Generative answers
Important
Power Virtual Agents capabilities and features are now part of Microsoft Copilot Studio following significant investments in generative AI and enhanced integrations across Microsoft Copilot.
Some articles and screenshots may refer to Power Virtual Agents while we update documentation and training content.
Generative answers in Microsoft Copilot Studio allow your copilot to find and present information from multiple sources, internal or external, without created topics. Generative answers can be used as primary information sources or as a fallback source when authored topics can't answer a user's query. As a result, you can quickly create and deploy a functional copilot. You don't need to manually author multiple topics that might not address all customer questions.
In the past, when a copilot can't determine a user's intent, it asks the user to rephrase their question. If after two prompts, the copilot still can't determine the user's intent, the copilot escalates to a live agent, using the system Escalate topic.
Today, before involving a live agent, the copilot uses natural language processing (NLP) to:
- Parse what a user types to determine what they're asking.
- Find, collate, and parse relevant information from a specified source. This source can be your company's website, or from multiple sources, including Sharepoint and OneDrive for Business.
- Summarize search results into plain language delivered to the copilot user.
This article helps you get started, using generative answers as a fallback topic, when a user's intent can't be addressed by existing copilot topics.
Note
Generative answers with search and summarize discuss how your copilot can query information sources, using generative answers in a single topic node.
Your workflow might look like:
You create a copilot and enable generative answers. You test it thoroughly.
After testing, you publish your copilot to instantly provide answers, help, and guidance to your copilot users.
You create individual topics for frequently asked questions. These topics might develop from analytics from previous copilots or existing support issues.
Generative answers as a fallback
When a copilot can't find a matching intent (topic) for the user's query, it uses generative answers and tries to answer the question. This behavior is known as generative answers for fallback. If the user's intent isn't matched to topics or generative answers, the Fallback system topic is used. System topics can escalate a query for the copilot.
Generative answers aren't limited to fallback scenarios. Generative answers aren't limited to fallback scenarios. Your copilot can also use other web sites, external or internal web sources, AI general knowledge, and knowledge sources such as SharePoint or OneDrive.
Generative answers can use these sources:
- External resources:
- AI general knowledge
- Bing Web Search (doesn't require external configuration)
- Bing Custom Search (requires external configuration)
- Internal resources:
- SharePoint (only specific file formats are supported)
- OneDrive
- Documents uploaded to Dataverse
- Custom data (internal or external): supply your own source, such as a Power Automate Flow or from Skill.
Note
You can expand your copilot's use of generative answers in Generative Answers with Search and Summarize.
Source authentication
In addition to URL considerations, you might need to authentication for your sources. For example, if you use an internal SharePoint site or OneDrive as a source for generative answers.
For more information, see Information sources.
Prerequisites
An account for Microsoft Copilot Studio.
Note
If you don't have a Microsoft Copilot Studio account, or you haven't created copilots before, see the Quickstart guide for building copilots with generative AI.
If you already have a copilot created, enable the generative answers option in the Generative AI page.
Review AI response generation training, model, and usage in the FAQ for generative answers and Learn more about Azure OpenAI.
Generative answers might be subject to usage limits or capacity throttling.
Increasing your copilot's reach
Go to the Microsoft Copilot Studio home page.
Select Create a copilot on the Home page or New copilot from the Copilots page.
Enter a name for your copilot.
Select a language for your copilot.
Provide a website you'd like the copilot to use for generating answers.
See the URL considerations section for the types of URLs you can use.
Select Create.
You now see your copilot's Overview page.
Content moderation
Adjust the content moderation settings from the Generative AI page.
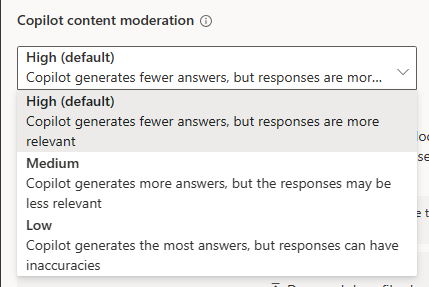
Under Copilot content moderation, select the level you want for your copilot.
High Medium Low Copilot’s answers are more relevant. (default) Copilot generates more answers, but might be irrelevant or undesirable. Copilot generates the most answers, but might be inaccurate. Select Save at the top of the page.
Test your copilot to see how well it responds to questions related to the content from your website. You might want to test edge case questions to decide if you need a lower moderation to be more inclusive.
URL considerations
The URL used in your copilot represents the scope of content for generating responses. There are requirements and restrictions on some URLs.
