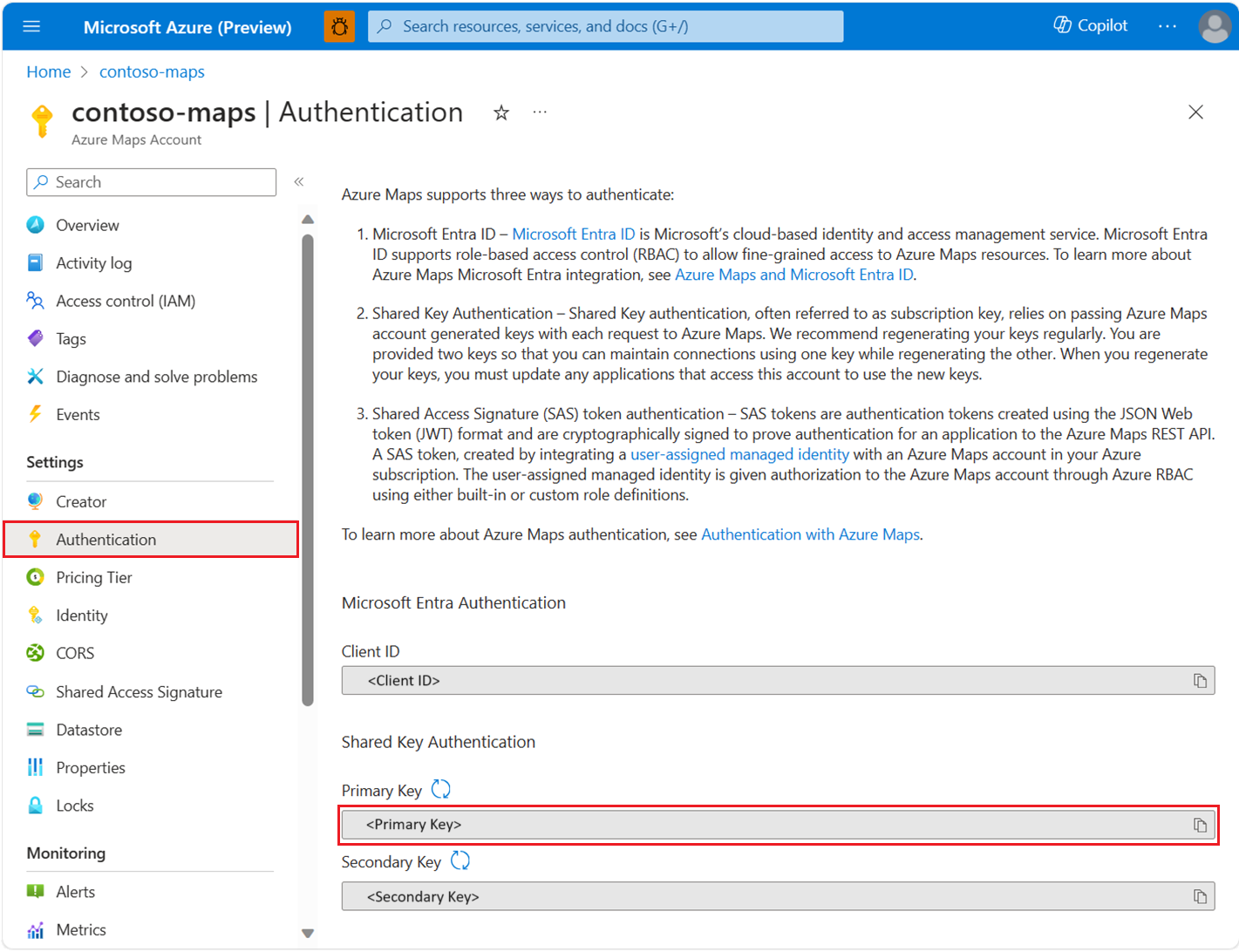
Manage authentication in Azure Maps
When you create an Azure Maps account, your client ID and shared keys are created automatically. These values are required for authentication when using either Microsoft Entra ID or Shared Key authentication.
Prerequisites
Sign in to the Azure portal. If you don't have an Azure subscription, create a free account before you begin.
- A familiarization with managed identities for Azure resources. Be sure to understand the two Managed identity types and how they differ.
- An Azure Maps account.
- A familiarization with Azure Maps Authentication.
View authentication details
Important
We recommend that you use the primary key as the subscription key when you use Shared Key authentication to call Azure Maps. It's best to use the secondary key in scenarios like rolling key changes.
To view your Azure Maps authentication details:
Sign in to the Azure portal.
Select All resources in the Azure services section, then select your Azure Maps account.
Select Authentication in the settings section of the left pane.
Choose an authentication category
Depending on your application needs, there are specific pathways to application security. Microsoft Entra ID defines specific authentication categories to support a wide range of authentication flows. To choose the best category for your application, see application categories.
