Migrate data to Azure Cosmos DB for NoSQL account using Striim
APPLIES TO:
NoSQL
The Striim image in the Azure marketplace offers continuous real-time data movement from data warehouses and databases to Azure. While moving the data, you can perform in-line denormalization, data transformation, enable real-time analytics, and data reporting scenarios. It’s easy to get started with Striim to continuously move enterprise data to Azure Cosmos DB for NoSQL. Azure provides a marketplace offering that makes it easy to deploy Striim and migrate data to Azure Cosmos DB.
This article shows how to use Striim to migrate data from an Oracle database to an Azure Cosmos DB for NoSQL account.
Prerequisites
If you don't have an Azure subscription, create a free account before you begin.
An Oracle database running on-premises with some data in it.
Deploy the Striim marketplace solution
Sign in to the Azure portal.
Select Create a resource and search for Striim in the Azure marketplace. Select the first option and Create.
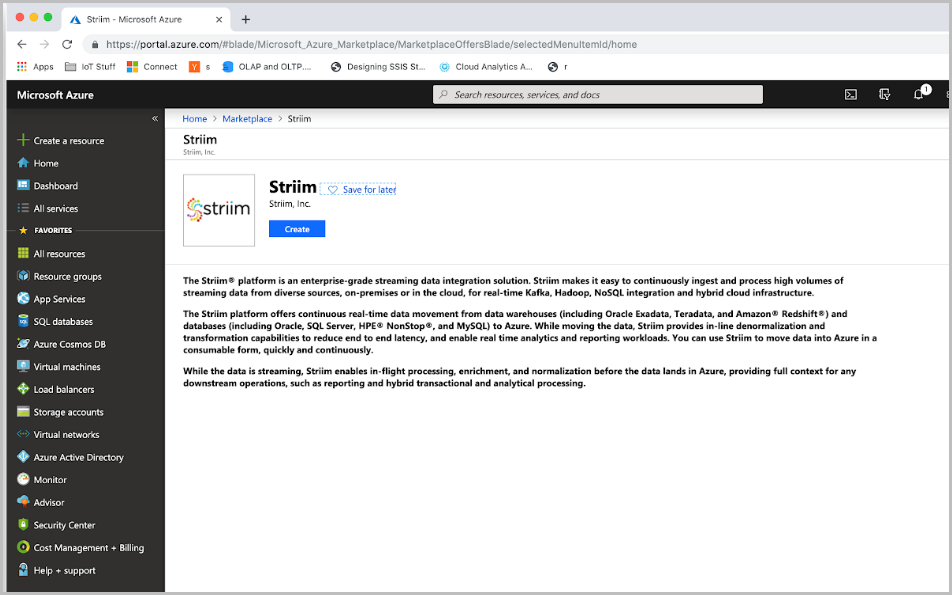
Next, enter the configuration properties of the Striim instance. The Striim environment is deployed in a virtual machine. From the Basics pane, enter the VM user name, VM password (this password is used to SSH into the VM). Select your Subscription, Resource Group, and Location details where you’d like to deploy Striim. Once complete, select OK.
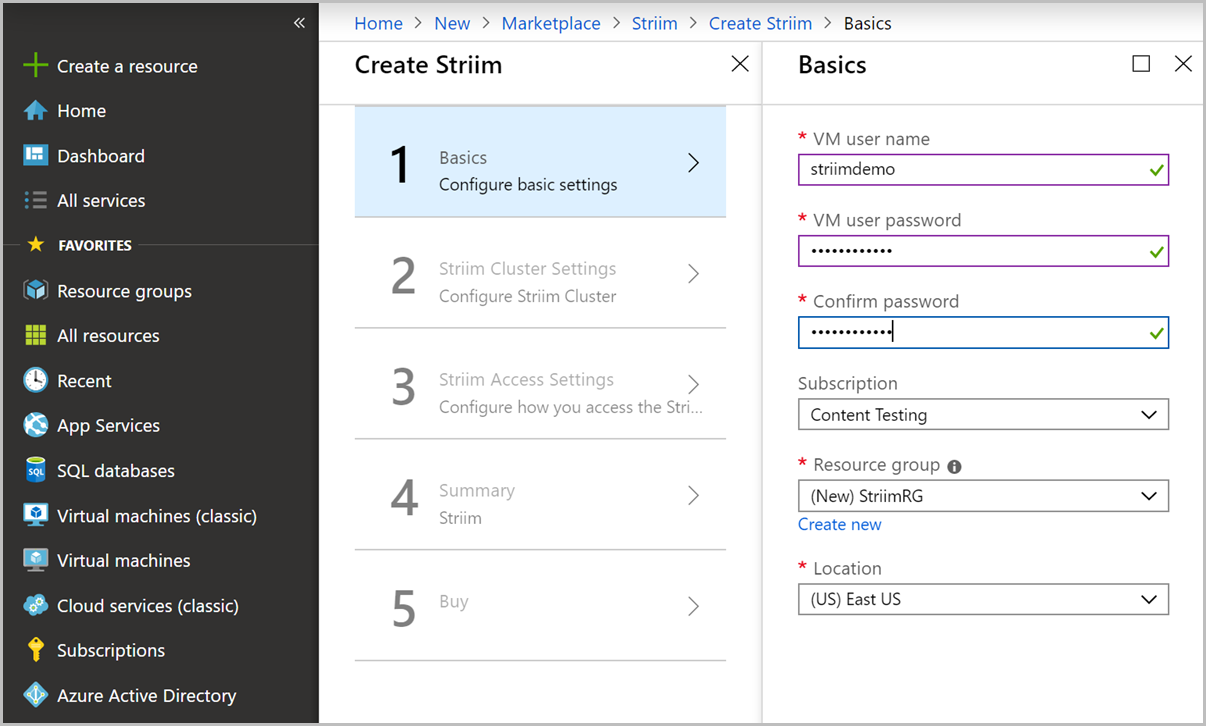
In the Striim Cluster settings pane, choose the type of Striim deployment and the virtual machine size.
Setting Value Description Striim deployment type Standalone Striim can run in a Standalone or Cluster deployment types. Standalone mode will deploy the Striim server on a single virtual machine and you can select the size of the VMs depending on your data volume. Cluster mode will deploy the Striim server on two or more VMs with the selected size. Cluster environments with more than 2 nodes offer automatic high availability and failover.
In this tutorial, you can select Standalone option. Use the default “Standard_F4s” size VM.Name of the Striim cluster <Striim_cluster_Name> Name of the Striim cluster. Striim cluster password <Striim_cluster_password> Password for the cluster. After you fill the form, select OK to continue.
