Quickstart: Route custom events to an Azure Function with Event Grid
Azure Event Grid is an eventing service for the cloud. Azure Functions is one of the supported event handlers. In this article, you use the Azure portal to create a custom topic, subscribe to the custom topic, and trigger the event to view the result. You send the events to an Azure Function.
If you don't have an Azure subscription, create an Azure free account before you begin.
Create an Azure function with Azure Event Grid trigger using Visual Studio Code
In this section, you use Visual Studio Code to create an Azure function with an Azure Event Grid trigger.
Prerequisites
- Visual Studio Code installed on one of the supported platforms.
- Azure Functions extension.
Create an Azure function
Launch Visual Studio Code.
On the left bar, select Azure.
In the left pane, In the WORKSPACE section, select Azure Functions button on the command bar, and then select Create Function.
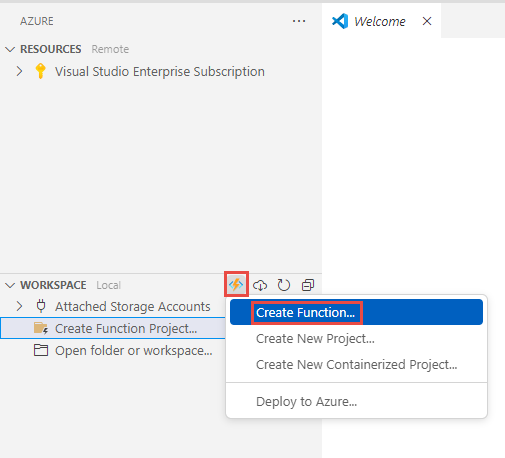
Select a folder where you want the Azure function code to be saved.
For the Create new project command, for language, select C#, and press ENTER.
For .NET runtime, select .NET 8.0 Isolated LTS, and press ENTER.
For the template for the function, select Azure Event Grid trigger, and press ENTER.
For function name, enter a name for your Azure function, and press ENTER.
Enter a name for the namespace for the function, and press ENTER.
Open the project in the current window or a new window or add to a workspace.
Wait for the function to be created. You see the status of the function creation in the bottom-right corner.
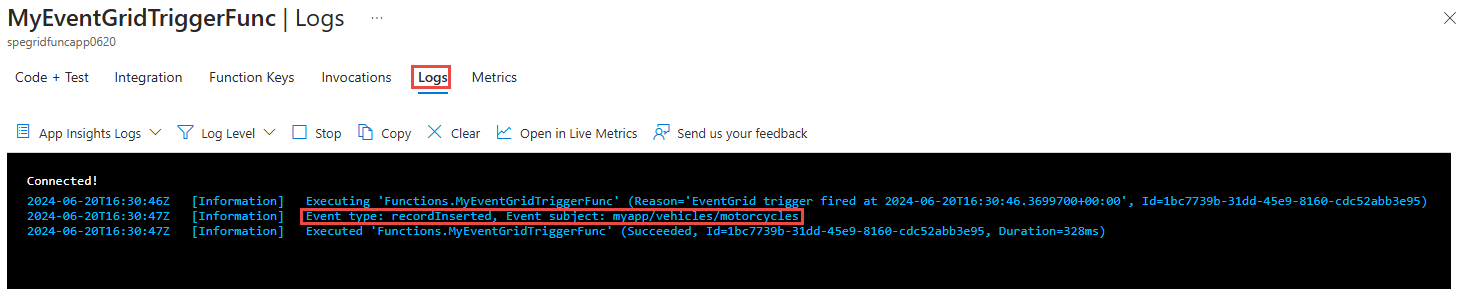
View the code in the YourFunctionName.cs file, specifically the
Runmethod. It prints the information using a logger.[Function(nameof(MyEventGridTriggerFunc))] public void Run([EventGridTrigger] CloudEvent cloudEvent) { _logger.LogInformation("Event type: {type}, Event subject: {subject}", cloudEvent.Type, cloudEvent.Subject); }
Deploy the function to Azure
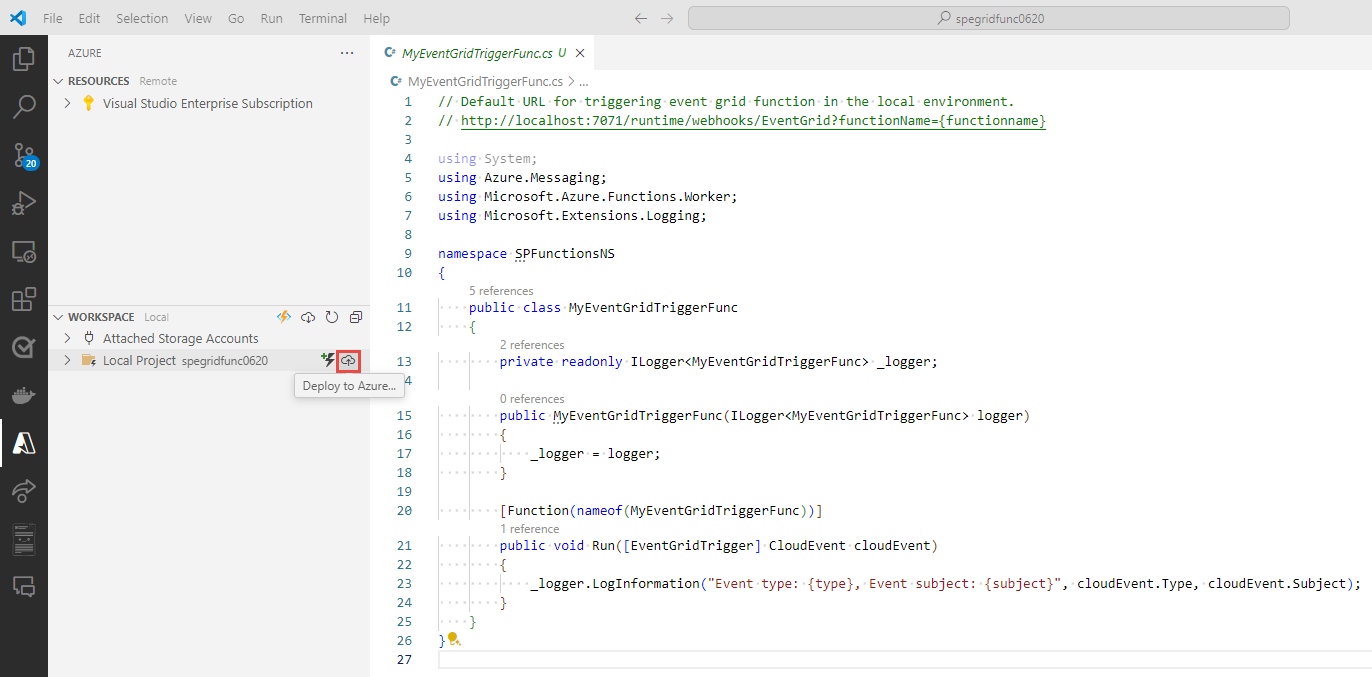
Select the Azure button on the left bar if it's not already open.
