How to create and manage read replicas in Azure Database for MariaDB using the Azure portal
Important
Azure Database for MariaDB is on the retirement path. We strongly recommend that you migrate to Azure Database for MySQL. For more information about migrating to Azure Database for MySQL, see What's happening to Azure Database for MariaDB?.
In this article, you will learn how to create and manage read replicas in the Azure Database for MariaDB service using the Azure portal.
Prerequisites
- An Azure Database for MariaDB server that will be used as the source server.
Important
The read replica feature is only available for Azure Database for MariaDB servers in the General Purpose or Memory Optimized pricing tiers. Ensure the source server is in one of these pricing tiers.
Create a read replica
Important
When you create a replica for a source that has no existing replicas, the source will first restart to prepare itself for replication. Take this into consideration and perform these operations during an off-peak period.
A read replica server can be created using the following steps:
Sign in to the Azure portal.
Select the existing Azure Database for MariaDB server that you want to use as a master. This action opens the Overview page.
Select Replication from the menu, under SETTINGS.
Select Add Replica.
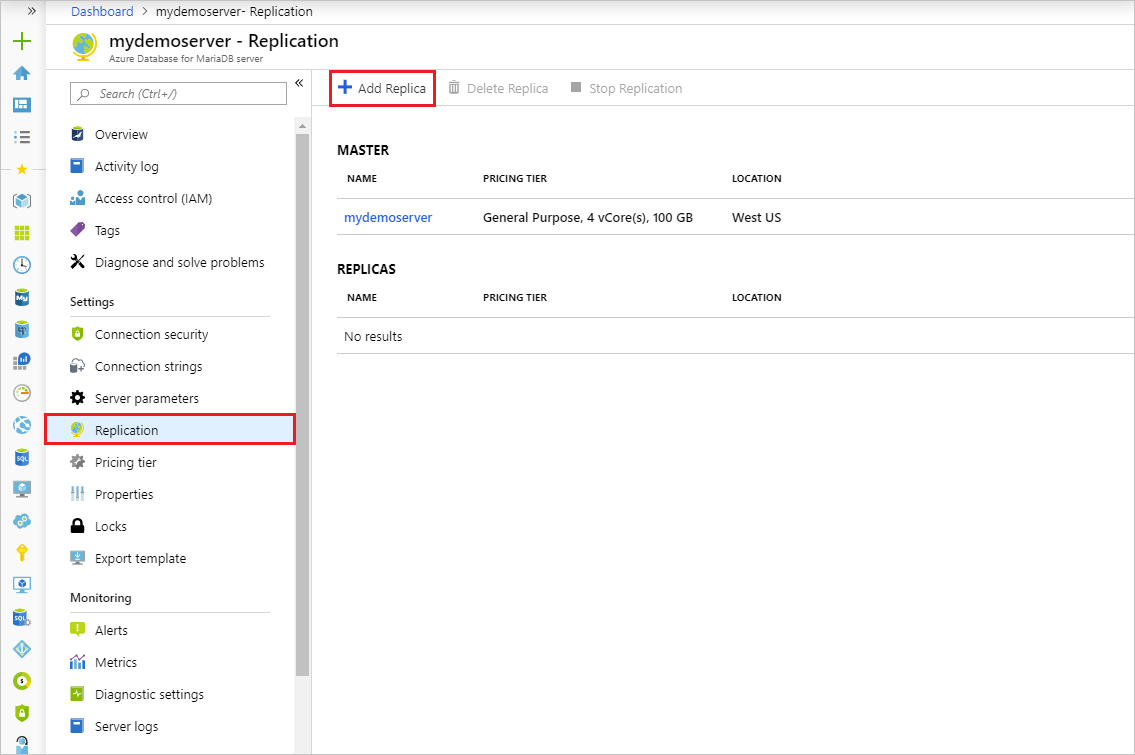
Enter a name for the replica server.
