Visualize your cluster with Service Fabric Explorer
Service Fabric Explorer (SFX) is an open-source tool for inspecting and managing Azure Service Fabric clusters. Service Fabric Explorer is a desktop application for Windows, macOS and Linux.
Running Service Fabric Explorer from the cluster
Service Fabric Explorer is also hosted in a Service Fabric cluster's HTTP management endpoint. To launch SFX in a web browser, browse to the cluster's HTTP management endpoint from any browser - for example https://clusterFQDN:19080.
For developer workstation setup, you can launch Service Fabric Explorer on your local cluster by navigating to https://localhost:19080/Explorer. Look at this article to prepare your development environment.
Note
If your cluster is secured by a self-signed certificate you will receive an error message from the web browser "This site is not secure". You can simply proceed through most modern web browsers by overriding the warning. In a production environment your cluster should be secured using common name and a certificate authority issued certificate.
Connect to a Service Fabric cluster
To connect to a Service Fabric cluster, you need the clusters management endpoint (FQDN/IP) and the HTTP management endpoint port (19080 by default). For example https://mysfcluster.westus.cloudapp.azure.com:19080. Use the "Connect to localhost" checkbox to connect to a local cluster on your workstation.
Connect to a secure cluster
You can control client access to your Service Fabric cluster either with certificates or using Microsoft Entra ID.
If you attempt to connect to a secure cluster, then depending on the cluster's configuration you will be required to present a client certificate or sign in using Microsoft Entra ID.
Video tutorial
Check this page for a training video to learn how to use Service Fabric Explorer.
[!NOTE]
This video shows Service Fabric Explorer hosted in a Service Fabric cluster, not the desktop version.
Understand the Service Fabric Explorer layout
You can navigate through Service Fabric Explorer by using the tree on the left. At the root of the tree, the cluster dashboard provides an overview of your cluster, including a summary of application and node health.
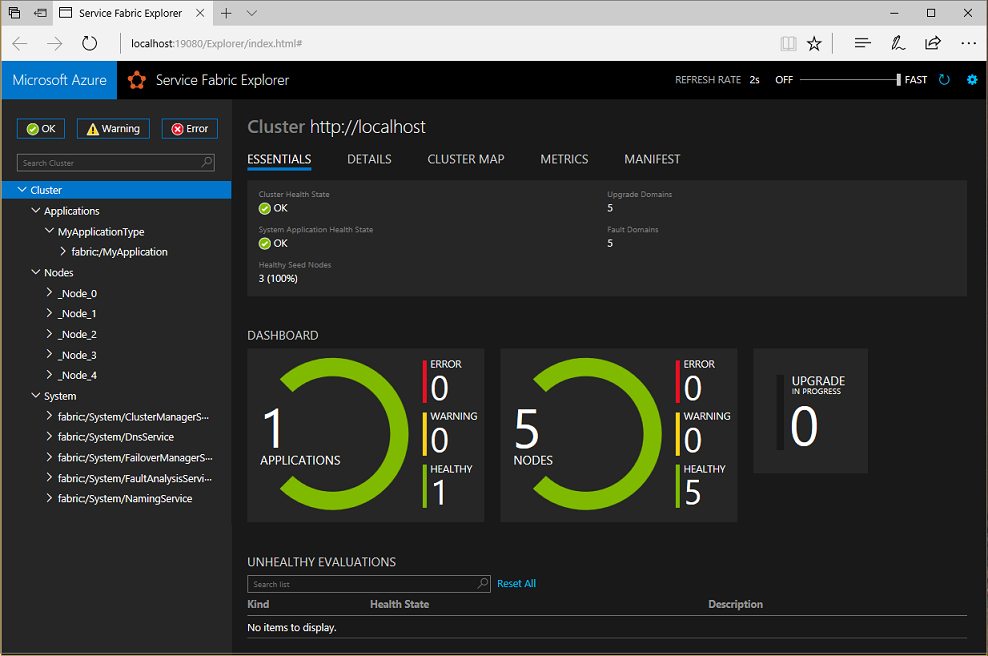
View the cluster's layout
Nodes in a Service Fabric cluster are placed across a two-dimensional grid of fault domains and upgrade domains. This placement ensures that your applications remain available in the presence of hardware failures and application upgrades. You can view how the current cluster is laid out by using the cluster map.