Note
Understanding categories and scenarios will help you secure your Azure Maps application, whether you use Microsoft Entra ID or shared key authentication.
How to add and remove managed identities
To enable Shared access signature (SAS) token authentication with the Azure Maps REST API, you need to add a user-assigned managed identity to your Azure Maps account.
Create a managed identity
You can create a user-assigned managed identity before or after creating a map account. You can add the managed identity through the portal, Azure management SDKs, or the Azure Resource Manager (ARM) template. To add a user-assigned managed identity through an ARM template, specify the resource identifier of the user-assigned managed identity.
"identity": {
"type": "UserAssigned",
"userAssignedIdentities": {
"/subscriptions/00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000/resourceGroups/example/providers/Microsoft.ManagedIdentity/userAssignedIdentities/exampleidentity": {}
}
}
Remove a managed identity
You can remove a system-assigned identity by disabling the feature through the portal or the Azure Resource Manager template in the same way that it was created. User-assigned identities can be removed individually. To remove all identities, set the identity type to "None".
Removing a system-assigned identity in this way also deletes it from Microsoft Entra ID. System-assigned identities are also automatically removed from Microsoft Entra ID when the Azure Maps account is deleted.
To remove all identities by using the Azure Resource Manager template, update this section:
"identity": {
"type": "None"
}
Choose an authentication and authorization scenario
This table outlines common authentication and authorization scenarios in Azure Maps. Each scenario describes a type of app that can be used to access Azure Maps REST API. Use the links to learn detailed configuration information for each scenario.
Important
For production applications, we recommend implementing Microsoft Entra ID with Azure role-based access control (Azure RBAC).
| Scenario | Authentication | Authorization | Development effort | Operational effort |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trusted daemon app or non-interactive client app | Shared Key | N/A | Medium | High |
| Trusted daemon or non-interactive client app | Microsoft Entra ID | High | Low | Medium |
| Web single page app with interactive single-sign-on | Microsoft Entra ID | High | Medium | Medium |
| Web single page app with non-interactive sign-on | Microsoft Entra ID | High | Medium | Medium |
| Web app, daemon app, or non-interactive sign-on app | SAS Token | High | Medium | Low |
| Web application with interactive single-sign-on | Microsoft Entra ID | High | High | Medium |
| IoT device or an input constrained application | Microsoft Entra ID | High | Medium | Medium |
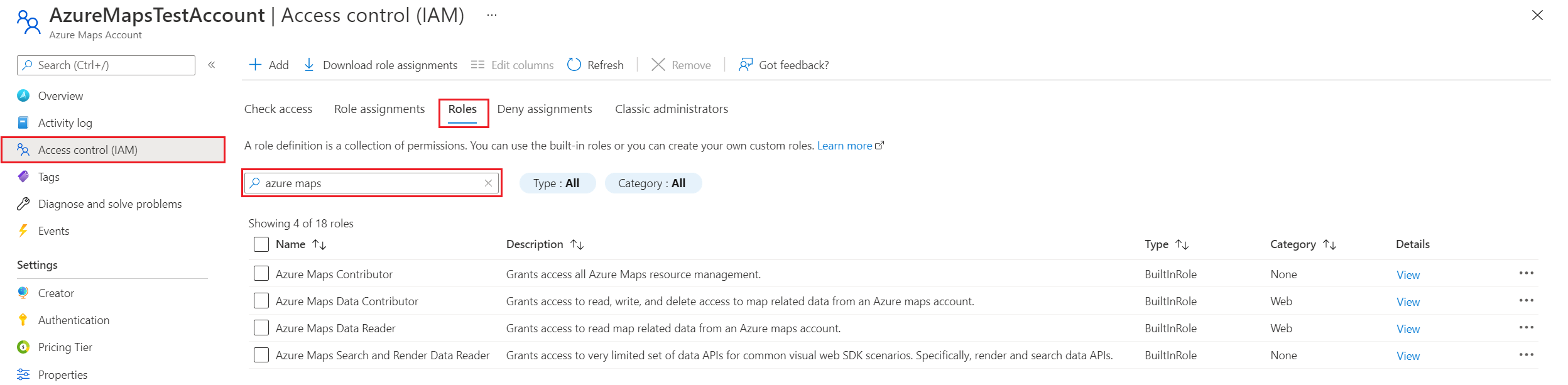
View built-in Azure Maps role definitions
To view the built-in Azure Maps role definition:
In the left pane, select Access control (IAM).
Select the Roles tab.
In the search box, enter Azure Maps.
The results display the available built-in role definitions for Azure Maps.