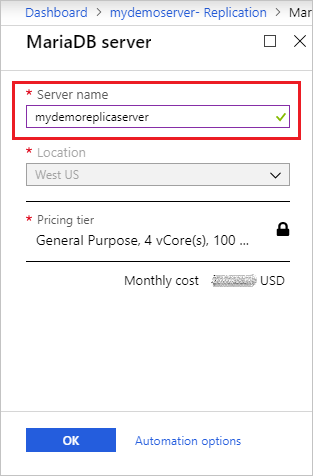
Select the location for the replica server. The default location is the same as the source server's.
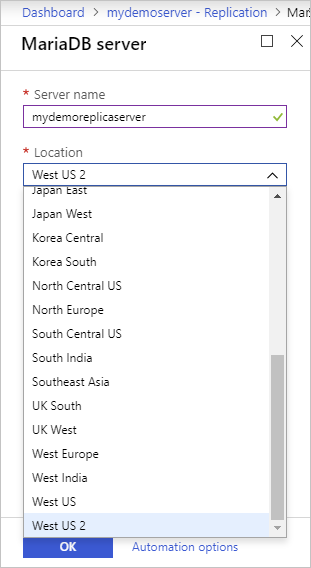
Select OK to confirm creation of the replica.
Note
Read replicas are created with the same server configuration as the master. The replica server configuration can be changed after it has been created. It is recommended that the replica server's configuration should be kept at equal or greater values than the source to ensure the replica is able to keep up with the master.
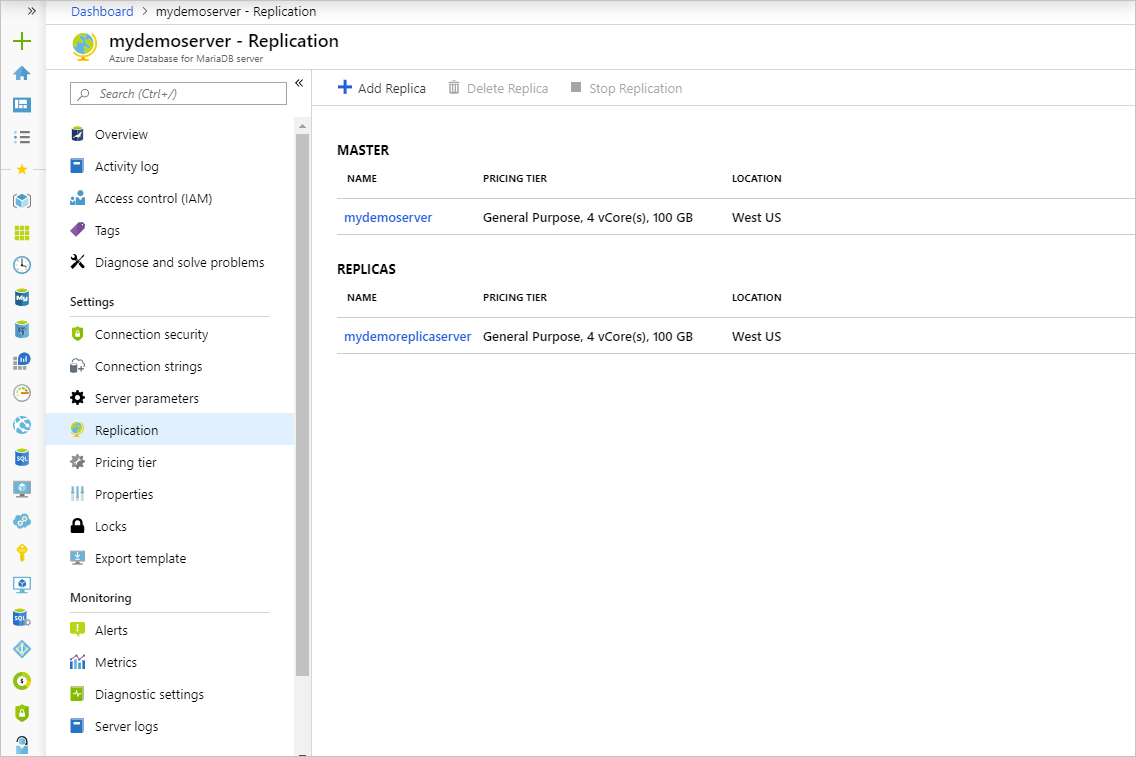
Once the replica server has been created, it can be viewed from the Replication blade.