In the Striim access settings pane, configure the Public IP address (choose the default values), Domain name for Striim, Admin password that you’d like to use to login to the Striim UI. Configure a VNET and Subnet (choose the default values). After filling in the details, select OK to continue.
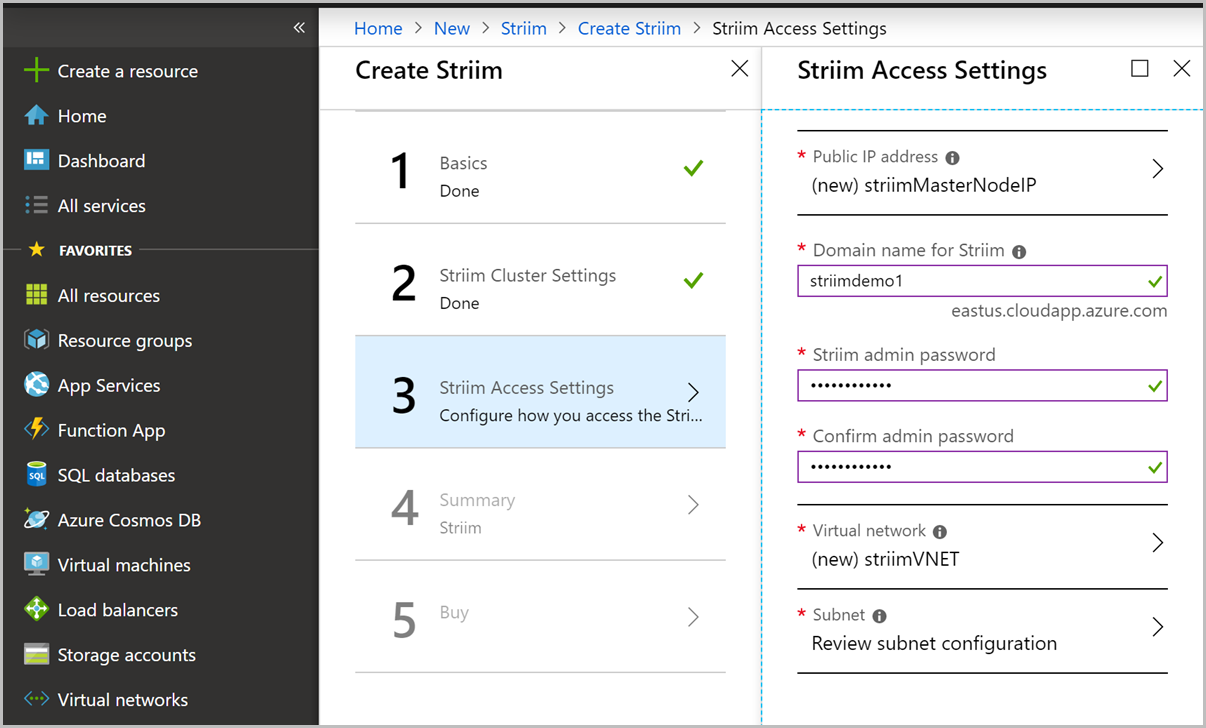
Azure will validate the deployment and make sure everything looks good; validation takes few minutes to complete. After the validation is completed, select OK.
Finally, review the terms of use and select Create to create your Striim instance.
Configure the source database
In this section, you configure the Oracle database as the source for data movement. Striim server comes with the Oracle JDBC driver that's used to connect to Oracle. To read changes from your source Oracle database, you can either use the LogMiner or the XStream APIs. The Oracle JDBC driver is present in Striim's Java classpath to read, write, or persist data from Oracle database.
Configure the target database
In this section, you will configure the Azure Cosmos DB for NoSQL account as the target for data movement.
Create an Azure Cosmos DB for NoSQL account using the Azure portal.
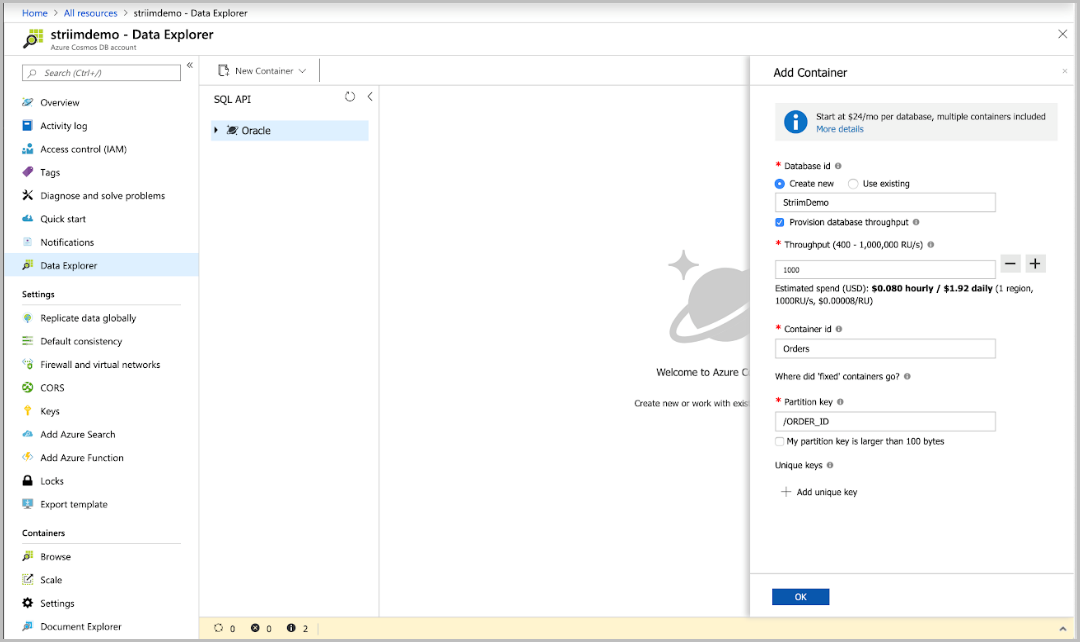
Navigate to the Data Explorer pane in your Azure Cosmos DB account. Select New Container to create a new container. Assume that you are migrating products and orders data from Oracle database to Azure Cosmos DB. Create a new database named StriimDemo with a container named Orders. Provision the container with 1000 RUs (this example uses 1000 RUs, but you should use the throughput estimated for your workload), and /ORDER_ID as the partition key. These values will differ depending on your source data.
Configure Oracle to Azure Cosmos DB data flow
Navigate to the Striim instance that you deployed in the Azure portal. Select the Connect button in the upper menu bar and from the SSH tab, copy the URL in Login using VM local account field.