Hover the mouse over your project, and select the Deploy to Azure button.
In the drop-down of the command palette, select + Create new function app, and press ENTER.
Enter a globally unique name for the new function app, and press ENTER.
For runtime stack, select .NET 8 Isolated.
For location for your Azure resources, select a region that's close to you.
Now, you see the status of Azure Functions app creation in the AZURE tab of the bottom pane. After the function app is created, you see the status of deploying the Azure function you created locally to the Functions app you created.
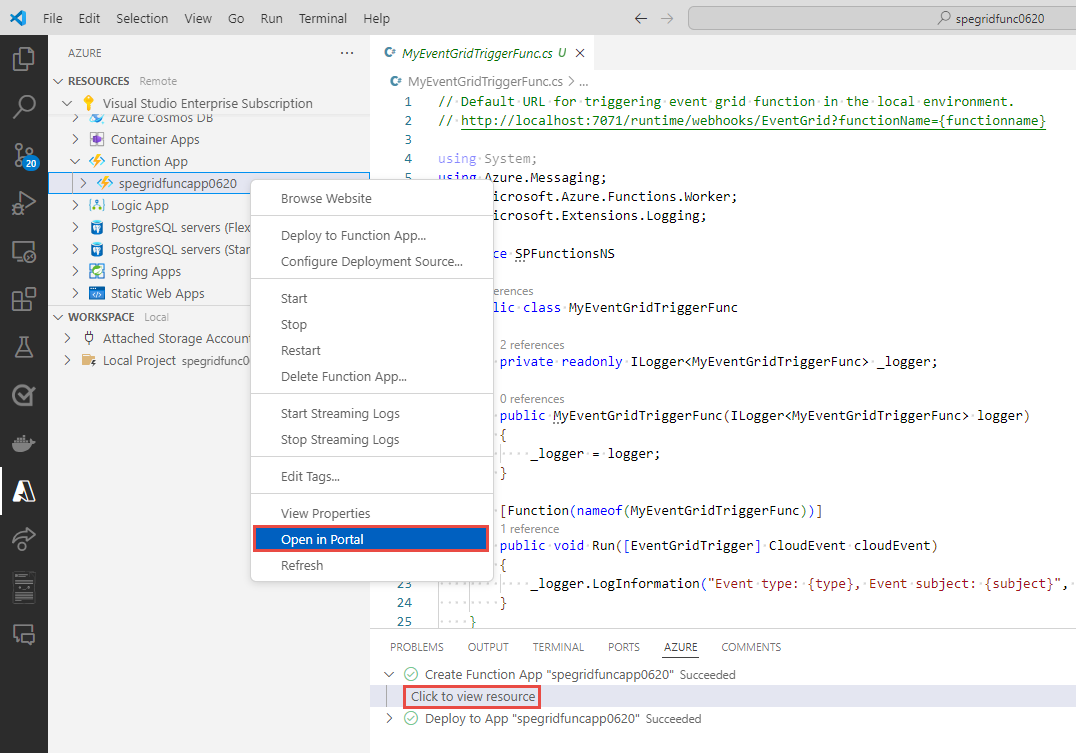
After the deployment succeeds, expand the Create Function App succeeded message and select Click to view resource. You see that your Azure function is selected in the RESOURCES section on the left pane.
Right-click on your Azure function, and select Open in Portal.