Stop replication to a replica server
Important
Stopping replication to a server is irreversible. Once replication has stopped between a source and replica, it cannot be undone. The replica server then becomes a standalone server and now supports both read and writes. This server cannot be made into a replica again.
To stop replication between a source and a replica server from the Azure portal, use the following steps:
In the Azure portal, select your source Azure Database for MariaDB server.
Select Replication from the menu, under SETTINGS.
Select the replica server you wish to stop replication for.
Select Stop replication.
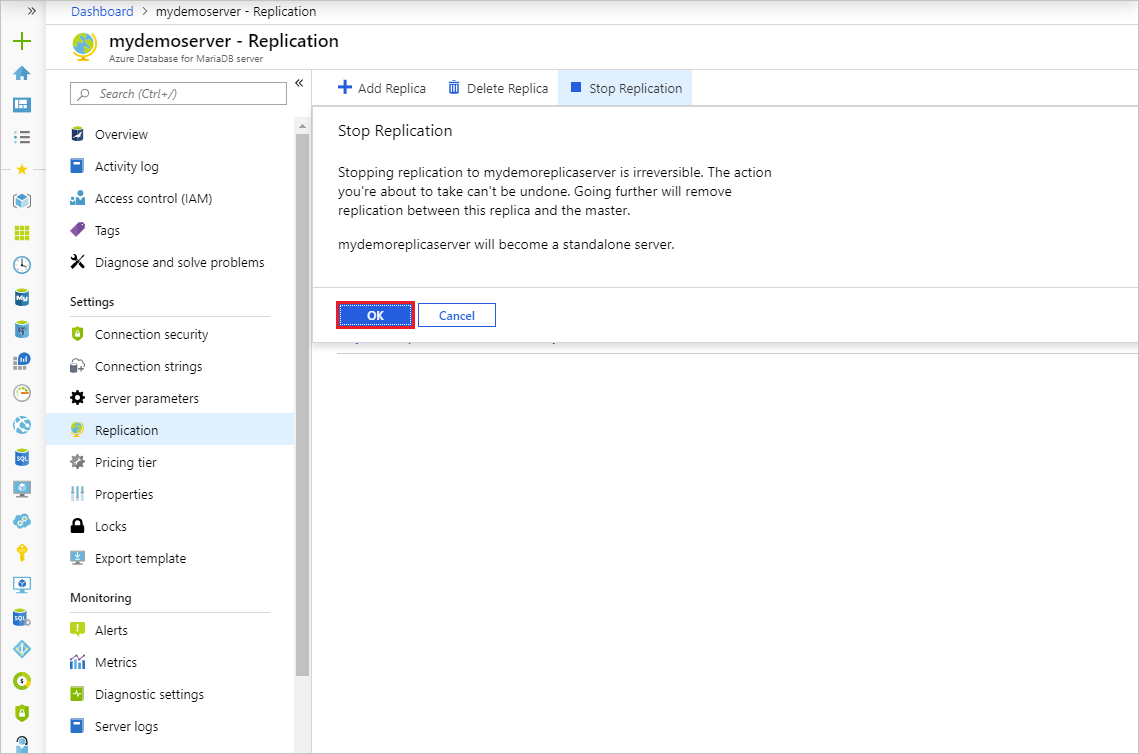
Confirm you want to stop replication by selecting OK.
Delete a replica server
To delete a read replica server from the Azure portal, use the following steps:
In the Azure portal, select your source Azure Database for MariaDB server.
Select Replication from the menu, under SETTINGS.
Select the replica server you wish to delete.