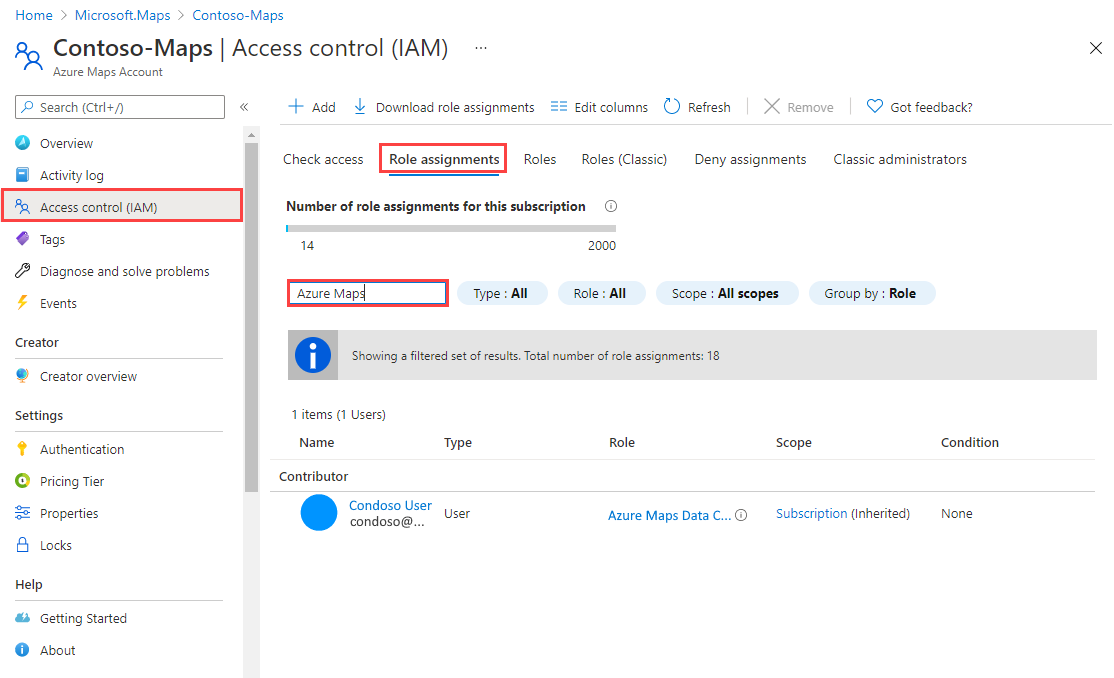
View role assignments
To view users and apps that have been granted access for Azure Maps, go to Access Control (IAM). There, select Role assignments, and then filter by Azure Maps.
In the left pane, select Access control (IAM).
Select the Role assignments tab.
In the search box, enter Azure Maps.
The results display the current Azure Maps role assignments.
Request tokens for Azure Maps
Request a token from the Microsoft Entra token endpoint. In your Microsoft Entra ID request, use the following details:
| Azure environment | Microsoft Entra token endpoint | Azure resource ID |
|---|---|---|
| Azure public cloud | https://login.microsoftonline.com |
https://atlas.microsoft.com/ |
| Azure Government cloud | https://login.microsoftonline.us |
https://atlas.microsoft.com/ |
For more information about requesting access tokens from Microsoft Entra ID for users and service principals, see Authentication scenarios for Microsoft Entra ID. To view specific scenarios, see the table of scenarios.
Manage and rotate shared keys
Your Azure Maps subscription keys are similar to a root password for your Azure Maps account. Always be careful to protect your subscription keys. Use Azure Key Vault to securely manage and rotate your keys. Avoid distributing access keys to other users, hard-coding them, or saving them anywhere in plain text that's accessible to others. If you believe that your keys may have been compromised, rotate them.
Note
If possible, we recommend using Microsoft Entra ID instead of Shared Key to authorize requests. Microsoft Entra ID has better security than Shared Key, and it's easier to use.
Manually rotate subscription keys
To help keep your Azure Maps account secure, we recommend periodically rotating your subscription keys. If possible, use Azure Key Vault to manage your access keys. If you aren't using Key Vault, you need to manually rotate your keys.
Two subscription keys are assigned so that you can rotate your keys. Having two keys ensures that your application maintains access to Azure Maps throughout the process.
To rotate your Azure Maps subscription keys in the Azure portal:
- Update your application code to reference the secondary key for the Azure Maps account and deploy.
- In the Azure portal, navigate to your Azure Maps account.
- Under Settings, select Authentication.
- To regenerate the primary key for your Azure Maps account, select the Regenerate button next to the primary key.
- Update your application code to reference the new primary key and deploy.
- Regenerate the secondary key in the same manner.
Warning
We recommend using the same key in all your applications. If you use the primary key in some places and the secondary key in others, you won't be able to rotate your keys without some applications losing access.
Next steps
Find the API usage metrics for your Azure Maps account:
Explore samples that show how to integrate Microsoft Entra ID with Azure Maps:
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for