What is Data Science in Microsoft Fabric?
Microsoft Fabric offers Data Science experiences to empower users to complete end-to-end data science workflows for the purpose of data enrichment and business insights. You can complete a wide range of activities across the entire data science process, all the way from data exploration, preparation and cleansing to experimentation, modeling, model scoring and serving of predictive insights to BI reports.
Microsoft Fabric users can access a Data Science Home page. From there, they can discover and access various relevant resources. For example, they can create machine learning Experiments, Models and Notebooks. They can also import existing Notebooks on the Data Science Home page.
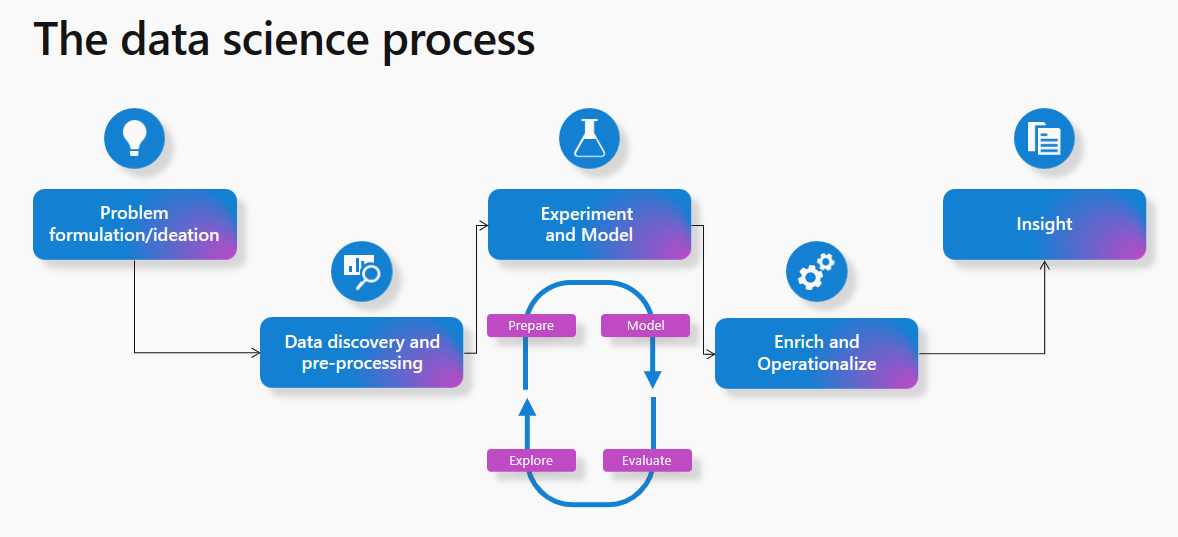
You might know how a typical data science process works. As a well-known process, most machine learning projects follow it.
At a high level, the process involves these steps:
- Problem formulation and ideation
- Data discovery and pre-processing
- Experimentation and modeling
- Enrich and operationalize
- Gain insights
This article describes the Microsoft Fabric Data Science capabilities from a data science process perspective. For each step in the data science process, this article summarizes the Microsoft Fabric capabilities that can help.
Problem formulation and ideation
Data Science users in Microsoft Fabric work on the same platform as business users and analysts. Data sharing and collaboration becomes more seamless across different roles as a result. Analysts can easily share Power BI reports and datasets with data science practitioners. The ease of collaboration across roles in Microsoft Fabric makes hand-offs during the problem formulation phase much easier.
Data discovery and pre-processing
Microsoft Fabric users can interact with data in OneLake using the Lakehouse item. Lakehouse easily attaches to a Notebook to browse and interact with data.
Users can easily read data from a Lakehouse directly into a Pandas dataframe. For exploration, this makes seamless data reads from OneLake possible.
A powerful set of tools is available for data ingestion and data orchestration pipelines with data integration pipelines - a natively integrated part of Microsoft Fabric. Easy-to-build data pipelines can access and transform the data into a format that machine learning can consume.
Data exploration
An important part of the machine learning process is to understand data through exploration and visualization.
Depending on the data storage location, Microsoft Fabric offers a set of different tools to explore and prepare the data for analytics and machine learning. Notebooks become one of the quickest ways to get started with data exploration.