Select Delete replica
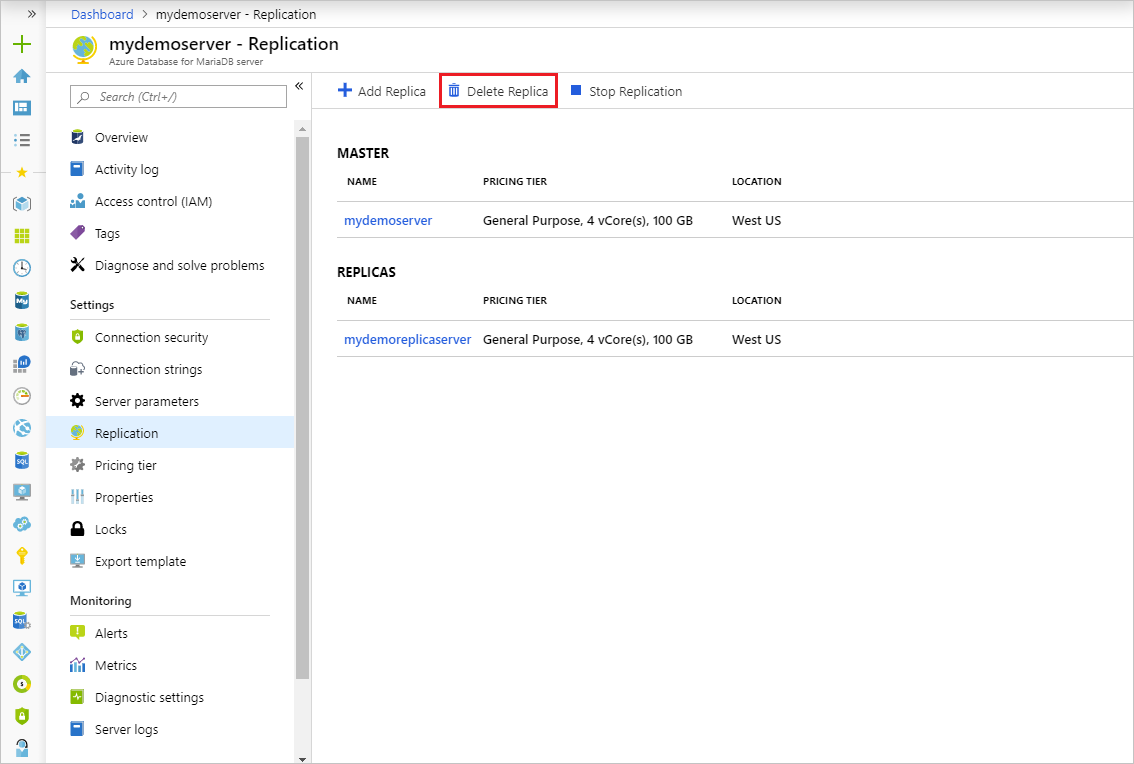
Type the name of the replica and select Delete to confirm deletion of the replica.
Delete a source server
Important
Deleting a source server stops replication to all replica servers and deletes the source server itself. Replica servers become standalone servers that now support both read and writes.
To delete a source server from the Azure portal, use the following steps:
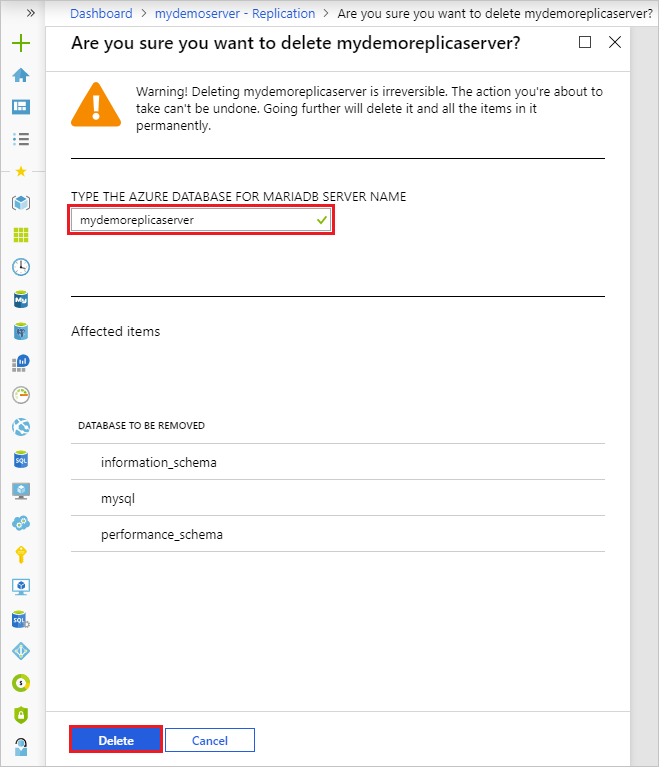
In the Azure portal, select your source Azure Database for MariaDB server.