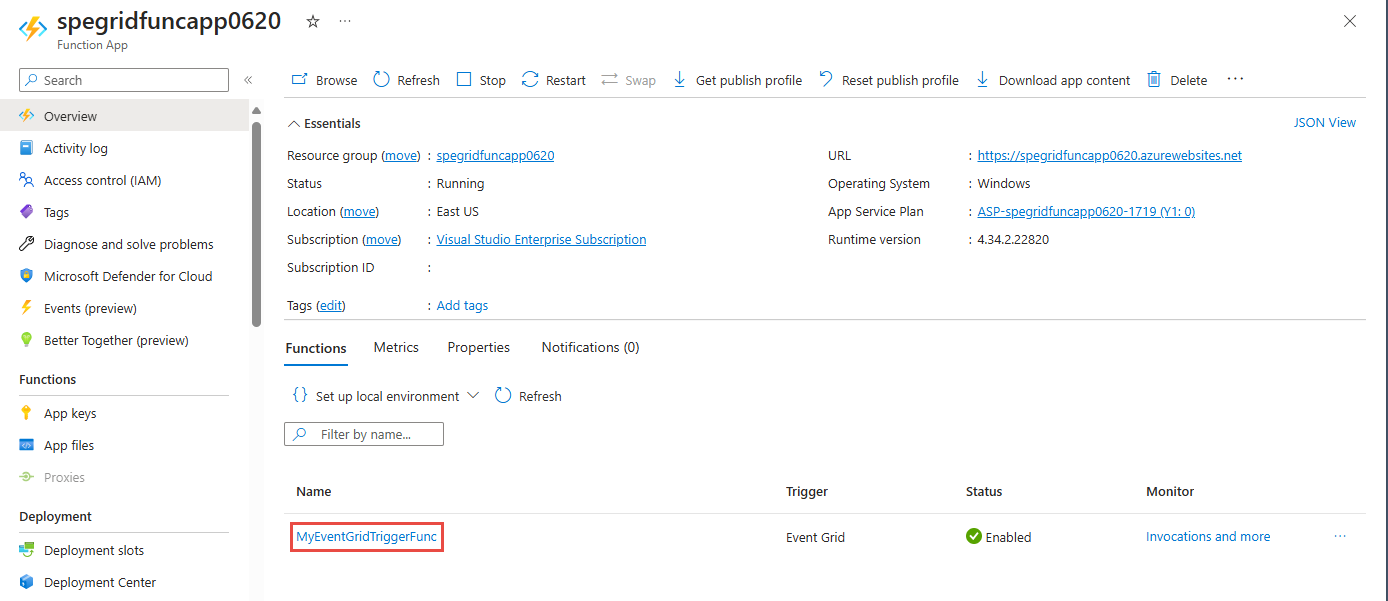
Sign-in to Azure if needed, and you should see the Function App page for your Azure function.
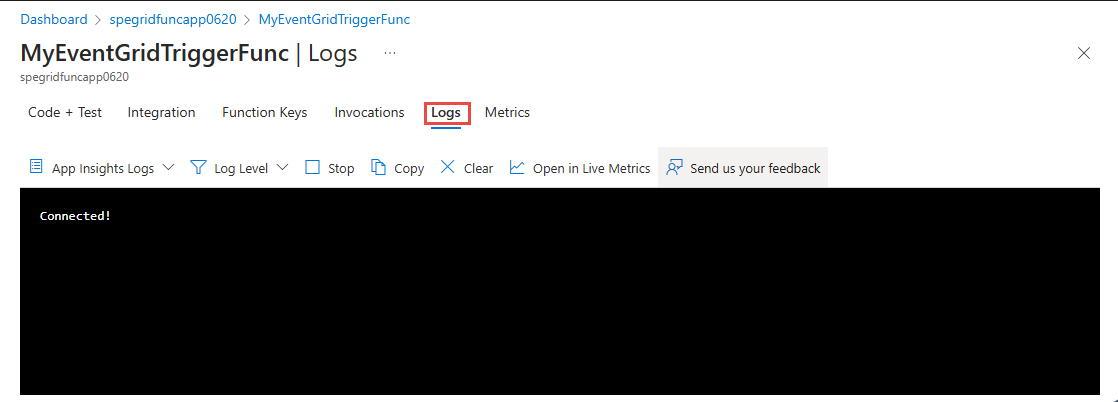
Select your function in the bottom page as shown in the following image.
Switch to the Logs tab and keep this tab or window open so that you can see logged messages when you send an event to an Event Grid later in this tutorial.