URL type and structure
The URL can have up to two levels of depth—subpaths indicated by a forward slash
/. A trailing forward slash, however, is allowed.Valid Not valid www.contoso.com
www.fabrikam.com/engines/rotary
www.fabrikam.com/engines/rotary/www.fabrikam.com/engines/rotary/dual-shaft If the URL redirects to another top-level site, the content isn't included in results:
For example, if www.fabrikam.com redirects to www.contoso.fabrikam.com, your copilot doesn't generate responses from content on either of those URLs.
URLs that point to a website, requiring authentication or ones not indexed by Bing.
For example, wikis and SharePoint sites require authentication, therefore can't be used:
- fabrikam.visualstudio.com/project/_wiki
- fabrikam.sharepoint.com
URL domain structure
Any publicly viewable content in the URL you specify, including subdomains under a top-level domain, generate content for your copilot.
Examples:
If you use www.fabrikam.com/engines/rotary, the content on www.fabrikam.com/engines/rotary/dual-shaft is also used by the copilot to generate responses.
Content on www.fabrikam.com/tools isn't used, since tools isn't a subdomain of rotary.
If you use www.fabrikam.com (the www exists), the content on news.fabrikam.com (the www doesn't exist) isn't used, since news. is a subdomain under the top-level domain fabrikam.com.
If you use fabrikam.com, then content on www.fabrikam.com and news.fabrikam.com is used, since they sit under the top-level domain fabrikam.com.
Social network & forum URLs
Your copilot might generate nonsensical, irrelevant, or inappropriate answers if you use a forum or social network site as your URL. Therefore, community content on social networks often increases the risk of more answers being rejected.
For more information, see the FAQ for generative answers. AI is trained to avoid generating malicious and offensive responses.
Search engine URLs
Don't include URLs of search engines like bing.com, as they don't provide useful responses.
Test your copilot's generative answers reach
Select Test your copilot at the bottom of the navigation pane.
In the Test copilot pane, ask your copilot questions that take advantage of the generative answers capability.
Generative answers works well with a large variety of question types.
However, some types might produce less helpful responses, including:
- Personal questions.
- Questions that require authenticated access to content.
- Questions that have no related content at a specified URL.
Forming questions
Your copilot has difficulty answering questions that require calculations, comparisons, or form submissions. Your copilot might not understand comparative and superlative terms such as better or best, latest, or cheapest in a question.
If the copilot can't generate an answer to a question, it prompts you to rephrase the question. After two of these prompts, the copilot initiates the system Escalate topic. System topics are topics automatically included with each copilot.
To learn more about how Bing interprets the question against the URL you specify, add
site: \<your URL here>to the end of your question to see the top Bing results for the question.You might need to disable the sample topics, lessons 1-3, that automatically come with a new copilot. They're used before any URLs are accessed.
Select the
...next to a sample topic on your Topics page and use the Status toggle to enable or disable the topic.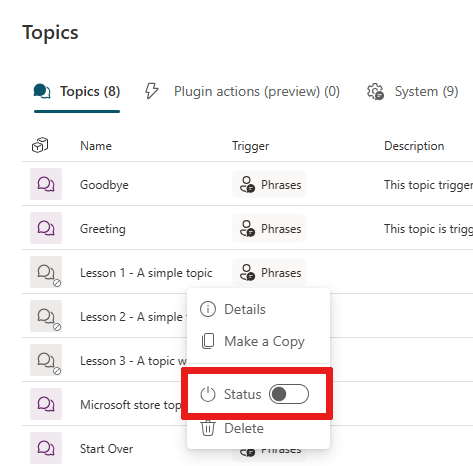
For more information, see Use lesson topics in Microsoft Copilot Studio.
Tip
In your chat window, you can provide feedback on how well the AI does by selecting the "thumbs up" or "thumbs down" icon underneath the generated answer.
If you see an irrelevant or inappropriate generated response, select the thumbs down icon to let us know. You can also include more detailed feedback.
We'll use this feedback to improve the quality of the AI.
What's supported
Quotas
Quotas are default constraints applied to copilots that limit how often messages can be sent to a copilot. The purpose of quotas is to throttle the client's service load, which protects a service from being overloaded and the client from unexpected resource usage.
Copilots with generative answers enabled have a limit on the number of queries they can make derive answers from the URL you specified. Normal conversations that use copilot topics follow the usual quotas and limitations.
Pricing
The use of the boosted conversations capability isn't billable and follows the usual quotas and limitations.
Languages
See Supported languages for the list of supported languages by this feature and their respective stage.
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for