From the Overview, select Delete.
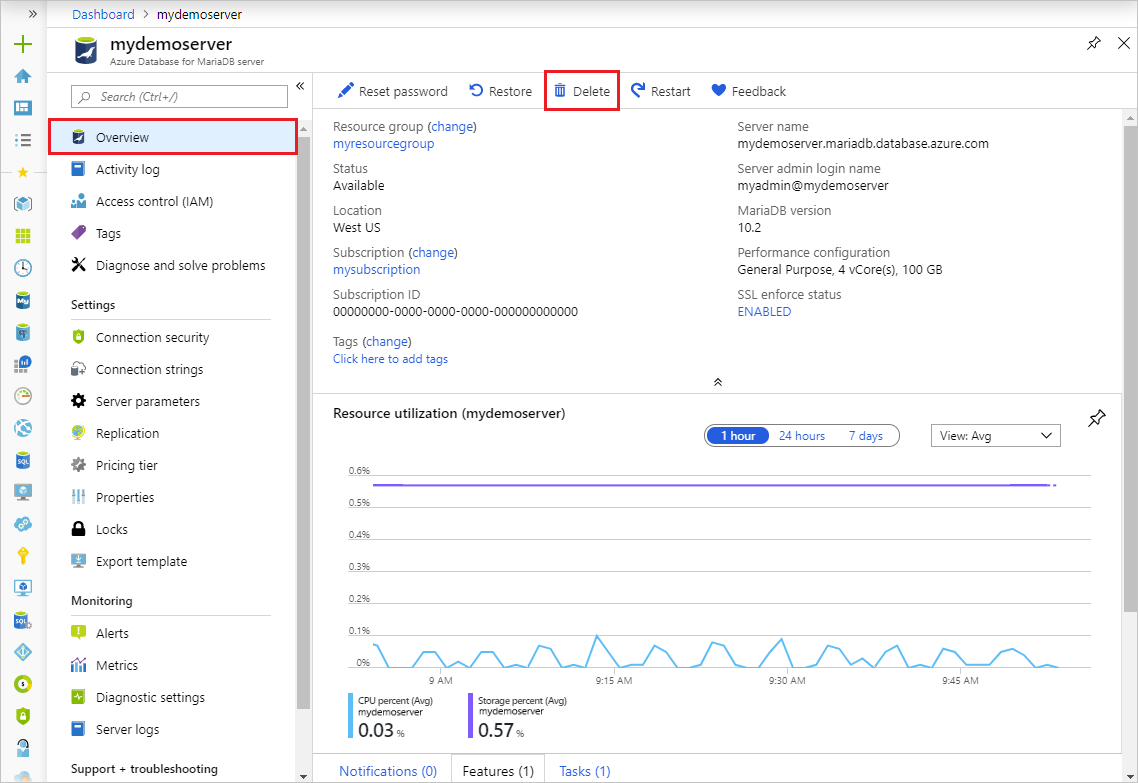
Type the name of the source server and select Delete to confirm deletion of the source server.
Monitor replication
In the Azure portal, select the replica Azure Database for MariaDB server you want to monitor.
Under the Monitoring section of the sidebar, select Metrics:
Select Replication lag in seconds from the dropdown list of available metrics.