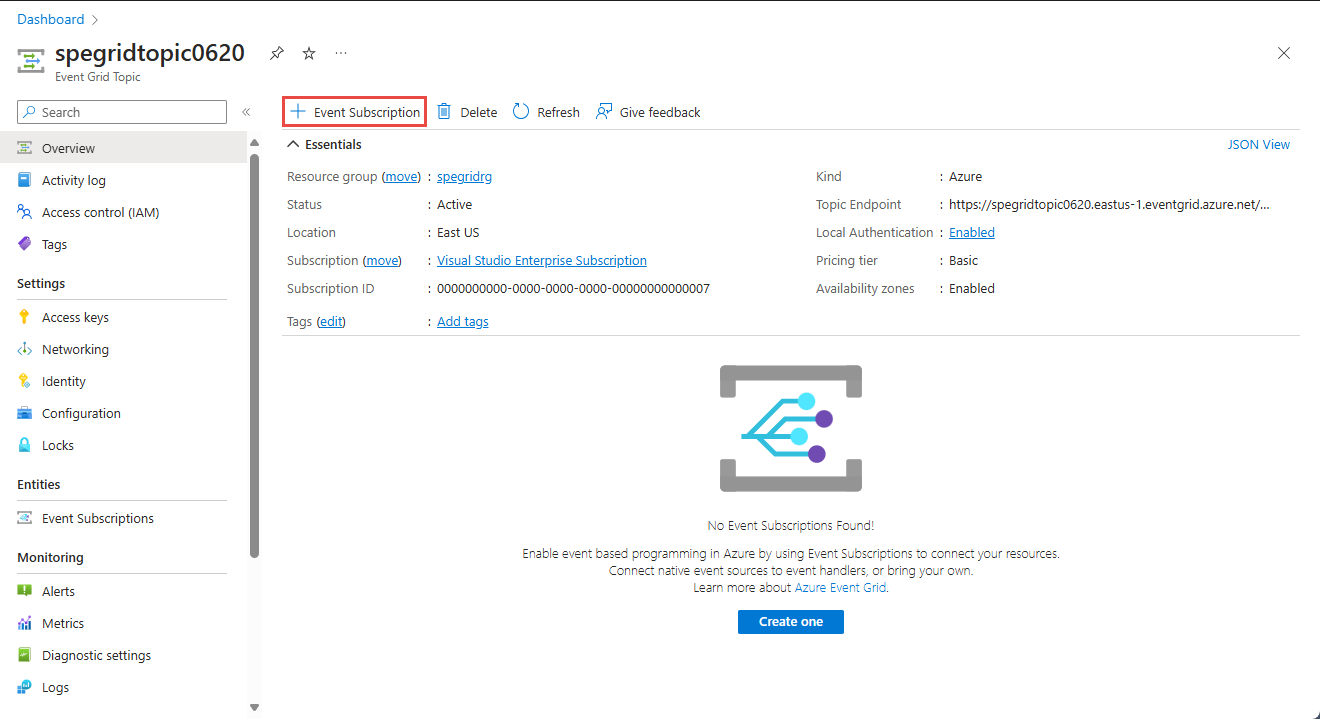
Create a custom topic
An Event Grid topic provides a user-defined endpoint that you post your events to.
On a new tab of the web browser window, sign in to Azure portal.
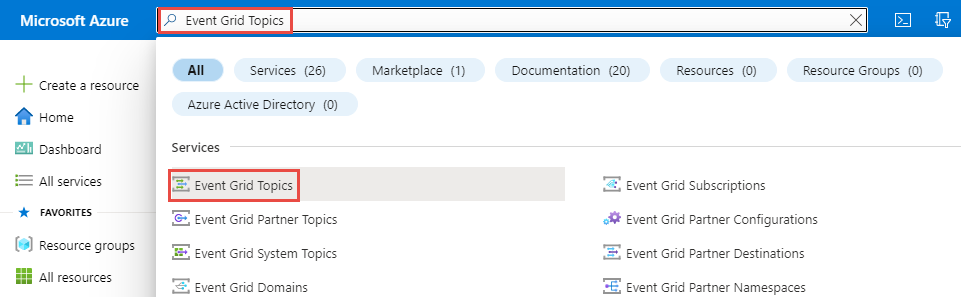
In the search bar at the topic, search for Event Grid Topics, and select Event Grid Topics.
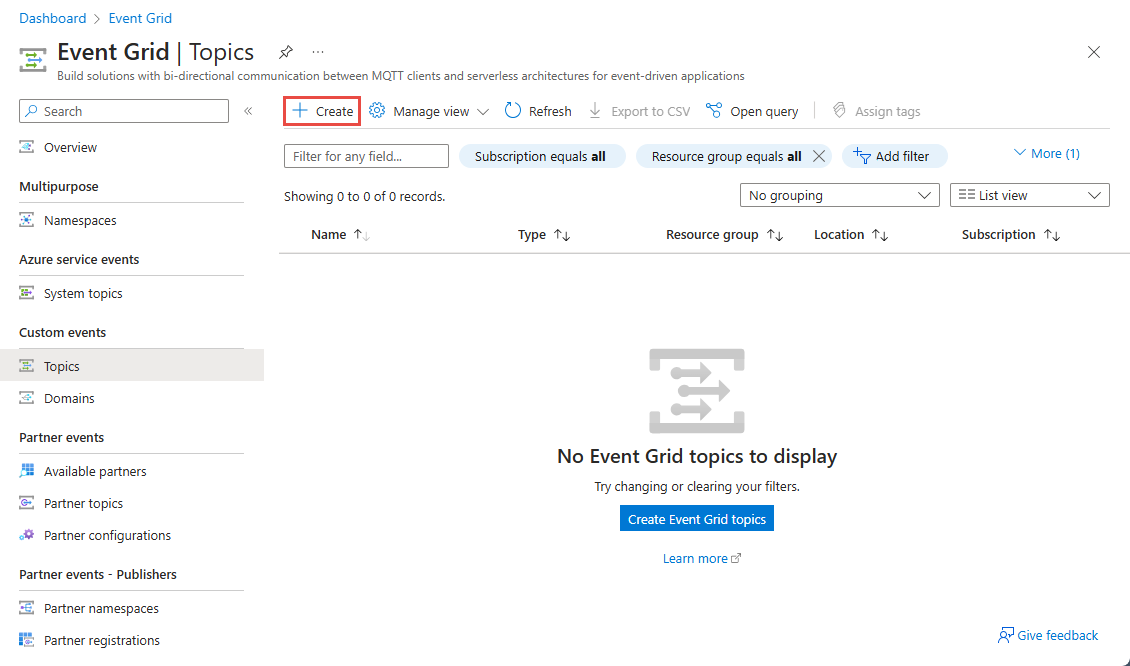
On the Event Grid Topics page, select + Create on the command bar.
On the Create Topic page, follow these steps:
Select your Azure subscription.
Select the same resource group from the previous steps.
