Secure Java Spring Boot apps using Microsoft Entra ID
This article demonstrates a Java Spring Boot web app that signs in users on your Microsoft Entra ID tenant using the Microsoft Entra ID Spring Boot Starter client library for Java. It uses the OpenID Connect protocol.
The following diagram shows the topology of the app:
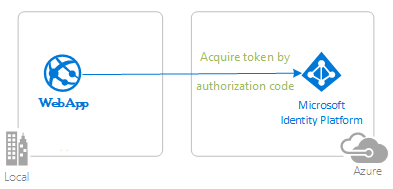
The client app uses the Microsoft Entra ID Spring Boot Starter client library for Java to sign-in a user and obtain an ID token from Microsoft Entra ID. The ID token proves that the user is authenticated with Microsoft Entra ID and enables the user to access protected routes.
Prerequisites
- JDK version 17. This sample was developed on a system with Java 17, but it might be compatible with other versions.
- Maven 3
- Java Extension Pack for Visual Studio Code is recommended for running this sample in Visual Studio Code.
- A Microsoft Entra ID tenant. For more information, see How to get a Microsoft Entra ID tenant.
- A user account in your Microsoft Entra ID tenant. This sample doesn't work with a personal Microsoft account. Therefore, if you signed in to the Azure portal with a personal account and you don't have a user account in your directory, you need to create one now.
- Visual Studio Code
- Azure Tools for Visual Studio Code
Recommendations
- Some familiarity with the Spring Framework
- Some familiarity with Linux/OSX terminal or Windows PowerShell
- jwt.ms for inspecting your tokens.
- Fiddler for monitoring your network activity and troubleshooting.
- Follow the Microsoft Entra ID Blog to stay up-to-date with the latest developments.
Set up the sample
The following sections show you how to set up the sample application.
Clone or download the sample repository
To clone the sample, open a Bash window and use the following command:
git clone https://github.com/Azure-Samples/ms-identity-msal-java-samples.git
cd 4-spring-web-app/1-Authentication/sign-in
Alternatively, navigate to the ms-identity-msal-java-samples repository, then download it as a .zip file and extract it to your hard drive.
Important
To avoid path length limitations on Windows, we recommend cloning into a directory near the root of your drive.
Register the sample applications with your Microsoft Entra ID tenant
There's one project in this sample. The following sections show you how to register the app using the Azure portal.
Choose the Microsoft Entra ID tenant where you want to create your applications
To choose your tenant, use the following steps:
Sign in to the Azure portal.
If your account is present in more than one Microsoft Entra ID tenant, select your profile in the corner of the Azure portal, and then select Switch directory to change your session to the desired Microsoft Entra ID tenant.
Register the app (java-spring-webapp-auth)
To register the app, use the following steps:
Navigate to the Azure portal and select Microsoft Entra ID.
Select App Registrations on the navigation pane, then select New registration.
In the Register an application page that appears, enter the following application registration information:
- In the Name section, enter a meaningful application name for display to users of the app - for example,
java-spring-webapp-auth. - Under Supported account types, select Accounts in this organizational directory only.
- In the Redirect URI (optional) section, select Web in the combo-box and enter the following redirect URI:
http://localhost:8080/login/oauth2/code/.
- In the Name section, enter a meaningful application name for display to users of the app - for example,
Select Register to create the application.
On the app's registration page, find and copy the Application (client) ID value to use later. You use this value in your app's configuration file or files.
On the app's registration page, select Certificates & secrets on the navigation pane to open the page where you can generate secrets and upload certificates.
In the Client secrets section, select New client secret.
Type a description - for example, app secret.
Select one of the available durations: In 1 year, In 2 years, or Never Expires.
Select Add. The generated value is displayed.
Copy and save the generated value for use in later steps. You need this value for your code's configuration files. This value isn't displayed again, and you can't retrieve it by any other means. So, be sure to save it from the Azure portal before you navigate to any other screen or pane.
Configure the app (java-spring-webapp-auth) to use your app registration
Use the following steps to configure the app:
Note
In the following steps, ClientID is the same as Application ID or AppId.
Open the project in your IDE.
Open the src\main\resources\application.yml file.
Find the placeholder
Enter_Your_Tenant_ID_Hereand replace the existing value with your Microsoft Entra tenant ID.Find the placeholder
Enter_Your_Client_ID_Hereand replace the existing value with the application ID orclientIdof thejava-spring-webapp-authapp copied from the Azure portal.Find the placeholder
Enter_Your_Client_Secret_Hereand replace the existing value with the value you saved during the creation ofjava-spring-webapp-authcopied from the Azure portal.