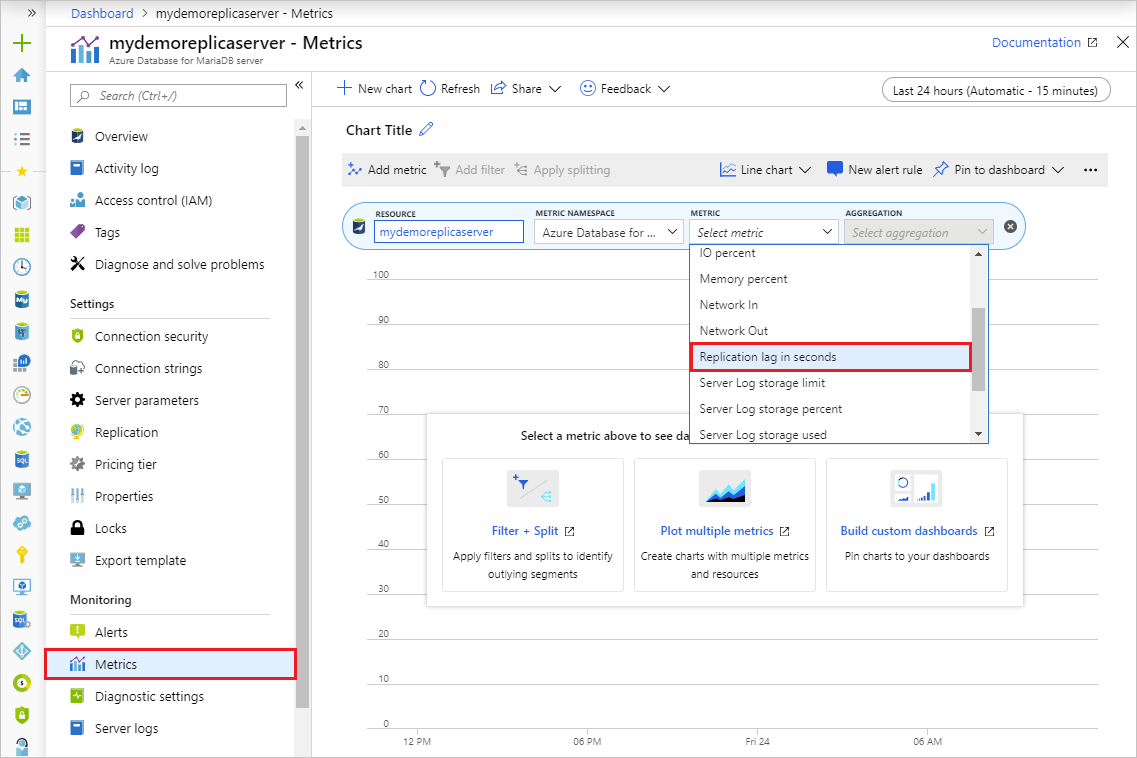
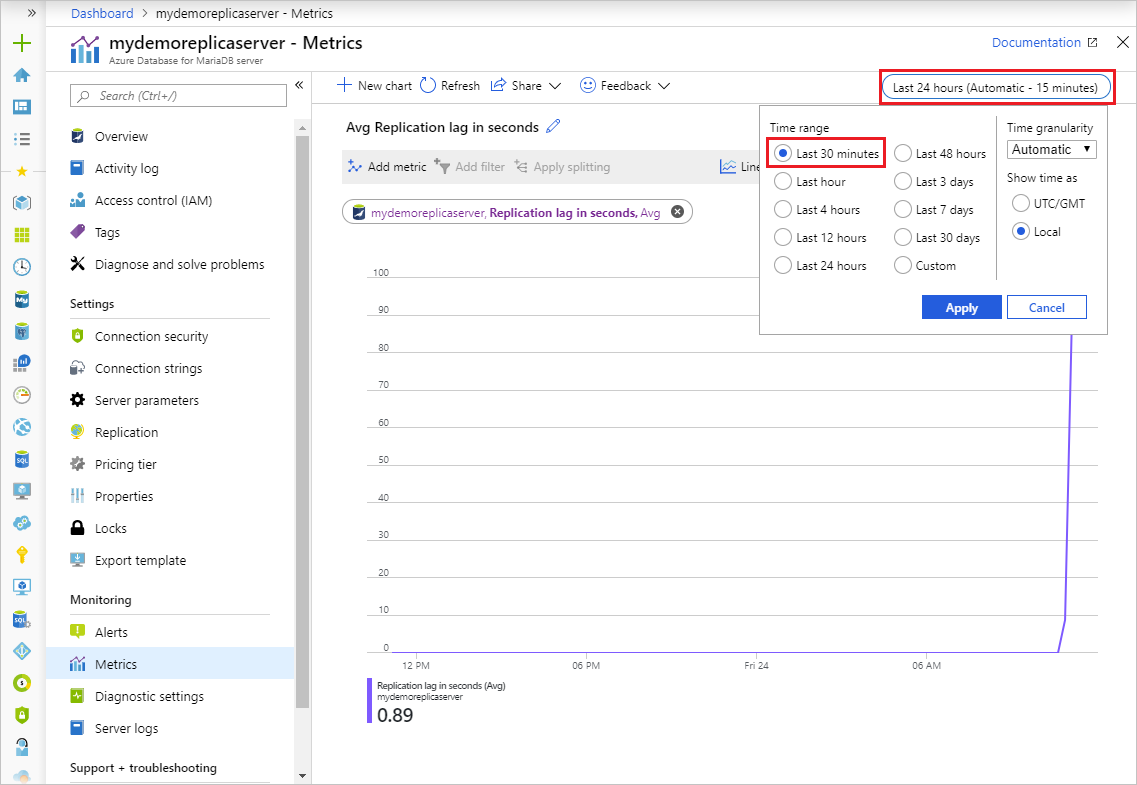
Select the time range you wish to view. The image below selects a 30 minute time range.
