Overview of enterprise security in Azure HDInsight
Azure HDInsight offers a number of methods to address your enterprise security needs. Most of these solutions aren't activated by default. This flexibility allows you to choose the security features that are most important to you and helps you to avoid paying for features that you don't want. This flexibility also means it's your responsibility to make sure correct solutions are enabled for your setup and environment.
This article looks at security solutions by dividing security solutions into four traditional security pillars: perimeter security, authentication, authorization, and encryption.
This article also introduces the Azure HDInsight Enterprise Security Package (ESP), which provides Active Directory-based authentication, multi-user support, and role-based access control for HDInsight clusters.
Enterprise security pillars
One way of looking at enterprise security divides security solutions into four main groups based on the type of control. These groups are also called security pillars and are the following types: perimeter security, authentication, authorization, and encryption.
Perimeter security
Perimeter security in HDInsight is achieved through virtual networks. An enterprise admin can create a cluster inside a virtual network (VNET) and use network security groups (NSG) to restrict access to the virtual network. Only the allowed IP addresses in the inbound NSG rules can communicate with the HDInsight cluster. This configuration provides perimeter security.
All clusters deployed in a VNET will also have a private endpoint. The endpoint resolves to a private IP inside the VNET for private HTTP access to the cluster gateways.
Authentication
Enterprise Security Package from HDInsight provides Active Directory-based authentication, multi-user support, and role-based access control. The Active Directory integration is achieved through the use of Microsoft Entra Domain Services. With these capabilities, you can create an HDInsight cluster joined to an Active Directory domain. Then configure a list of employees from the enterprise who can authenticate to the cluster.
With this setup, enterprise employees can sign in to the cluster nodes by using their domain credentials. They can also use their domain credentials to authenticate with other approved endpoints. Like Apache Ambari Views, ODBC, JDBC, PowerShell, and REST APIs to interact with the cluster.
Authorization
A best practice most enterprises follow is making sure that not every employee has full access to all enterprise resources. Likewise, the admin can define role-based access control policies for the cluster resources. This action is only available in the ESP clusters.
The Hadoop admin can configure role-based access control (RBAC). The configurations secure Apache Hive, HBase, and Kafka with Apache Ranger plugins. Configuring RBAC policies allows you to associate permissions with a role in the organization. This layer of abstraction makes it easier to ensure people have only the permissions needed to do their work responsibilities. Ranger also allows you to audit the data access of employees and any changes done to access control policies.
For example, the admin can configure Apache Ranger to set access control policies for Hive. This functionality ensures row-level and column-level filtering (data masking). And filters the sensitive data from unauthorized users.
Auditing
Auditing cluster resource access is necessary to track unauthorized or unintentional access of the resources. It's as important as protecting the cluster resources from unauthorized access.
The admin can view and report all access to the HDInsight cluster resources and data. The admin can view and report changes to the access control policies.
To access Apache Ranger and Ambari audit logs, and ssh access logs, enable Azure Monitor and view the tables that provide auditing records.
Encryption
Protecting data is important for meeting organizational security and compliance requirements. Along with restricting access to data from unauthorized employees, you should encrypt it.
HDInsight supports data encryption at rest with both platform managed and customer managed keys. Encryption of data in transit is handled with both TLS and IPSec. See Encryption in transit for Azure HDInsight for more information.
Compliance
Azure compliance offerings are based on various types of assurances, including formal certifications. Also, attestations, validations, and authorizations. Assessments produced by independent third-party auditing firms. Contractual amendments, self-assessments, and customer guidance documents produced by Microsoft. For HDInsight compliance information, see the Microsoft Trust Center.
Shared responsibility model
The following image summarizes the major system security areas and the security solutions that are available to you in each. It also highlights which security areas are your responsibility as a customer. And which areas are the responsibility of HDInsight as the service provider.