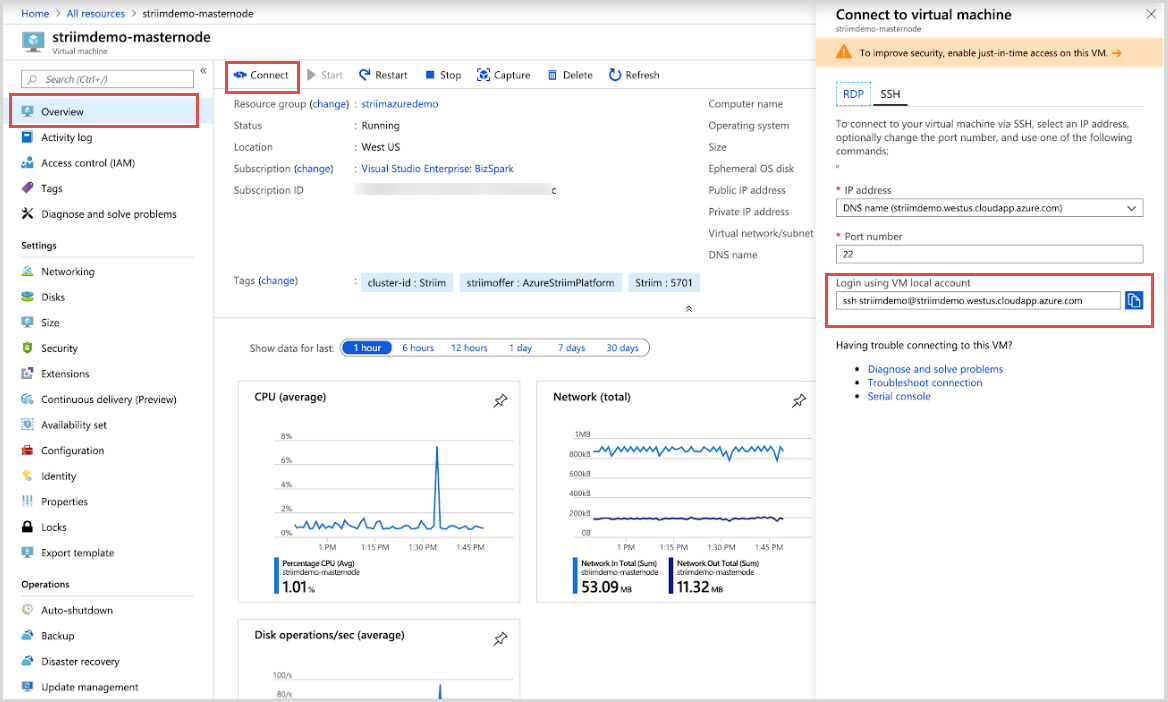
Open a new terminal window and run the SSH command you copied from the Azure portal. This article uses terminal in a MacOS, you can follow the similar instructions using an SSH client on a Windows machine. When prompted, type yes to continue and enter the password you have set for the virtual machine in the previous step.
From the same terminal window, restart the Striim server by executing the following commands:
systemctl stop striim-node systemctl stop striim-dbms systemctl start striim-dbms systemctl start striim-nodeStriim will take a minute to start up. If you’d like to see the status, run the following command:
tail -f /opt/striim/logs/striim-node.logNow, navigate back to Azure and copy the Public IP address of your Striim VM.
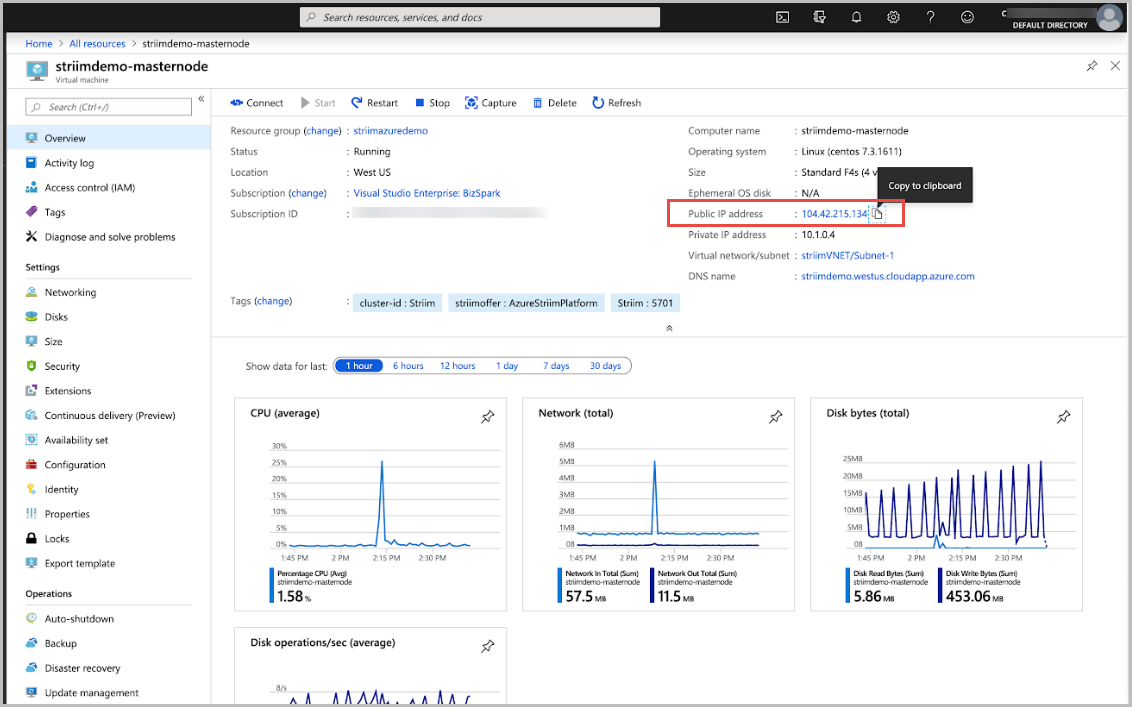
To navigate to the Striim’s Web UI, open a new tab in a browser and copy the public IP followed by: 9080. Sign in by using the admin username, along with the admin password you specified in the Azure portal.

Now you’ll arrive at Striim’s home page. There are three different panes – Dashboards, Apps, and SourcePreview. The Dashboards pane allows you to move data in real time and visualize it. The Apps pane contains your streaming data pipelines, or data flows. On the right hand of the page is SourcePreview where you can preview your data before moving it.
Select the Apps pane, we’ll focus on this pane for now. There are a variety of sample apps that you can use to learn about Striim, however in this article you will create our own. Select the Add App button in the top right-hand corner.