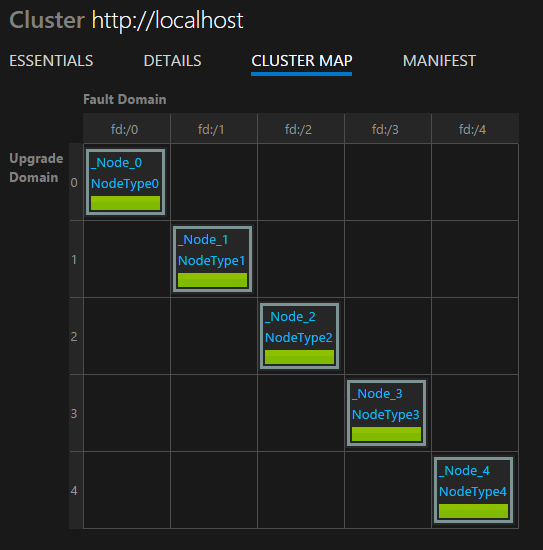
View applications and services
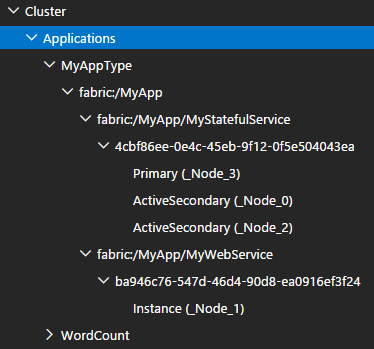
The cluster contains two subtrees: one for applications and another for nodes.
You can use the application view to navigate through Service Fabric's logical hierarchy: applications, services, partitions, and replicas.
In the example below, the application MyApp consists of two services, MyStatefulService and WebService. Since MyStatefulService is stateful, it includes a partition with one primary and two secondary replicas. By contrast, WebSvcService is stateless and contains a single instance.
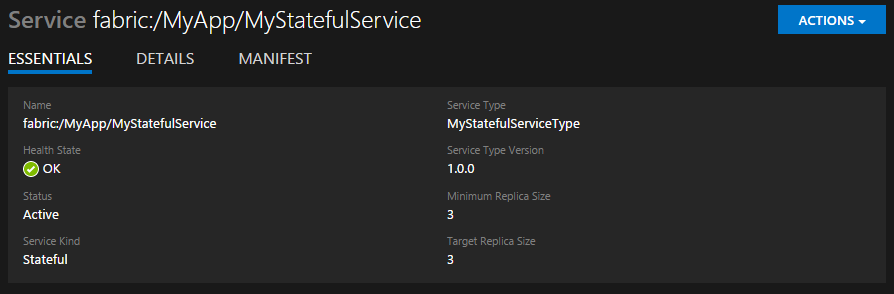
At each level of the tree, the main pane shows pertinent information about the item. For example, you can see the health status and version for a particular service.
View the cluster's nodes
The node view shows the physical layout of the cluster. For a given node, you can inspect which applications have code deployed on that node. More specifically, you can see which replicas are currently running there.
Actions
Service Fabric Explorer offers a quick way to invoke actions on nodes, applications, and services within your cluster.
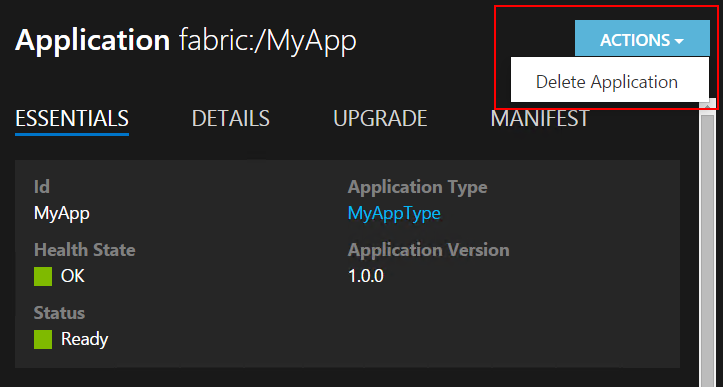
For example, to delete an application instance, choose the application from the tree on the left, and then choose Actions > Delete Application.