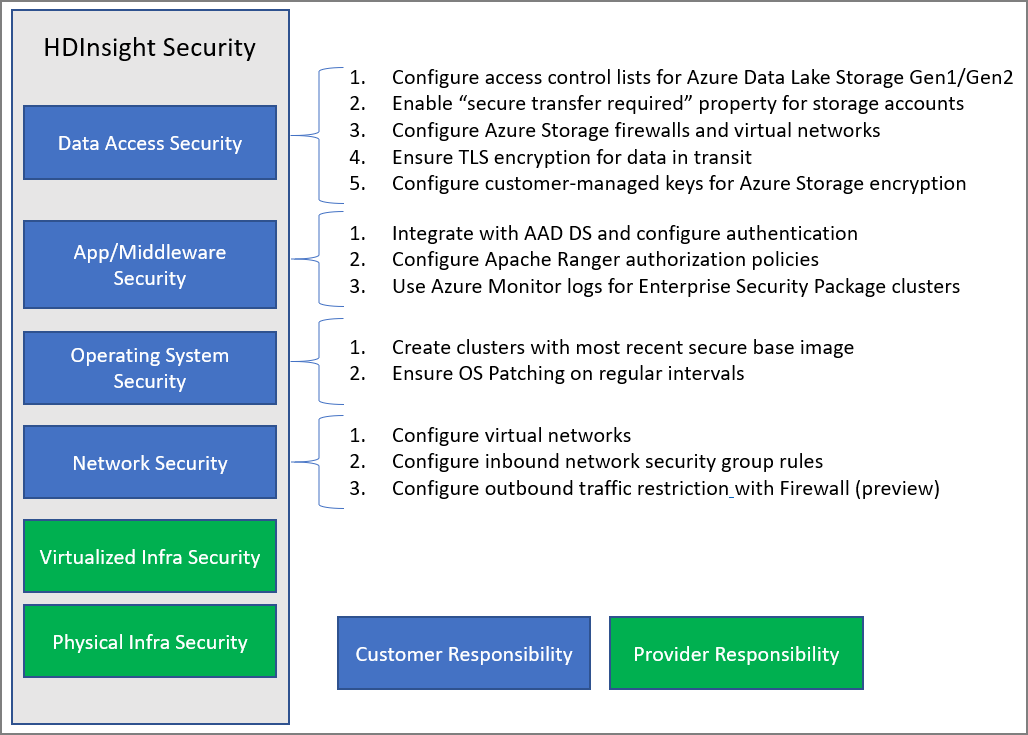
The following table provides links to resources for each type of security solution.
| Security area | Solutions available | Responsible party |
|---|---|---|
| Data Access Security | Configure access control lists ACLs for Azure Data Lake Storage Gen1 and Gen2 | Customer |
| Enable the "Secure transfer required" property on storage accounts. | Customer | |
| Configure Azure Storage firewalls and virtual networks | Customer | |
| Configure Azure virtual network service endpoints for Azure Cosmos DB and Azure SQL DB | Customer | |
| Ensure that the Encryption in transit feature is enabled to use TLS and IPSec for intra-cluster communication. | Customer | |
| Configure customer-managed keys for Azure Storage encryption | Customer | |
| Control access to your data by Azure support using Customer lockbox | Customer | |
| Application and middleware security | Integrate with Microsoft Entra Domain Services and Configure ESP or use HIB for OAuth Authentication | Customer |
| Configure Apache Ranger Authorization policies | Customer | |
| Use Azure Monitor logs | Customer | |
| Operating system security | Create clusters with most recent secure base image | Customer |
| Ensure OS Patching on regular intervals | Customer | |
| Ensure CMK disk encryption for VMs | Customer | |
| Network security | Configure a virtual network | |
| Configure Inbound network security group (NSG) rules or private link | Customer | |
| Configure Outbound traffic restriction with Firewall | Customer | |
| Configure IPSec encryption in transit between cluster nodes | Customer | |
| Virtualized infrastructure | N/A | HDInsight (Cloud provider) |
| Physical infrastructure security | N/A | HDInsight (cloud provider) |
Next steps
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for