"styleId": "microsoft-maps:indoor_2022-01-01"
}
]
},
{
"name": "indoor_dark",
"displayName": "Indoor dark",
"description": "A base style for Azure Maps.",
"thumbnail": "indoor_dark_2022-01-01.png",
"baseMap": "microsoft_dark",
"layers": [
{
"tilesetId": "fa37d225-924e-3f32-8441-6128d9e5519a",
"styleId": "microsoft-maps:indoor_dark_2022-01-01"
}
]
}
]
}
| Style Object Properties | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | The name of the style. |
| displayName | The display name of the style. |
| description | The user defined description of the style. |
| thumbnail | Use to specify the thumbnail used in the style picker for this style. For more information, see the style picker control. |
| baseMap | Use to Set the base map style. |
| layers | The layers array consists of one or more tileset + Style tuples, each being a layer of the map. This enables multiple buildings on a map, each building represented in its own tileset. |
Additional information
- For more information how to modify styles using the style editor, see Create custom styles for indoor maps.
- For more information on style Rest API, see style in the Maps Creator Rest API reference.
- For more information on the map configuration Rest API, see Creator - map configuration Rest API.
Feature statesets
Feature statesets are collections of dynamic properties (states) that are assigned to dataset features, such as rooms or equipment. An example of a state can be temperature or occupancy. Each state is a key/value pair that contains the name of the property, the value, and the timestamp of the last update.
You can use the Feature State service to create and manage a feature stateset for a dataset. The stateset is defined by one or more states. Each feature, such as a room, can have one state attached to it.
The value of each state in a stateset is updated or retrieved by IoT devices or other applications. For example, using the Feature State Update API, devices measuring space occupancy can systematically post the state change of a room.
An application can use a feature stateset to dynamically render features in a facility according to their current state and respective map style. For more information about using feature statesets to style features in a rendering map, see Indoor Maps module.
Note
Like tilesets, changing a dataset doesn't affect the existing feature stateset, and deleting a feature stateset doesn't affect the dataset to which it's attached.
Wayfinding (preview)
The Wayfinding service enables you to provide your customers with the shortest path between two points within a facility. Once you've imported your indoor map data and created your dataset, you can use that to create a routeset. The routeset provides the data required to generate paths between two points. The wayfinding service takes into account things such as the minimum width of openings and can optionally exclude elevators or stairs when navigating between levels as a result.
Creator wayfinding is powered by Havok.
Wayfinding paths
When a wayfinding path is successfully generated, it finds the shortest path between two points in the specified facility. Each floor in the journey is represented as a separate leg, as are any stairs or elevators used to move between floors.
For example, the first leg of the path might be from the origin to the elevator on that floor. The next leg is the elevator, and then the final leg is the path from the elevator to the destination. The estimated travel time is also calculated and returned in the HTTP response JSON.
Structure
For wayfinding to work, the facility data must contain a structure. The wayfinding service calculates the shortest path between two selected points in a facility. The service creates the path by navigating around structures, such as walls and any other impermeable structures.
Vertical penetration
If the selected origin and destination are on different floors, the wayfinding service determines what verticalPenetration objects such as stairs or elevators, are available as possible pathways for navigating vertically between levels. By default, the option that results in the shortest path is used.
The Wayfinding service includes stairs or elevators in a path based on the value of the vertical penetration's direction property. For more information on the direction property, see verticalPenetration in the Facility Ontology article. See the avoidFeatures and minWidth properties in the wayfinding API documentation to learn about other factors that can affect the path selection between floor levels.
For more information, see the Indoor maps wayfinding service how-to article.
Using indoor maps
Render - Get Map Tile API
The Azure Maps [Render - Get Map Tile] API has been extended to support Creator tilesets.
Applications can use the Render - Get Map Tile API to request tilesets. The tilesets can then be integrated into a map control or SDK. For an example of a map control that uses the Render service, see Indoor Maps Module.
Web Feature service API
You can use the Web Feature service (WFS) to query datasets. WFS follows the Open Geospatial Consortium API Features. You can use the WFS API to query features within the dataset itself. For example, you can use WFS to find all mid-size meeting rooms of a specific facility and floor level.
Alias API
Creator services such as Conversion, Dataset, Tileset and Feature State return an identifier for each resource that's created from the APIs. The Alias API allows you to assign an alias to reference a resource identifier.
Indoor Maps module
The Azure Maps Web SDK includes the Indoor Maps module. This module offers extended functionalities to the Azure Maps Map Control library. The Indoor Maps module renders indoor maps created in Creator. It integrates widgets such as floor picker that help users to visualize the different floors.
You can use the Indoor Maps module to create web applications that integrate indoor map data with other Azure Maps services. The most common application setups include adding knowledge from other maps - such as road, imagery, weather, and transit - to indoor maps.
The Indoor Maps module also supports dynamic map styling. For a step-by-step walkthrough to implement feature stateset dynamic styling in an application, see Use the Indoor Map module.
Azure Maps integration
As you begin to develop solutions for indoor maps, you can discover ways to integrate existing Azure Maps capabilities. For example, you can implement asset tracking or safety scenarios by using the Geofence service with Creator indoor maps. For example, you can use the Geofence API to determine whether a worker enters or leaves specific indoor areas. For more information about how to connect Azure Maps with IoT telemetry, see Tutorial: Implement IoT spatial analytics by using Azure Maps.
Data maintenance
You can use the Azure Maps Creator List, Update, and Delete API to list, update, and delete your datasets, tilesets, and feature statesets.
Note
When you review a list of items to determine whether to delete them, consider the impact of that deletion on all dependent API or applications. For example, if you delete a tileset that's being used by an application by means of the [Render - Get Map Tile] API, the application fails to render that tileset.
Example: Updating a dataset
The following example shows how to update a dataset, create a new tileset, and delete an old tileset:
- Follow steps in the Upload a drawing package and Convert a drawing package sections to upload and convert the new drawing package.
- Use Dataset Create to append the converted data to the existing dataset.
- Use Tileset Create to generate a new tileset out of the updated dataset.
- Save the new tilesetId for the next step.
- To enable the visualization of the updated campus dataset, update the tileset identifier in your application. If the old tileset is no longer used, you can delete it.
Next steps
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for