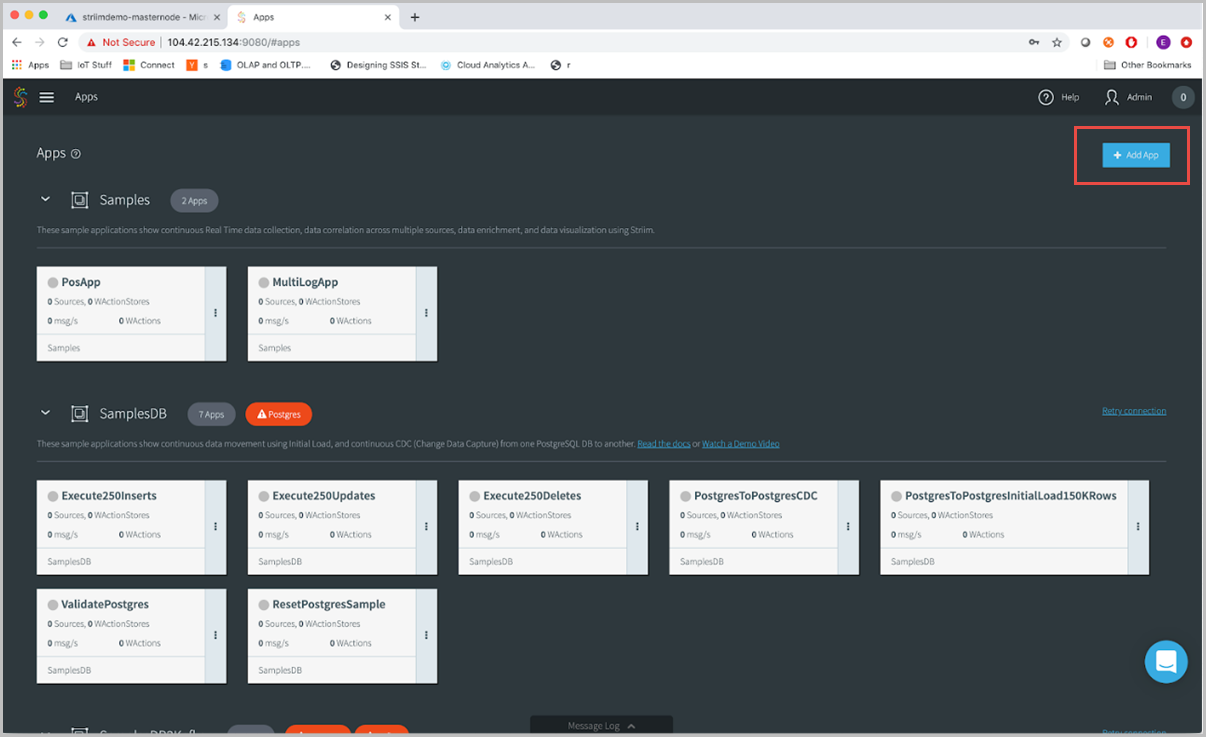
There are a few different ways to create Striim applications. Select Start with Template to start with an existing template.
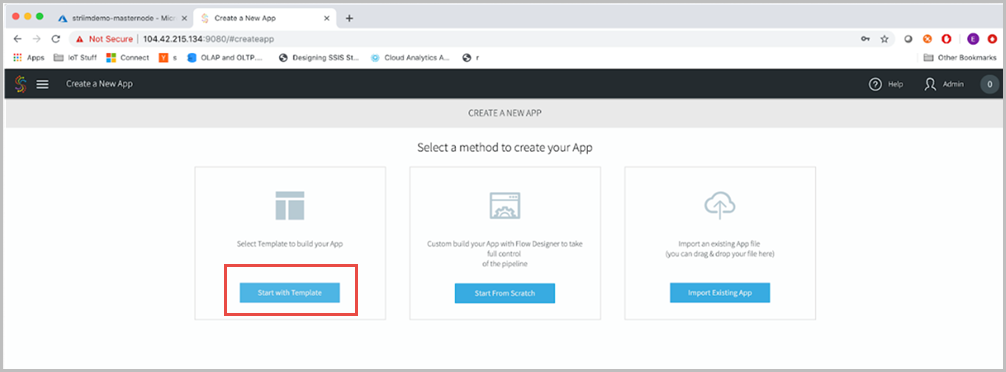
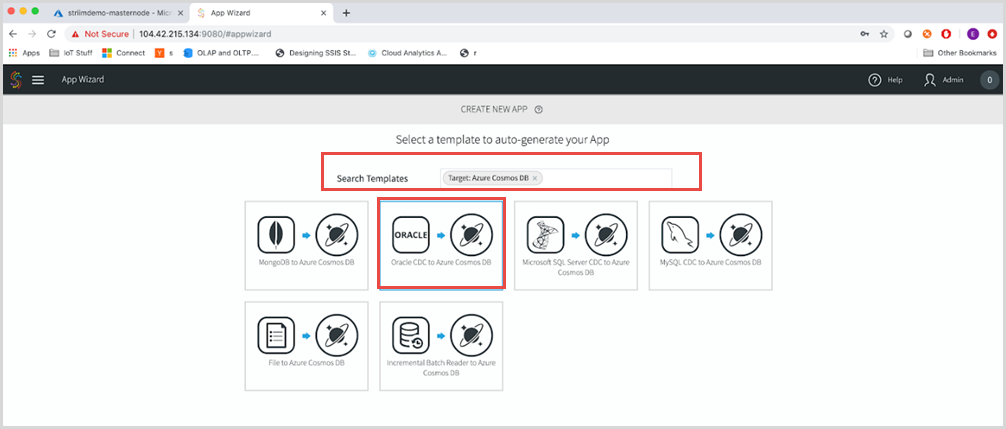
In the Search templates field, type “Cosmos” and select Target: Azure Cosmos DB and then select Oracle CDC to Azure Cosmos DB.
In the next page, name your application. You can provide a name such as oraToCosmosDB and then select Save.