Apache Spark and Python for data preparation
Microsoft Fabric offers capabilities to transform, prepare, and explore your data at scale. With Spark, users can leverage PySpark/Python, Scala, and SparkR/SparklyR tools for data pre-processing at scale. Powerful open-source visualization libraries can enhance the data exploration experience to help better understand the data.
Data Wrangler for seamless data cleansing
The Microsoft Fabric Notebook experience added a feature to use Data Wrangler, a code tool that prepares data and generates Python code. This experience makes it easy to accelerate tedious and mundane tasks - for example, data cleansing, and build repeatability and automation through generated code. Learn more about Data Wrangler in the Data Wrangler section of this document.
Experimentation and ML modeling
With tools like PySpark/Python, SparklyR/R, notebooks can handle machine learning model training.
ML algorithms and libraries can help train machine learning models. Library management tools can install these libraries and algorithms. Users have therefore the option to leverage a large variety of popular machine learning libraries to complete their ML model training in Microsoft Fabric.
Additionally, popular libraries like Scikit Learn can also develop models.
MLflow experiments and runs can track the ML model training. Microsoft Fabric offers a built-in MLflow experience with which users can interact, to log experiments and models. Learn more about how to use MLflow to track experiments and manage models in Microsoft Fabric.
SynapseML
The SynapseML (previously known as MMLSpark) open-source library, that Microsoft owns and maintains, simplifies massively scalable machine learning pipeline creation. As a tool ecosystem, it expands the Apache Spark framework in several new directions. SynapseML unifies several existing machine learning frameworks and new Microsoft algorithms into a single, scalable API. The open-source SynapseML library includes a rich ecosystem of ML tools for development of predictive models, as well as leveraging pre-trained AI models from Azure AI services. Learn more about SynapseML.
Enrich and operationalize
Notebooks can handle machine learning model batch scoring with open-source libraries for prediction, or the Microsoft Fabric scalable universal Spark Predict function, which supports MLflow packaged models in the Microsoft Fabric model registry.
Gain insights
In Microsoft Fabric, Predicted values can easily be written to OneLake, and seamlessly consumed from Power BI reports, with the Power BI Direct Lake mode. This makes it very easy for data science practitioners to share results from their work with stakeholders and it also simplifies operationalization.
Notebooks that contain batch scoring can be scheduled to run using the Notebook scheduling capabilities. Batch scoring can also be scheduled as part of data pipeline activities or Spark jobs. Power BI automatically gets the latest predictions without need for loading or refresh of the data, thanks to the Direct lake mode in Microsoft Fabric.
Data exploration with semantic link (preview)
Important
This feature is in preview.
Data scientists and business analysts spend lots of time trying to understand, clean, and transform data before they can start any meaningful analysis. Business analysts typically work with semantic models and encode their domain knowledge and business logic into Power BI measures. On the other hand, data scientists can work with the same data, but typically in a different code environment or language.
Semantic link (preview) allows data scientists to establish a connection between Power BI semantic models and the Synapse Data Science in Microsoft Fabric experience via the SemPy Python library. SemPy simplifies data analytics by capturing and leveraging data semantics as users perform various transformations on the semantic models. By leveraging semantic link, data scientists can:
- avoid the need to re-implement business logic and domain knowledge in their code
- easily access and use Power BI measures in their code
- use semantics to power new experiences, such as semantic functions
- explore and validate functional dependencies and relationships between data
Through the use of SemPy, organizations can expect to see:
- increased productivity and faster collaboration across teams that operate on the same datasets
- increased cross-collaboration across business intelligence and AI teams
- reduced ambiguity and an easier learning curve when onboarding onto a new model or dataset
For more information on semantic link, see What is semantic link (preview)?.
Related content
- Get started with end-to-end data science samples, see Data Science Tutorials
- Learn more about data preparation and cleansing with Data Wrangler, see Data Wrangler
- Learn more about tracking experiments, see Machine learning experiment
- Learn more about managing models, see Machine learning model
- Learn more about batch scoring with Predict, see Score models with PREDICT
- Serve predictions from Lakehouse to Power BI with Direct lake Mode
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for