Tip
You can perform the same actions by clicking the ellipsis next to each element.
Every action that can be performed through Service Fabric Explorer can also be performed through PowerShell or a REST API, to enable automation.
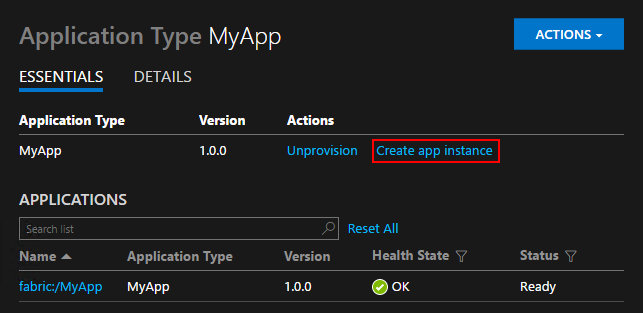
You can also use Service Fabric Explorer to create application instances for a given application type and version. Choose the application type in the tree view, then click the Create app instance link next to the version you'd like in the right pane.
Note
Service Fabric Explorer does not support parameters when creating application instances. Application instances use default parameter values.
Event Store
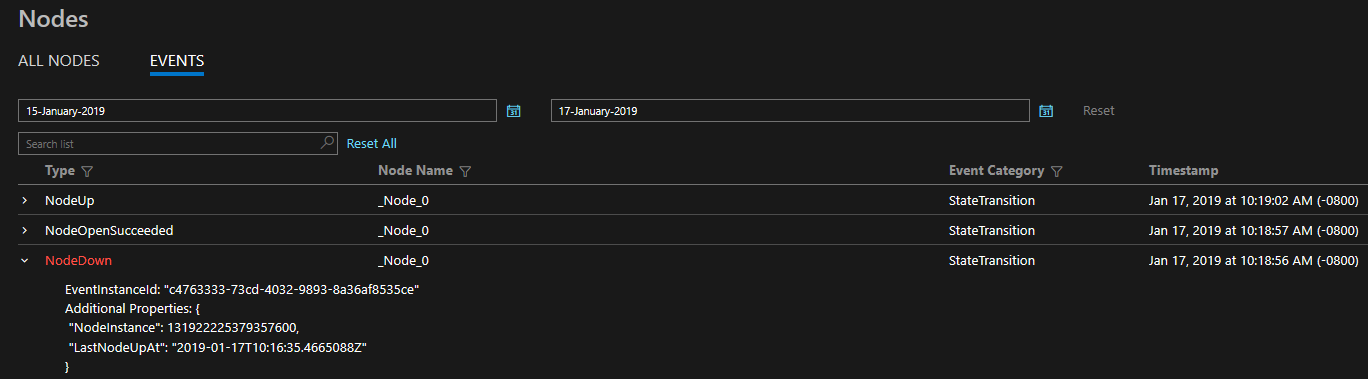
EventStore is a feature offered by the platform that provides Service Fabric platform events available in the Service Fabric Explorer and through REST API. You can see a snapshot view of what's going on in your cluster for each entity e.g. node, service, application and query based on the time of the event. You can also Read more about the EventStore at the EventStore Overview.
Note
As of Service Fabric version 6.4. EventStore is not enabled by default and must be enabled in the resource manager template
Note
As of Service Fabric version 6.4. the EventStore APIs are only available for Windows clusters running on Azure only. We are working on porting this functionality to Linux as well as our Standalone clusters.