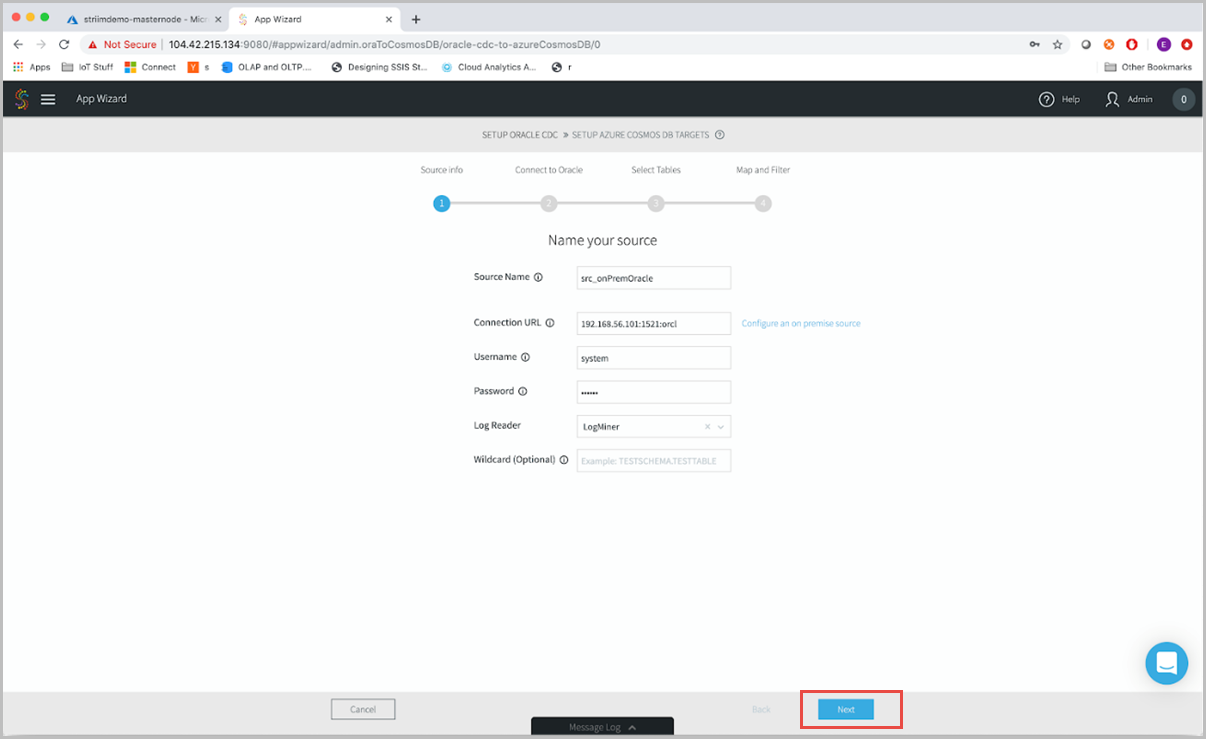
Next, enter the source configuration of your source Oracle instance. Enter a value for the Source Name. The source name is just a naming convention for the Striim application, you can use something like src_onPremOracle. Enter values for rest of the source parameters URL, Username, Password, choose LogMiner as the reader to read data from Oracle. Select Next to continue.
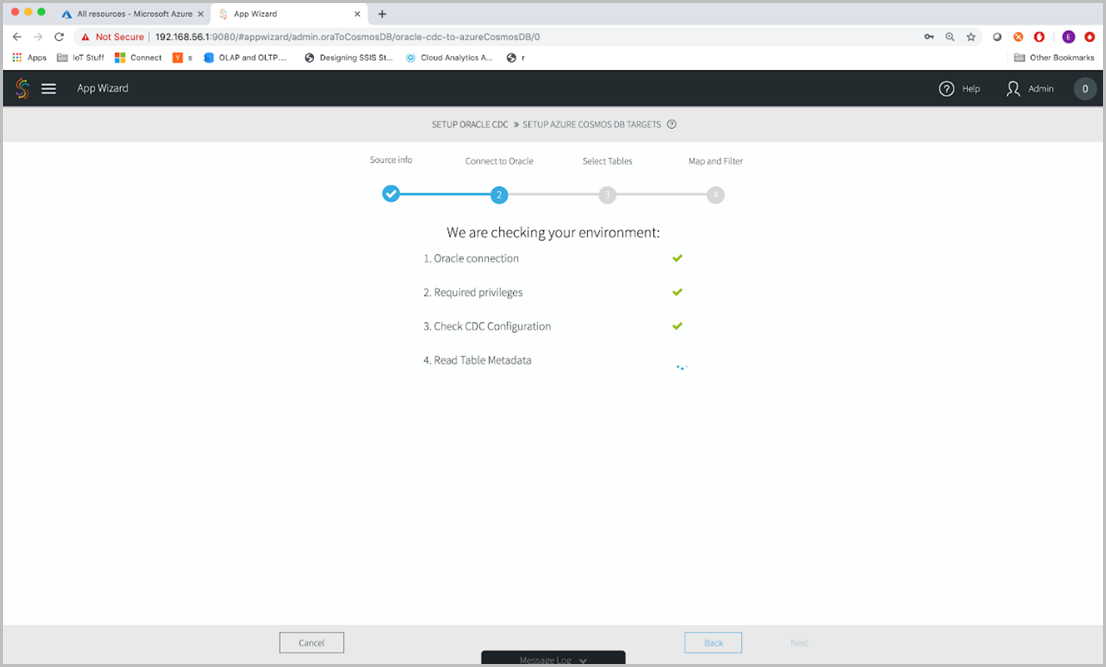
Striim will check your environment and make sure that it can connect to your source Oracle instance, have the right privileges, and that CDC was configured properly. Once all the values are validated, select Next.
Select the tables from Oracle database that you’d like to migrate. For example, let’s choose the Orders table and select Next.