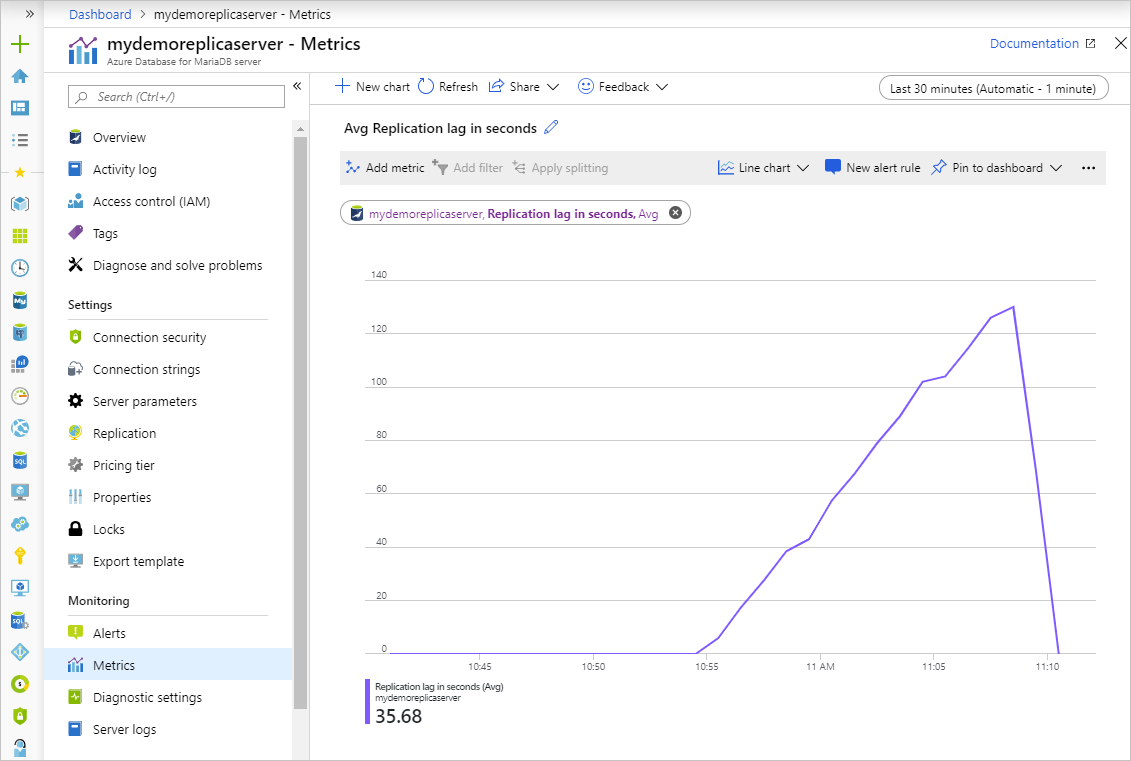
View the replication lag for the selected time range. The image below displays the last 30 minutes for a large workload.
Next steps
- Learn more about read replicas
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for