Run the sample
The following sections show you how to deploy the sample to Azure Spring Apps.
Prerequisites
If you're deploying an Azure Spring Apps Enterprise plan instance for the first time in the target subscription, see the Requirements section of Enterprise plan in Azure Marketplace.
Maven Plugin for Azure Spring Apps. If Maven isn't your preferred development tool, see the following similar tutorials that use other tools:
Prepare the Spring project
Use the following steps to prepare the project:
Use the following Maven command to build the project:
mvn clean packageRun the sample project locally by using the following command:
mvn spring-boot:run
Configure the Maven plugin
Run the following command in the root of the project to configure the app using the Maven plugin for Azure Spring Apps:
mvn com.microsoft.azure:azure-spring-apps-maven-plugin:1.19.0:config
The following list describes the command interactions:
- OAuth2 login: You need to authorize the sign-in to Azure based on the OAuth2 protocol.
- Select subscription: Select the subscription list number where you want to create your Azure Spring Apps instance, which defaults to the first subscription in the list. If you want to use the default number, press Enter.
- Input the Azure Spring Apps name: Enter the name for the spring apps instance you want to create. If you want to use the default name, press Enter.
- Input the resource group name: Enter the name for the resource group you want to create your spring apps instance in. If you want to use the default name, press Enter.
- Skus: Select the SKU you want to use for your spring apps instance. If you want to use the default number, press Enter.
- Input the app name (demo): Provide an app name. If you want to use the default project artifact ID, press Enter.
- Runtimes: Select the runtime you want to use for your spring apps instance. In this case, you should use the default number, so press Enter.
- Expose public access for this app (boot-for-azure): Press y.
- Confirm to save all the above configurations: Press y. If you press n, the configuration isn't saved in the .pom file.
The following example shows the output of the deployment process:
Summary of properties:
Subscription id : 12345678-1234-1234-1234-123456789101
Resource group name : rg-ms-identity-spring-boot-webapp
Azure Spring Apps name : cluster-ms-identity-spring-boot-webapp
Runtime Java version : Java 11
Region : eastus
Sku : Standard
App name : ms-identity-spring-boot-webapp
Public access : true
Instance count/max replicas : 1
CPU count : 1
Memory size(GB) : 2
Confirm to save all the above configurations (Y/n):
[INFO] Configurations are saved to: /home/user/ms-identity-msal-java-samples/4-spring-web-app/1-Authentication/sign-in/pom. xml
[INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------------
[INFO] BUILD SUCCESS
[INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------------
[INFO] Total time: 01:57 min
[INFO] Finished at: 2024-02-14T13:50:44Z
[INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------------
After you've confirmed your choices, the plugin adds the required plugin element and settings to your project's pom.xml file to configure your app to run in Azure Spring Apps.
The relevant portion of the pom.xml file should look similar to the following example:
<plugin>
<groupId>com.microsoft.azure</groupId>
<artifactId>azure-spring-apps-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>1.19.0</version>
<configuration>
<subscriptionId>12345678-1234-1234-1234-123456789101</subscriptionId>
<resourceGroup>rg-ms-identity-spring-boot-webapp</resourceGroup>
<clusterName>cluster-ms-identity-spring-boot-webapp</clusterName>
<region>eastus</region>
<sku>Standard</sku>
<appName>ms-identity-spring-boot-webapp</appName>
<isPublic>true</isPublic>
<deployment>
<cpu>1</cpu>
<memoryInGB>2</memoryInGB>
<instanceCount>1</instanceCount>
<runtimeVersion>Java 11</runtimeVersion>
<resources>
<resource>
<directory>${project.basedir}/target</directory>
<includes>
<include>*.jar</include>
</includes>
</resource>
</resources>
</deployment>
</configuration>
</plugin>
You can modify the configurations for Azure Spring Apps directly in your pom.xml file. Some common configurations are listed in the following table:
| Property | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
subscriptionId |
false | The subscription ID. |
resourceGroup |
true | The Azure resource group for your Azure Spring Apps instance. |
clusterName |
true | The Azure Spring Apps cluster name. In case you're using a subscription and resource group that already have an Azure Spring Apps instance deployed, you can also use this existing cluster to deploy to. |
appName |
true | The name of your app in Azure Spring Apps. |
region |
false | The region in which to host your Azure Spring Apps instance. The default value is eastus. For valid regions, see Supported Regions. |
sku |
false | The pricing tier for your Azure Spring Apps instance. The default value is Basic, which is suited only for development and test environments. |
runtime |
false | The runtime environment configuration. For more information, see Configuration Details. |
deployment |
false | The deployment configuration. For more information, see Configuration Details. |
For the complete list of configurations, see the plugin reference documentation. All the Azure Maven plugins share a common set of configurations. For these configurations, see Common Configurations. For configurations specific to Azure Spring Apps, see Azure Spring Apps: Configuration Details.