Image Store Viewer
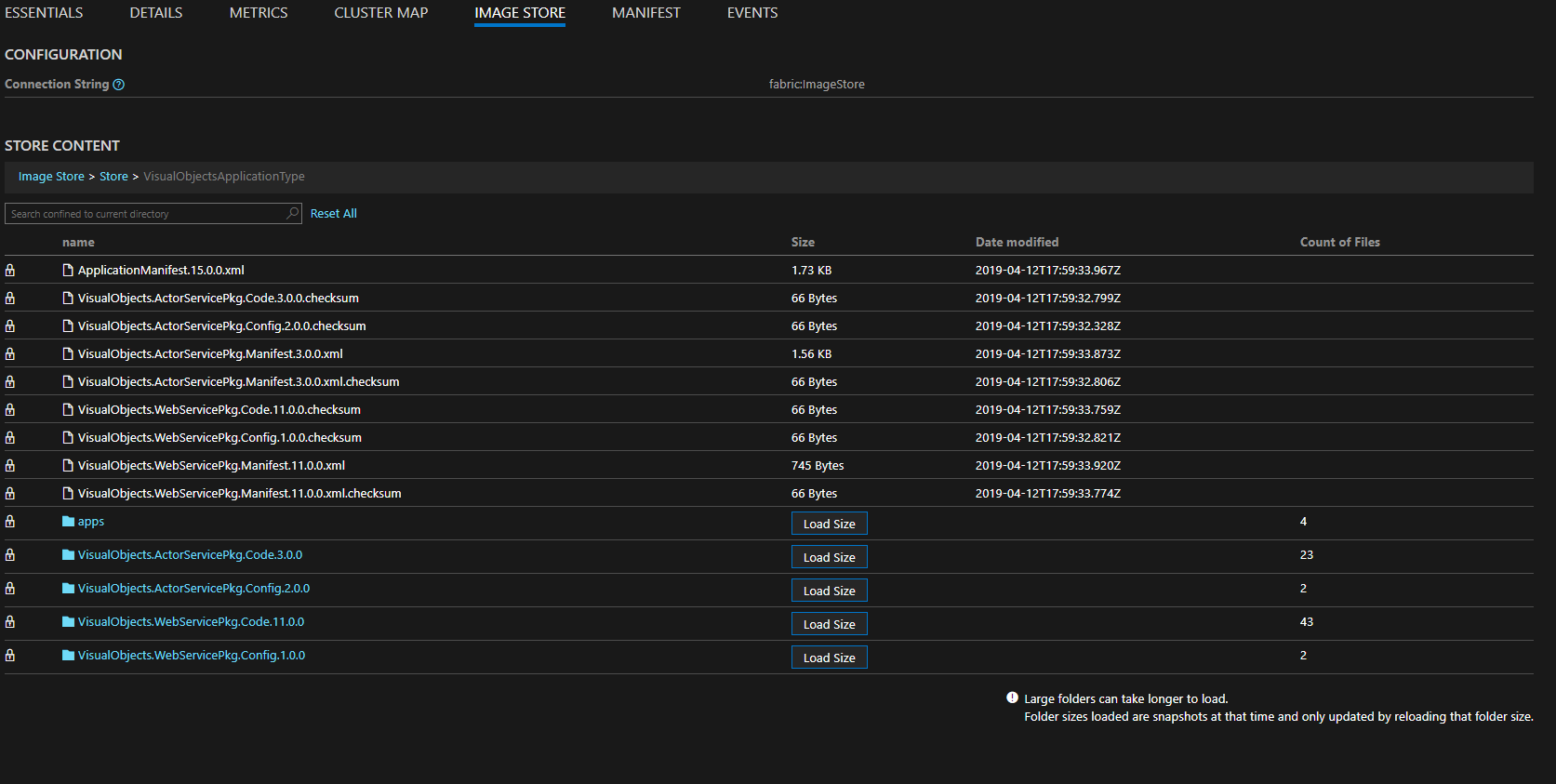
Image store viewer is a feature offered if using Native Image Store that allows for viewing the current contents of the Image store and get file and folder information, along with removing files/folders.
Backup and Restore
Service Fabric Explorer offers the ability to interface with Backup and Restore. In order to see Backup and Restore features in SFX, advanced mode must be enabled.
The following operations are possible:
- Create, edit, and delete a Backup Policy.
- Enable and disable Backup for an application, service, or partition.
- Suspend and resume Backup for an application, service, or partition.
- Trigger and track Backup of a partition.
- Trigger and track Restore for a partition.
For more on the Backup and Restore service, see the REST API reference.
Next steps
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for