Provide a unique name for the custom topic. The topic name must be unique because it's represented by a DNS entry. Don't use the name shown in the image. Instead, create your own name - it must be between 3-50 characters and contain only values a-z, A-Z, 0-9, and
-.Select a location for the Event Grid topic.
Select Review + create.
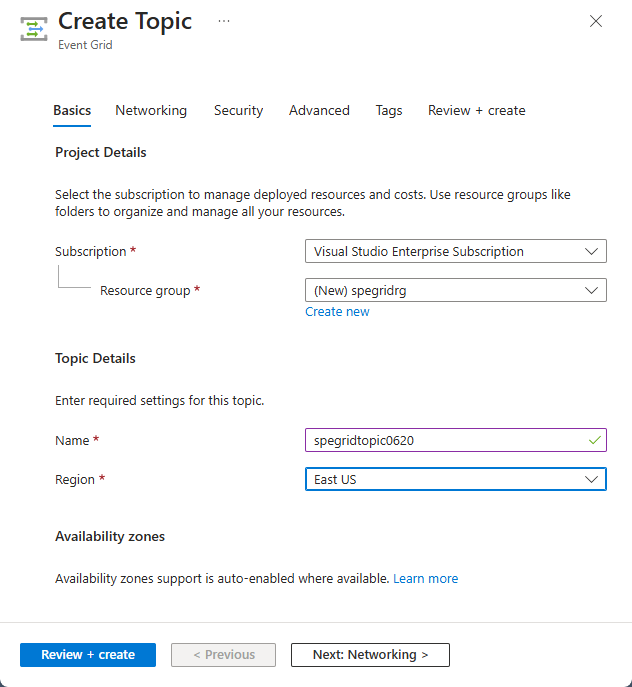
On the Review + create page, review settings and select Create.
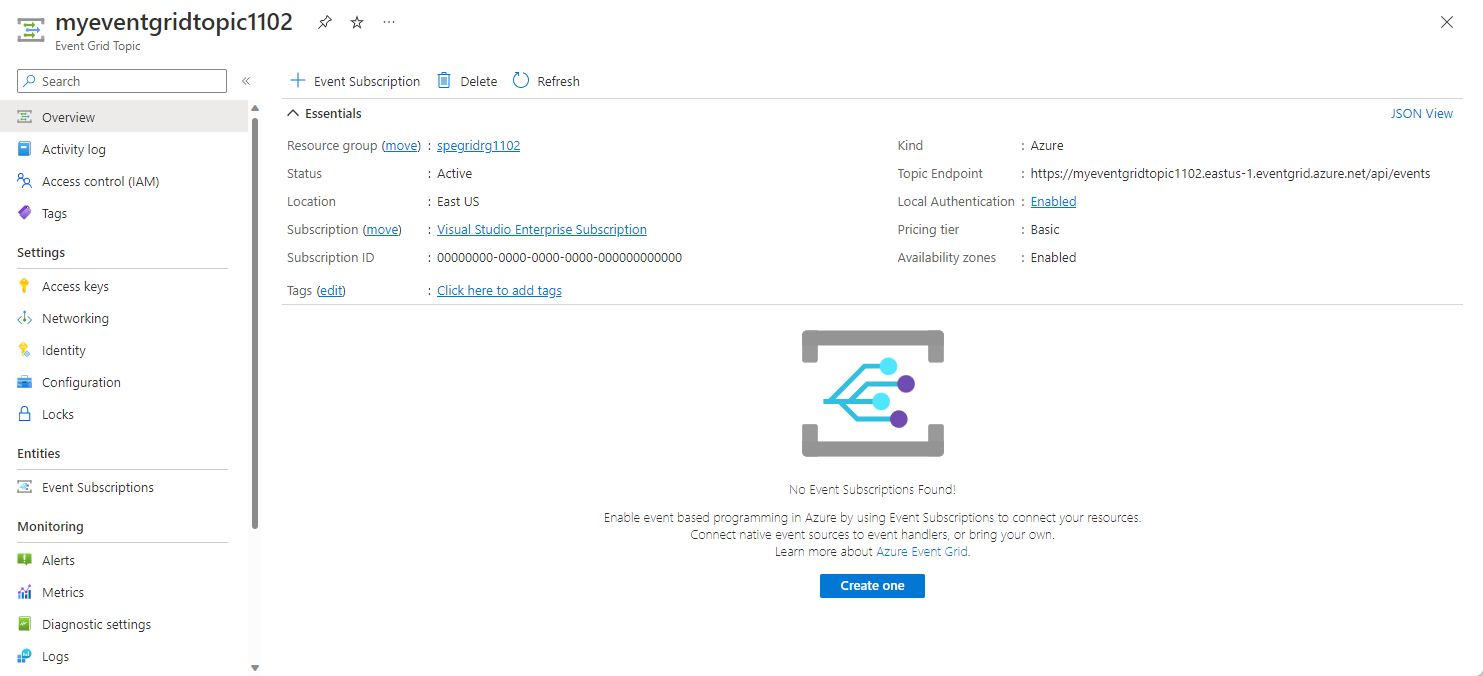
After the custom topic has been created, select Go to resource link to see the following Event Grid topic page for the topic you created.
Subscribe to custom topic
You subscribe to an Event Grid topic to tell Event Grid which events you want to track, and where to send the events.
Now, on the Event Grid Topic page for your custom topic, select + Event Subscription on the toolbar.
On the Create Event Subscription page, follow these steps:
Enter a name for the event subscription.