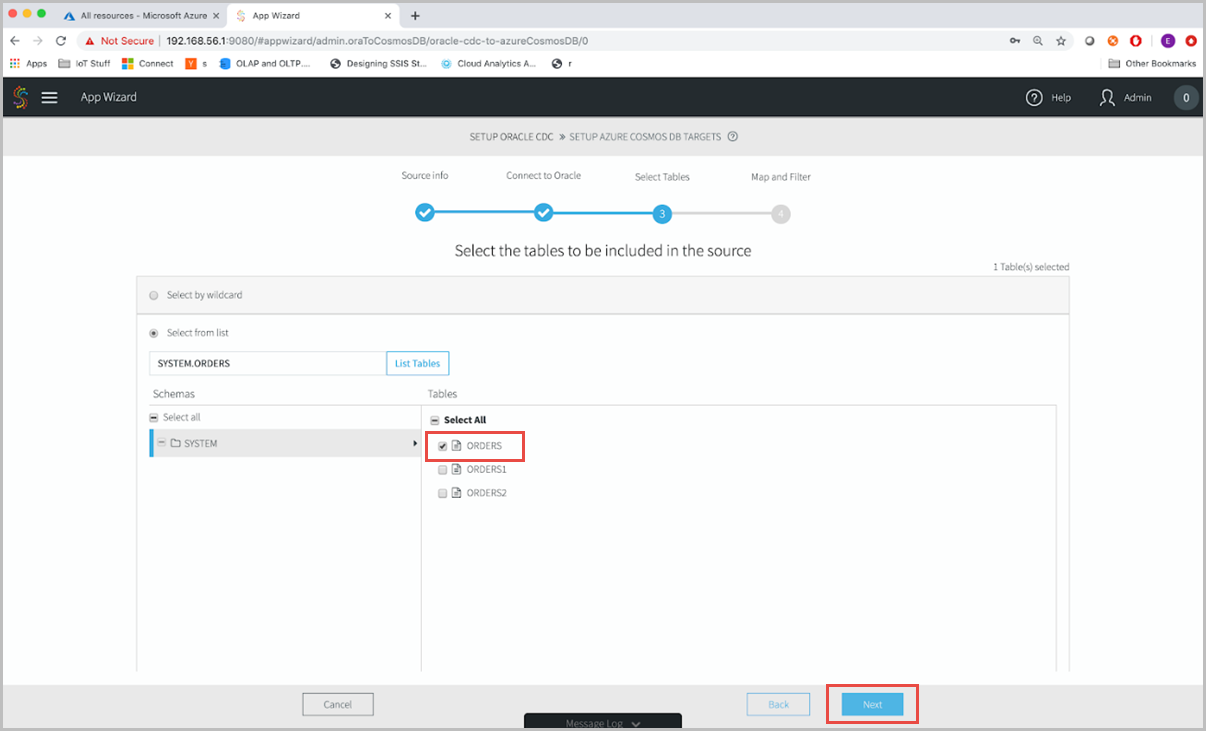
After selecting the source table, you can do more complicated operations such as mapping and filtering. In this case, you will just create a replica of your source table in Azure Cosmos DB. So, select Next to configure the target
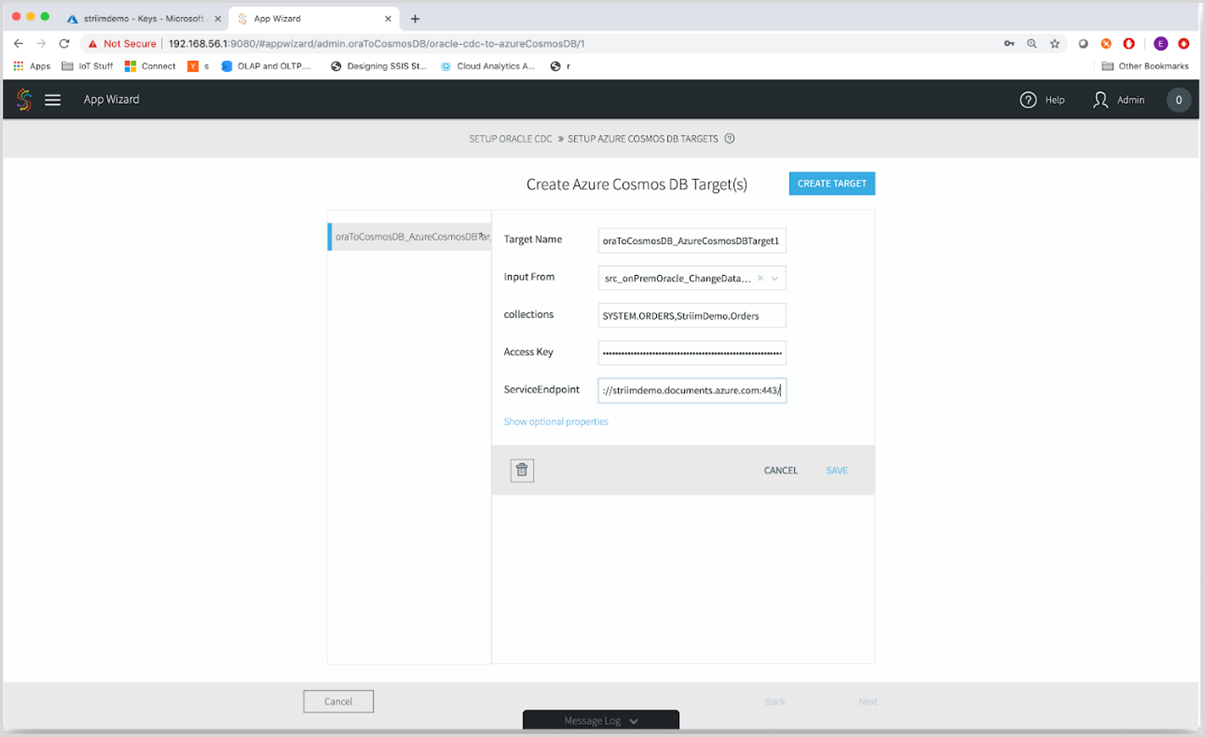
Now, let’s configure the target:
- Target Name - Provide a friendly name for the target.
- Input From - From the dropdown list, select the input stream from the one you created in the source Oracle configuration.
- Collections- Enter the target Azure Cosmos DB configuration properties. The collections syntax is SourceSchema.SourceTable, TargetDatabase.TargetContainer. In this example, the value would be “SYSTEM.ORDERS, StriimDemo.Orders”.
- AccessKey - The PrimaryKey of your Azure Cosmos DB account.
- ServiceEndpoint – The URI of your Azure Cosmos DB account, they can be found under the Keys section of the Azure portal.
Select Save and Next.
