What is custom text classification?
Custom text classification is one of the custom features offered by Azure AI Language. It is a cloud-based API service that applies machine-learning intelligence to enable you to build custom models for text classification tasks.
Custom text classification enables users to build custom AI models to classify text into custom classes pre-defined by the user. By creating a custom text classification project, developers can iteratively label data, train, evaluate, and improve model performance before making it available for consumption. The quality of the labeled data greatly impacts model performance. To simplify building and customizing your model, the service offers a custom web portal that can be accessed through the Language studio. You can easily get started with the service by following the steps in this quickstart.
Custom text classification supports two types of projects:
- Single label classification - you can assign a single class for each document in your dataset. For example, a movie script could only be classified as "Romance" or "Comedy".
- Multi label classification - you can assign multiple classes for each document in your dataset. For example, a movie script could be classified as "Comedy" or "Romance" and "Comedy".
This documentation contains the following article types:
- Quickstarts are getting-started instructions to guide you through making requests to the service.
- Concepts provide explanations of the service functionality and features.
- How-to guides contain instructions for using the service in more specific or customized ways.
Example usage scenarios
Custom text classification can be used in multiple scenarios across a variety of industries:
Automatic emails or ticket triage
Support centers of all types receive a high volume of emails or tickets containing unstructured, freeform text and attachments. Timely review, acknowledgment, and routing to subject matter experts within internal teams is critical. Email triage at this scale requires people to review and route to the right departments, which takes time and resources. Custom text classification can be used to analyze incoming text, and triage and categorize the content to be automatically routed to the relevant departments for further action.
Knowledge mining to enhance/enrich semantic search
Search is foundational to any app that surfaces text content to users. Common scenarios include catalog or document searches, retail product searches, or knowledge mining for data science. Many enterprises across various industries are seeking to build a rich search experience over private, heterogeneous content, which includes both structured and unstructured documents. As a part of their pipeline, developers can use custom text classification to categorize their text into classes that are relevant to their industry. The predicted classes can be used to enrich the indexing of the file for a more customized search experience.
Project development lifecycle
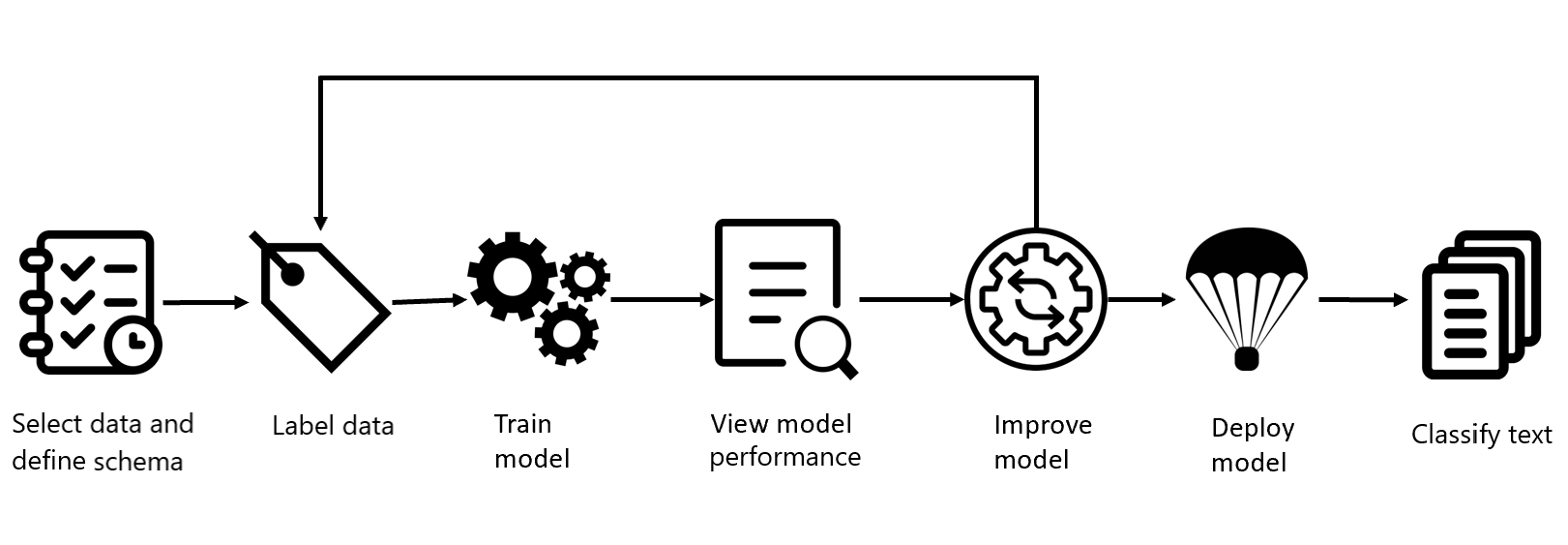
Creating a custom text classification project typically involves several different steps.
Follow these steps to get the most out of your model:
Define your schema: Know your data and identify the classes you want differentiate between, to avoid ambiguity.
Label your data: The quality of data labeling is a key factor in determining model performance. Documents that belong to the same class should always have the same class, if you have a document that can fall into two classes use Multi label classification projects. Avoid class ambiguity, make sure that your classes are clearly separable from each other, especially with single label classification projects.
Train the model: Your model starts learning from your labeled data.
View the model's performance: View the evaluation details for your model to determine how well it performs when introduced to new data.
Deploy the model: Deploying a model makes it available for use via the Analyze API.
Classify text: Use your custom model for custom text classification tasks.
Reference documentation and code samples
As you use custom text classification, see the following reference documentation and samples for Azure AI Language:
| Development option / language | Reference documentation | Samples |
|---|---|---|
| REST APIs (Authoring) | REST API documentation | |
| REST APIs (Runtime) | REST API documentation | |
| C# (Runtime) | C# documentation | C# samples - Single label classification C# samples - Multi label classification |
| Java (Runtime) | Java documentation | Java Samples - Single label classification Java Samples - Multi label classification |
| JavaScript (Runtime) | JavaScript documentation | JavaScript samples - Single label classification JavaScript samples - Multi label classification |
| Python (Runtime) | Python documentation | Python samples - Single label classification Python samples - Multi label classification |
Responsible AI
An AI system includes not only the technology, but also the people who will use it, the people who will be affected by it, and the environment in which it is deployed. Read the transparency note for custom text classification to learn about responsible AI use and deployment in your systems. You can also see the following articles for more information:
Next steps
Use the quickstart article to start using custom text classification.
As you go through the project development lifecycle, review the glossary to learn more about the terms used throughout the documentation for this feature.
Remember to view the service limits for information such as regional availability.
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for