For Event Schema, select Cloud Event Schema v1.0.
Select Azure Function for the Endpoint type.
Choose Configure an endpoint.
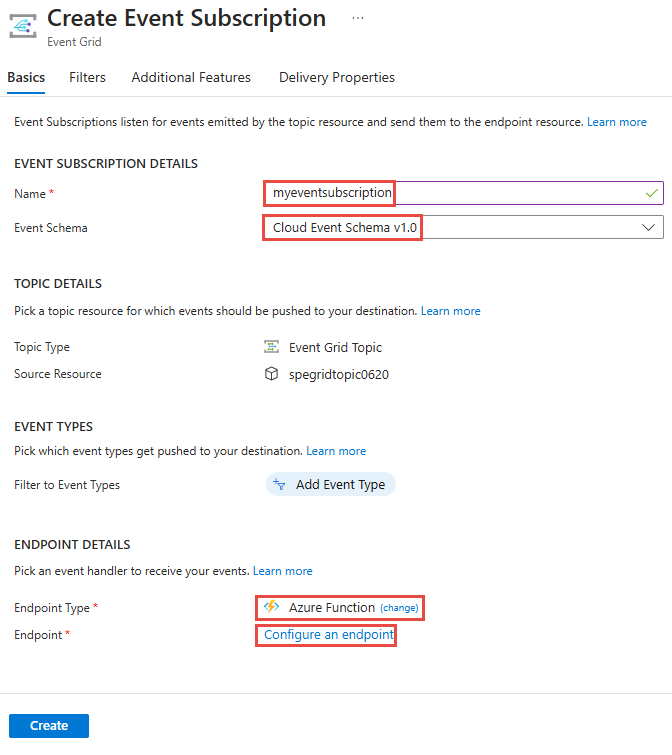
On the Select Azure Function page, follow these steps:
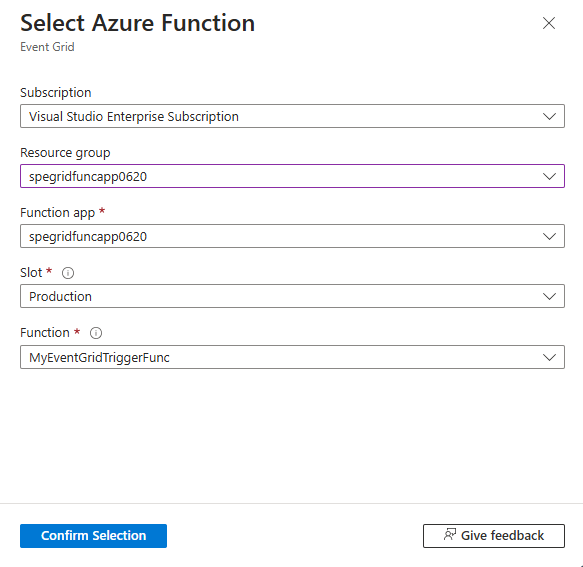
Select the Azure Subscription that has the Azure function.
Select the resource group that has the function.
Select your Azure Functions app.
Select the Azure function in the Functions app.
Select Confirm Selection.
This step is optional, but recommended for production scenarios. On the Create Event Subscription page, switch to the Advanced Features tab, and set values for Max events per batch and Preferred batch size in kilobytes.
Batching can give you high-throughput. For Max events per batch, set the maximum number of events that a subscription will include in a batch. Preferred batch size sets the preferred upper bound of batch size in kilo bytes, but can be exceeded if a single event is larger than this threshold.
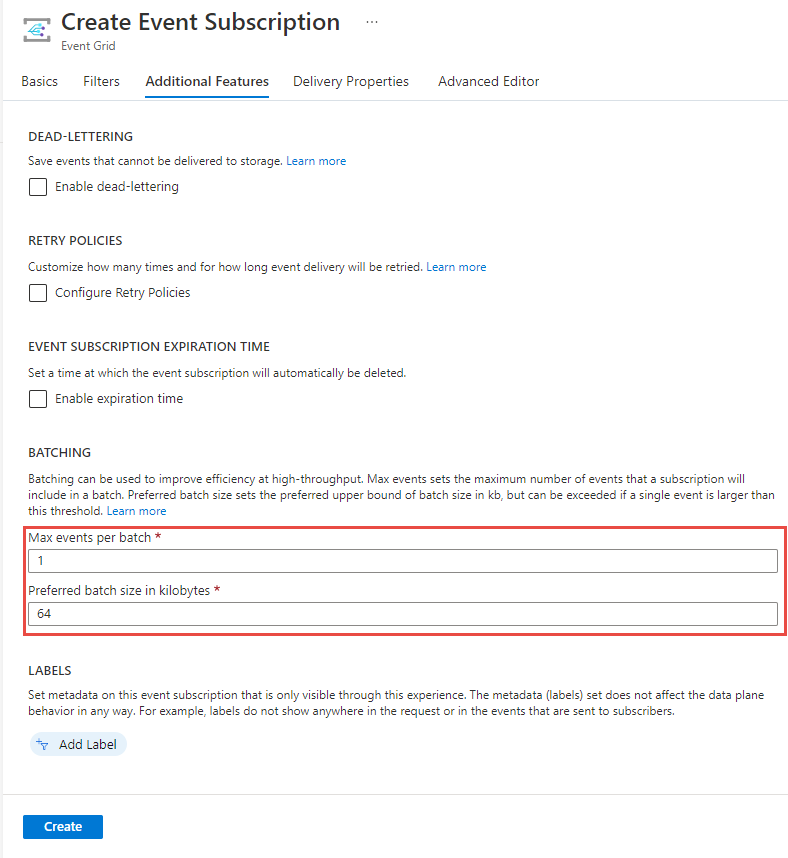
On the Create Event Subscription page, select Create.