Be sure to save aside the clusterName and appName values for later use.
Prepare the app for deployment
When you deploy your application to Azure Spring Apps, your redirect URL changes to the redirect URL of your deployed app instance in Azure Spring Apps. Use the following steps to change these settings in your application.yml file:
Navigate to your app's src\main\resources\application.yml file and change the value of
post-logout-redirect-urito your deployed app's domain name, as shown in the following example. For example, if you chosecluster-ms-identity-spring-boot-webappfor your Azure Spring Apps instance in the previous step andms-identity-spring-boot-webappfor your app name, you must now usehttps://cluster-ms-identity-spring-boot-webapp-ms-identity-spring-boot-webapp.azuremicroservices.iofor thepost-logout-redirect-urivalue.post-logout-redirect-uri: https://<cluster-name>-<app-name>.azuremicroservices.ioAfter saving this file, use the following command to rebuild your app:
mvn clean package
Important
The application.yml file of the application currently holds the value of your client secret in the client-secret parameter. It isn't good practice to keep this value in this file. You might also be taking a risk if you commit it to a Git repository.
As an extra security step, you can store this value in Azure Key Vault and load the secret from Key Vault to make it available in your application.
Update your Microsoft Entra ID app registration
Because the redirect URI changes to your deployed app on Azure Spring Apps, you also need to change the redirect URI in your Microsoft Entra ID app registration. Use the following steps to make this change:
Navigate to the Microsoft identity platform for developers App registrations page.
Use the search box to search for your app registration - for example,
java-servlet-webapp-authentication.Open your app registration by selecting its name.
Select Authentication from the menu.
In the Web - Redirect URIs section, select Add URI.
Fill out the URI of your app, appending
/login/oauth2/code/- for example,https://<cluster-name>-<app-name>.azuremicroservices.io/login/oauth2/code/.Select Save.
Deploy the app
Use the following command to deploy the app:
mvn azure-spring-apps:deploy
The following list describes the command interaction:
- OAuth2 login: You need to authorize the sign-in to Azure based on the OAuth2 protocol.
After the command is executed, you can see from the following log messages that the deployment was successful:
[INFO] Deployment(default) is successfully created
[INFO] Starting Spring App after deploying artifacts...
[INFO] Deployment Status: Running
[INFO] InstanceName:demo-default-x-xxxxxxxxxx-xxxxx Status:Running Reason:null DiscoverStatus:UNREGISTERED
[INFO] InstanceName:demo-default-x-xxxxxxxxx-xxxxx Status:Terminating Reason:null DiscoverStatus:UNREGISTERED
[INFO] Getting public url of app(demo)...
[INFO] Application url: https://<your-Azure-Spring-Apps-instance-name>-demo.azuremicroservices.io
Validate the app
After the deployment finishes, access the application with the output application URL. Use the following steps to check the app's logs to investigate any deployment issue:
Access the output application URL from the Outputs page of the Deployment section.
From the navigation pane of the Azure Spring Apps instance Overview page, select Logs to check the app's logs.
Explore the sample
Use the following steps to explore the sample:
- Notice the signed-in or signed-out status displayed at the center of the screen.
- Select the context-sensitive button in the corner. This button reads Sign In when you first run the app. Alternatively, select token details. Because this page is protected and requires authentication, you're automatically redirected to the sign-in page.
- On the next page, follow the instructions and sign in with an account in the Microsoft Entra ID tenant.
- On the consent screen, notice the scopes that are being requested.
- Upon successful completion of the sign-in flow, you should be redirected to the home page - which shows the sign in status - or the token details page, depending on which button triggered your sign-in flow.
- Notice that the context-sensitive button now says Sign out and displays your user name.
- If you're on the home page, select ID Token Details to see some of the ID token's decoded claims.
- Use the button in the corner to sign out. The status page reflects the new state.