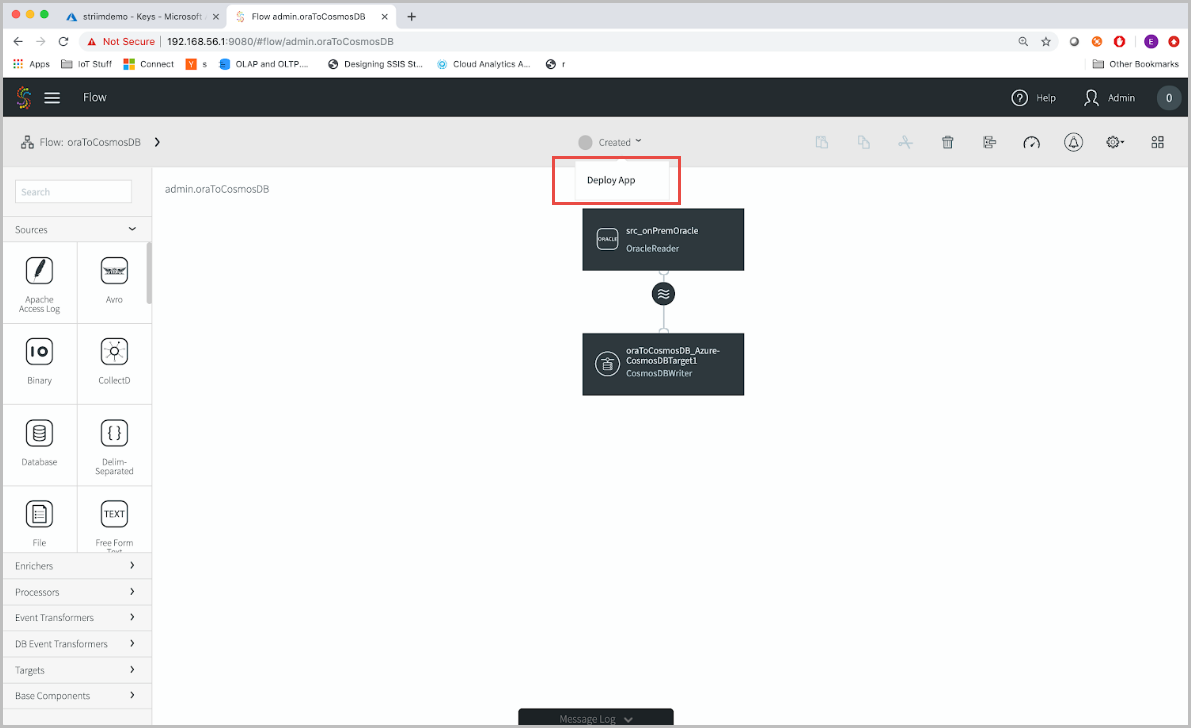
Next, you’ll arrive at the flow designer, where you can drag and drop out of the box connectors to create your streaming applications. You will not make any modifications to the flow at this point. so go ahead and deploy the application by selecting the Deploy App button.
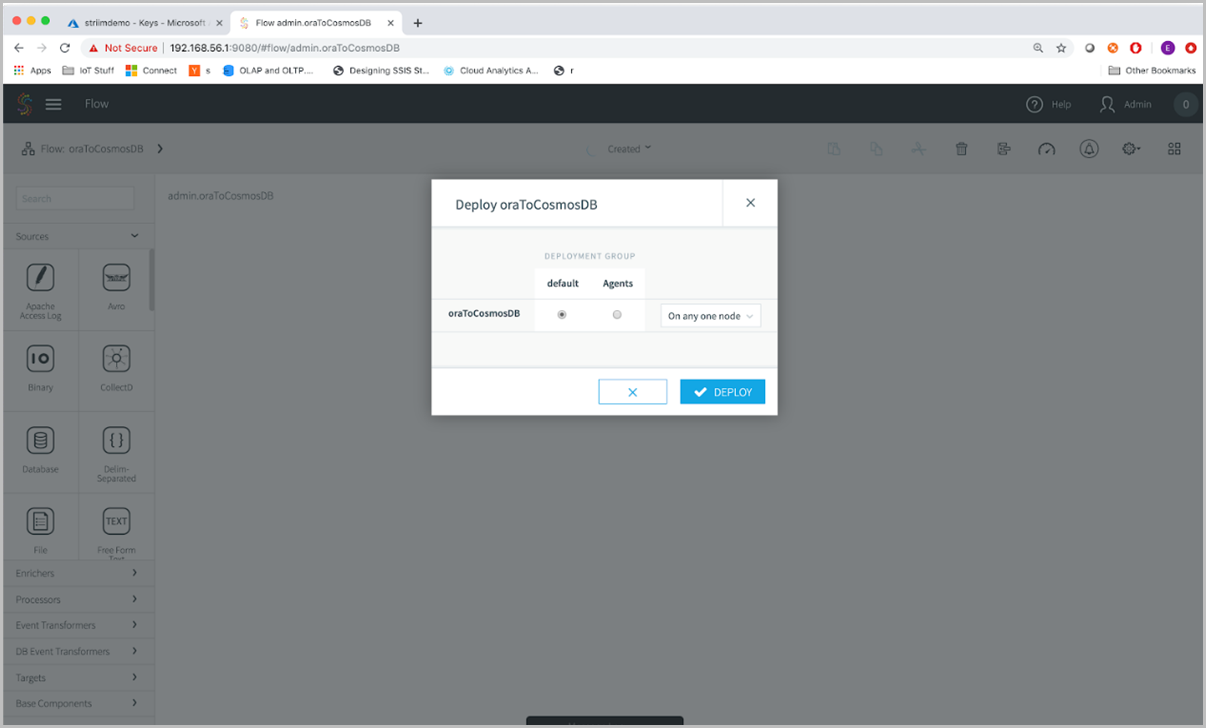
In the deployment window, you can specify if you want to run certain parts of your application on specific parts of your deployment topology. Since we’re running in a simple deployment topology through Azure, we’ll use the default option.
After deploying, you can preview the stream to see data flowing through. Select the wave icon and the eyeball next to it. Select the Deployed button in the top menu bar, and select Start App.