Send an event to your topic
Now, let's trigger an event to see how Event Grid distributes the message to your endpoint. Use either Azure CLI or PowerShell to send a test event to your custom topic. Typically, an application or Azure service would send the event data.
The first example uses Azure CLI. It gets the URL and key for the custom topic, and sample event data. Use your custom topic name for <topic name>. It creates sample event data. The data element of the JSON is the payload of your event. Any well-formed JSON can go in this field. You can also use the subject field for advanced routing and filtering. CURL is a utility that sends HTTP requests.
Azure CLI
In the Azure portal, select Cloud Shell. If you are in the PowerShell mode, select Switch to Bash.
Set the
topicnameandresourcegroupnamevariables that are used in the commands.Replace
TOPICNAMEwith the name of your Event Grid topic.topicname="TOPICNAME"Replace
RESOURCEGROUPNAMEwith the name of the Azure resource group that contains the Event Grid topic.resourcegroupname="RESOURCEGROUPNAME"Run the following command to get the endpoint for the topic: After you copy and paste the command, update the topic name and resource group name before you run the command.
endpoint=$(az eventgrid topic show --name $topicname -g $resourcegroupname --query "endpoint" --output tsv)Run the following command to get the key for the custom topic: After you copy and paste the command, update the topic name and resource group name before you run the command.
key=$(az eventgrid topic key list --name $topicname -g $resourcegroupname --query "key1" --output tsv)Copy the following statement with the event definition, and press ENTER.
event='[ {"id": "'"$RANDOM"'", "eventType": "recordInserted", "subject": "myapp/vehicles/motorcycles", "eventTime": "'`date +%Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%S%z`'", "data":{ "make": "Ducati", "model": "Monster"},"dataVersion": "1.0"} ]'Run the following Curl command to post the event:
curl -X POST -H "aeg-sas-key: $key" -d "$event" $endpointConfirm that you see the message from the Azure function in the Logs tab of your Azure function in the Azure portal.
Azure PowerShell
The second example uses PowerShell to perform similar steps.
In the Azure portal, select Cloud Shell (alternatively go to
https://shell.azure.com/). Select Switch to PowerShell in the top-left corner of the Cloud Shell window. See the sample Cloud Shell window image in the Azure CLI section.Set the following variables. After you copy and paste each command, update the topic name and resource group name before you run the command:
$resourceGroupName = "RESOURCEGROUPNAME"$topicName = "TOPICNAME"Run the following commands to get the endpoint and the keys for the topic:
$endpoint = (Get-AzEventGridTopic -ResourceGroupName $resourceGroupName -Name $topicName).Endpoint $keys = Get-AzEventGridTopicKey -ResourceGroupName $resourceGroupName -Name $topicNamePrepare the event. Copy and run the statements in the Cloud Shell window.
$eventID = Get-Random 99999 #Date format should be SortableDateTimePattern (ISO 8601) $eventDate = Get-Date -Format s #Construct body using Hashtable $htbody = @{ id= $eventID eventType="recordInserted" subject="myapp/vehicles/motorcycles" eventTime= $eventDate data= @{ make="Ducati" model="Monster" } dataVersion="1.0" } #Use ConvertTo-Json to convert event body from Hashtable to JSON Object #Append square brackets to the converted JSON payload since they are expected in the event's JSON payload syntax $body = "["+(ConvertTo-Json $htbody)+"]"Use the Invoke-WebRequest cmdlet to send the event.
Invoke-WebRequest -Uri $endpoint -Method POST -Body $body -Headers @{"aeg-sas-key" = $keys.Key1}Confirm that you see the message from the Azure function in the Logs tab of your Azure function in the Azure portal.
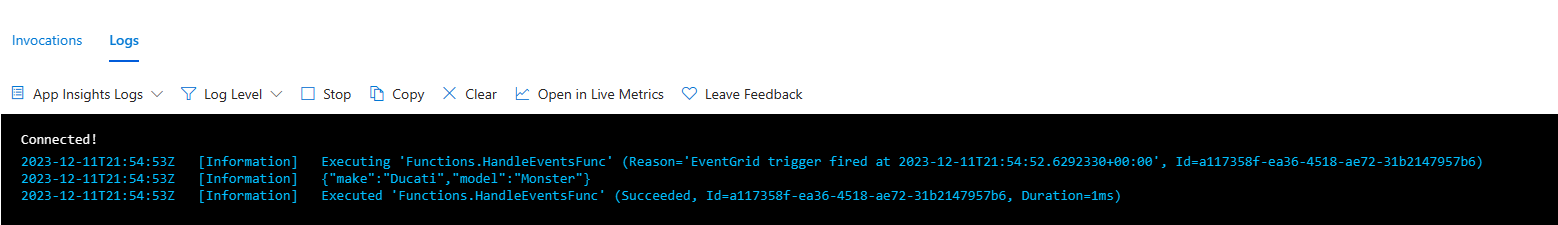
Verify that function received the event
You've triggered the event, and Event Grid sent the message to the endpoint you configured when subscribing.
On the Monitor page for your Azure function, you see an invocation.