About the code
This sample demonstrates how to use Microsoft Entra ID Spring Boot Starter client library for Java to sign in users into your Microsoft Entra ID tenant. The sample also makes use of the Spring Oauth2 Client and Spring Web boot starters. The sample uses claims from the ID token obtained from Microsoft Entra ID to display the details of the signed-in user.
Contents
The following table shows the contents of the sample project folder:
| File/folder | Description |
|---|---|
| pom.xml | Application dependencies. |
| src/main/resources/templates/ | Thymeleaf Templates for UI. |
| src/main/resources/application.yml | Application and Microsoft Entra ID Boot Starter Library Configuration. |
| src/main/java/com/microsoft/azuresamples/msal4j/msidentityspringbootwebapp/ | This directory contains the main application entry point, controller, and config classes. |
| .../MsIdentitySpringBootWebappApplication.java | Main class. |
| .../SampleController.java | Controller with endpoint mappings. |
| .../SecurityConfig.java | Security configuration - for example, which routes require authentication. |
| .../Utilities.java | Utility class - for example, filter ID token claims. |
| CHANGELOG.md | List of changes to the sample. |
| CONTRIBUTING.md | Guidelines for contributing to the sample. |
| LICENSE | The license for the sample. |
ID token claims
To extract token details, the app makes use of Spring Security's AuthenticationPrincipal and OidcUser object in a request mapping, as shown in the following example. See the Sample Controller for the full details of how this app makes use of ID token claims.
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.core.oidc.user.OidcUser;
import org.springframework.security.core.annotation.AuthenticationPrincipal;
//...
@GetMapping(path = "/some_path")
public String tokenDetails(@AuthenticationPrincipal OidcUser principal) {
Map<String, Object> claims = principal.getIdToken().getClaims();
}
Sign-in and sign-out links
For sign-in, the app makes a request to the Microsoft Entra ID sign-in endpoint automatically configured by Microsoft Entra ID Spring Boot Starter client library for Java, as shown in the following example:
<a class="btn btn-success" href="/oauth2/authorization/azure">Sign In</a>
For sign-out, the app makes a POST request to the logout endpoint, as shown in the following example:
<form action="#" th:action="@{/logout}" method="post">
<input class="btn btn-warning" type="submit" value="Sign Out" />
</form>
Authentication-dependent UI elements
The app has some simple logic in the UI template pages for determining content to display based on whether the user is authenticated, as shown in the following example using Spring Security Thymeleaf tags:
<div sec:authorize="isAuthenticated()">
this content only shows to authenticated users
</div>
<div sec:authorize="isAnonymous()">
this content only shows to not-authenticated users
</div>
Protect routes with AADWebSecurityConfigurerAdapter
By default, the app protects the ID Token Details page so that only signed-in users can access it. The app configures these routes by using the app.protect.authenticated property from the application.yml file. To configure your app's specific requirements, apply the AadWebApplicationHttpSecurityConfigurer#aadWebApplication method to the HttpSecurity instance. For an example, see this app's SecurityConfig class, shown in the following code:
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
@EnableMethodSecurity
public class SecurityConfig {
@Value("${app.protect.authenticated}")
private String[] allowedOrigins;
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChain filterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
// @formatter:off
http.apply(AadWebApplicationHttpSecurityConfigurer.aadWebApplication())
.and()
.authorizeHttpRequests(auth -> auth
.requestMatchers(allowedOrigins).authenticated()
.anyRequest().permitAll()
);
// @formatter:on
return http.build();
}
@Bean
@RequestScope
public ServletUriComponentsBuilder urlBuilder() {
return ServletUriComponentsBuilder.fromCurrentRequest();
}
}
More information
- Microsoft identity platform (Microsoft Entra ID for developers)
- Overview of Microsoft Authentication Library (MSAL)
- Quickstart: Register an application with the Microsoft identity platform
- Quickstart: Configure a client application to access web APIs
- Understanding Microsoft Entra ID application consent experiences
- Understand user and admin consent
- Application and service principal objects in Microsoft Entra ID
- National Clouds
- MSAL code samples
- Microsoft Entra ID Spring Boot Starter client library for Java
- Microsoft Authentication Library for Java (MSAL4J)
- MSAL4J Wiki
- ID tokens
- Access tokens in the Microsoft identity platform
For more information about how OAuth 2.0 protocols work in this scenario and other scenarios, see Authentication Scenarios for Microsoft Entra ID.
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for