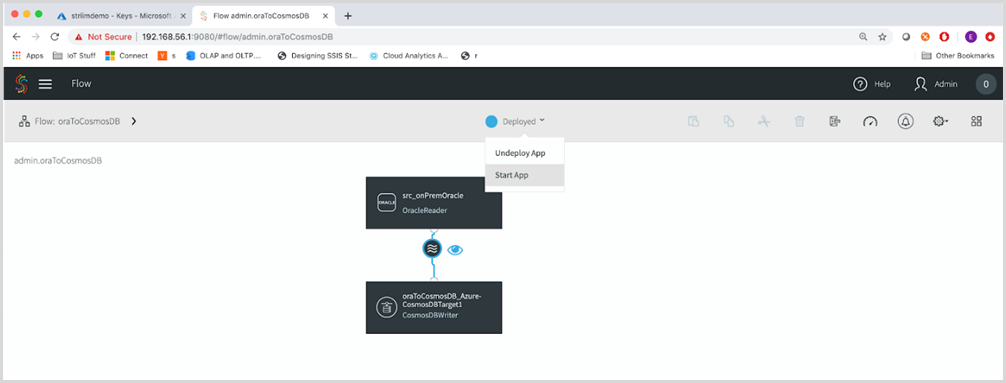
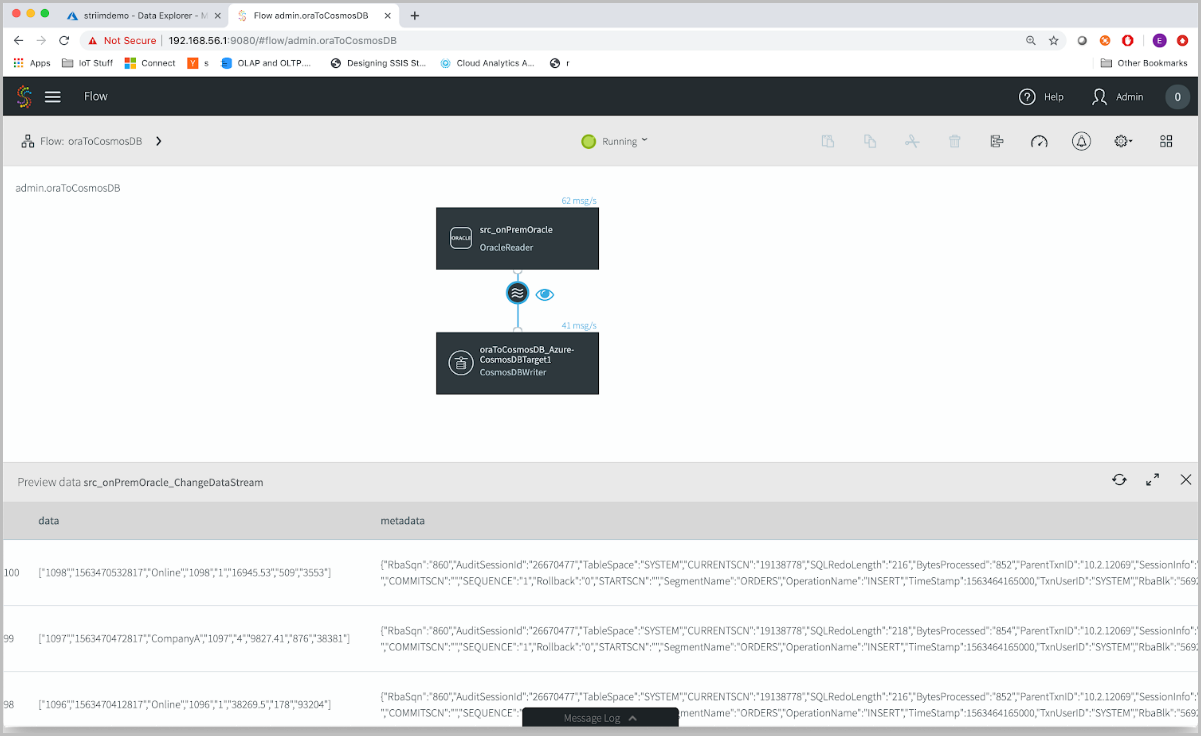
By using a CDC(Change Data Capture) reader, Striim will pick up only new changes on the database. If you have data flowing through your source tables, you’ll see it. However, since this is a demo table, the source isn’t connected to any application. If you use a sample data generator, you can insert a chain of events into your Oracle database.
You’ll see data flowing through the Striim platform. Striim picks up all the metadata associated with your table as well, which is helpful to monitor the data and make sure that the data lands on the right target.
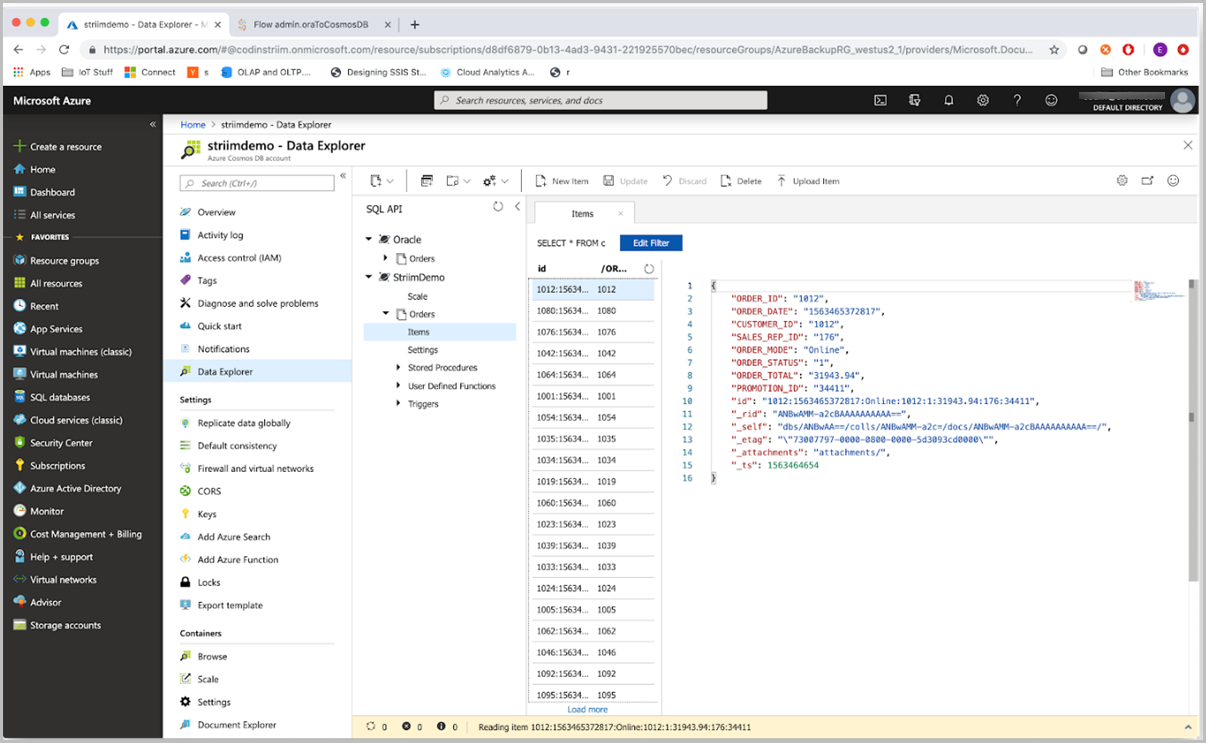
Finally, let’s sign into Azure and navigate to your Azure Cosmos DB account. Refresh the Data Explorer, and you can see that data has arrived.
By using the Striim solution in Azure, you can continuously migrate data to Azure Cosmos DB from various sources such as Oracle, Cassandra, MongoDB, and various others to Azure Cosmos DB. To learn more please visit the Striim website, download a free 30-day trial of Striim, and for any issues when setting up the migration path with Striim, file a support request.
Next steps
Trying to do capacity planning for a migration to Azure Cosmos DB?
- If all you know is the number of vcores and servers in your existing database cluster, read about estimating request units using vCores or vCPUs
- If you know typical request rates for your current database workload, read about estimating request units using Azure Cosmos DB capacity planner
If you are migrating data to Azure Cosmos DB for NoSQL, see how to migrate data to API for Cassandra account using Striim
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for