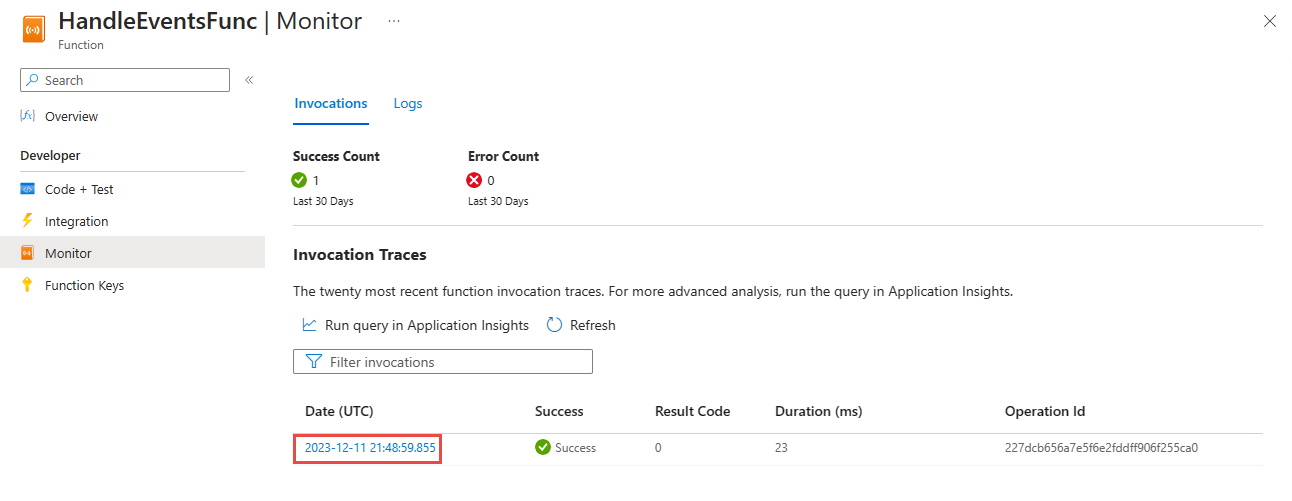
Select the invocation to see the details.
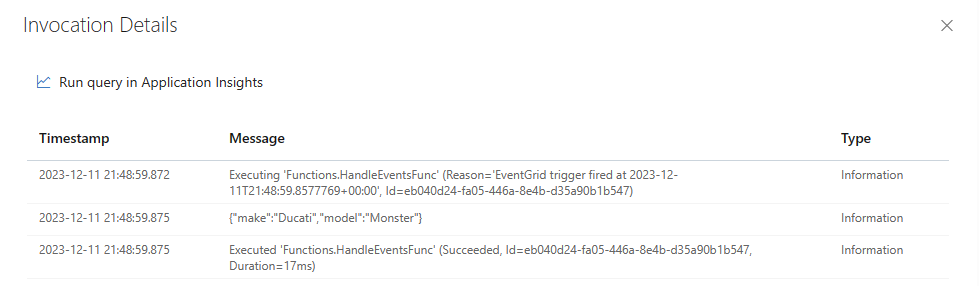
You can also use the Logs tab in the right pane to see the logged messages when you post events to the topic's endpoint.
Clean up resources
If you plan to continue working with this event, don't clean up the resources created in this article. Otherwise, delete the resources you created in this article.
Select Resource Groups on the left menu. If you don't see it on the left menu, select All Services on the left menu, and select Resource Groups.
Select the resource group to launch the Resource Group page.
Select Delete resource group on the toolbar.
Confirm deletion by entering the name of the resource group, and select Delete.
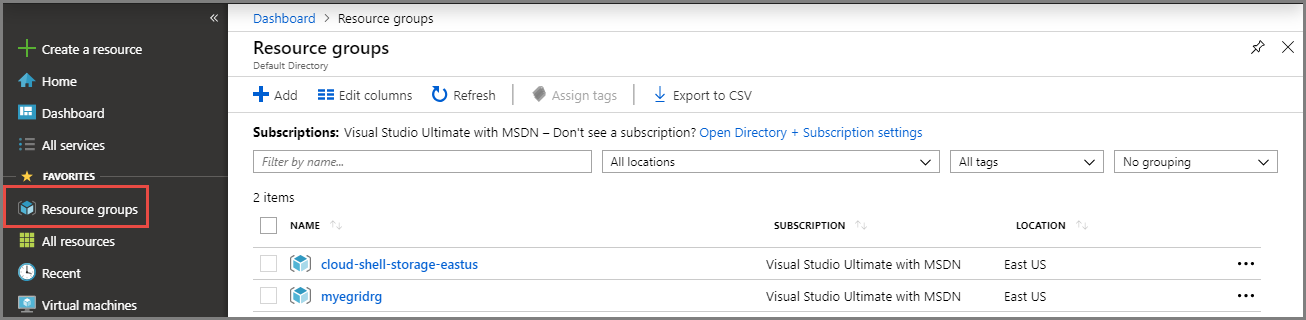
The other resource group you see in the image was created and used by the Cloud Shell window. Delete it if you don't plan to use the Cloud Shell window later.
Next steps
Now that you know how to create topics and event subscriptions, learn more about what Event Grid can help you do:
- About Event Grid
- Route Blob storage events to a custom web endpoint
- Monitor virtual machine changes with Azure Event Grid and Logic Apps
- Stream big data into a data warehouse
See the following samples to learn about publishing events to and consuming events from Event Grid using different programming languages.
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for