Azure Stream Analytics on IoT Edge
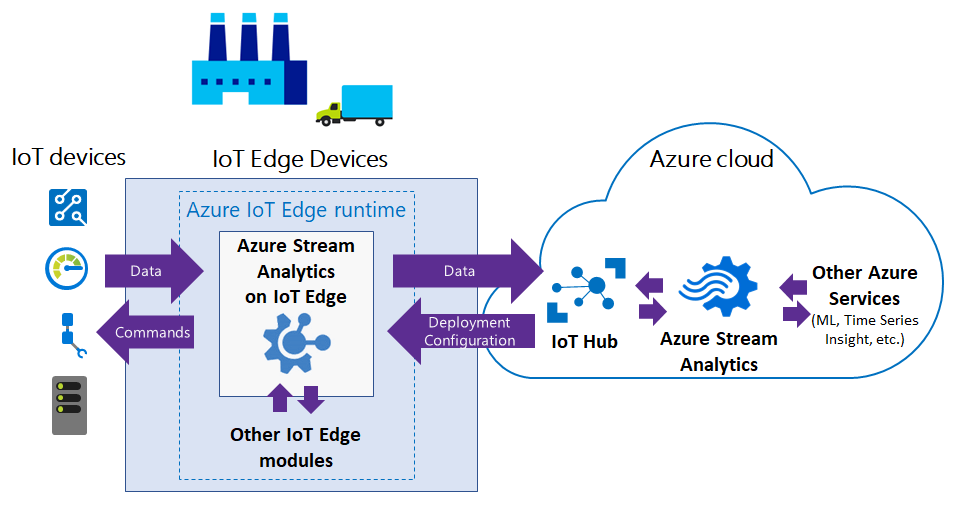
Azure Stream Analytics on IoT Edge empowers developers to deploy near-real-time analytical intelligence closer to IoT devices so that they can unlock the full value of device-generated data. Azure Stream Analytics is designed for low latency, resiliency, efficient use of bandwidth, and compliance. Enterprises can deploy control logic close to the industrial operations and complement Big Data analytics done in the cloud.
Azure Stream Analytics on IoT Edge runs within the Azure IoT Edge framework. Once the job is created in Stream Analytics, you can deploy and manage it using IoT Hub.
Common scenarios
This section describes the common scenarios for Stream Analytics on IoT Edge. The following diagram shows the flow of data between IoT devices and the Azure cloud.
Low-latency command and control
Manufacturing safety systems must respond to operational data with ultra-low latency. With Stream Analytics on IoT Edge, you can analyze sensor data in near real-time, and issue commands when you detect anomalies to stop a machine or trigger alerts.
Limited connectivity to the cloud
Mission critical systems, such as remote mining equipment, connected vessels, or offshore drilling, need to analyze and react to data even when cloud connectivity is intermittent. With Stream Analytics, your streaming logic runs independently of the network connectivity and you can choose what you send to the cloud for further processing or storage.
Limited bandwidth
The volume of data produced by jet engines or connected cars can be so large that data must be filtered or pre-processed before sending it to the cloud. Using Stream Analytics, you can filter or aggregate the data that needs to be sent to the cloud.
Compliance
Regulatory compliance may require some data to be locally anonymized or aggregated before being sent to the cloud.
Edge jobs in Azure Stream Analytics
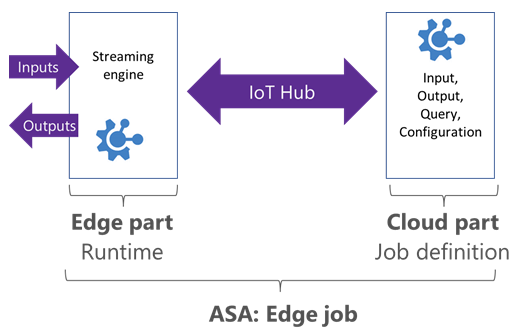
Stream Analytics Edge jobs run in containers deployed to Azure IoT Edge devices. Edge jobs are composed of two parts:
A cloud part that is responsible for the job definition: users define inputs, output, query, and other settings, such as out of order events, in the cloud.
A module running on your IoT devices. The module contains the Stream Analytics engine and receives the job definition from the cloud.
Stream Analytics uses IoT Hub to deploy edge jobs to device(s). For more information, see IoT Edge deployment.
Edge job limitations
The goal is to have parity between IoT Edge jobs and cloud jobs. Most SQL query language features are supported for both edge and cloud. However, the following features are not supported for edge jobs:
- User-defined functions (UDF) in JavaScript. UDF are available in C# for IoT Edge jobs (preview).
- User-defined aggregates (UDA).
- Azure ML functions.
- AVRO format for input/output. At this time, only CSV and JSON are supported.
- The following SQL operators:
- PARTITION BY
- GetMetadataPropertyValue
- Late arrival policy
Runtime and hardware requirements
To run Stream Analytics on IoT Edge, you need devices that can run Azure IoT Edge.
Stream Analytics and Azure IoT Edge use Docker containers to provide a portable solution that runs on multiple host operating systems (Windows, Linux).
Stream Analytics on IoT Edge is made available as Windows and Linux images, running on both x86-64 or ARM (Advanced RISC Machines) architectures.
Input and output
Stream Analytics Edge jobs can get inputs and outputs from other modules running on IoT Edge devices. To connect from and to specific modules, you can set the routing configuration at deployment time. More information is described on the IoT Edge module composition documentation.
For both inputs and outputs, CSV and JSON formats are supported.
For each input and output stream you create in your Stream Analytics job, a corresponding endpoint is created on your deployed module. These endpoints can be used in the routes of your deployment.
Supported stream input types are:
- Edge Hub
- Event Hub
- IoT Hub
Supported stream output types are:
- Edge Hub
- SQL Database
- Event Hub
- Blob Storage/ADLS Gen2
Reference input supports reference file type. Other outputs can be reached using a cloud job downstream. For example, a Stream Analytics job hosted in Edge sends output to Edge Hub, which can then send output to IoT Hub. You can use a second cloud-hosted Azure Stream Analytics job with input from IoT Hub and output to Power BI or another output type.
License and third-party notices
- Azure Stream Analytics on IoT Edge license.
- Third-party notice for Azure Stream Analytics on IoT Edge.
Azure Stream Analytics module image information
This version information was last updated on 2020-09-21:
Image:
mcr.microsoft.com/azure-stream-analytics/azureiotedge:1.0.9-linux-amd64- base image: mcr.microsoft.com/dotnet/core/runtime:2.1.13-alpine
- platform:
- architecture: amd64
- os: linux
Image:
mcr.microsoft.com/azure-stream-analytics/azureiotedge:1.0.9-linux-arm32v7- base image: mcr.microsoft.com/dotnet/core/runtime:2.1.13-bionic-arm32v7
- platform:
- architecture: arm
- os: linux
Image:
mcr.microsoft.com/azure-stream-analytics/azureiotedge:1.0.9-linux-arm64- base image: mcr.microsoft.com/dotnet/core/runtime:3.0-bionic-arm64v8
- platform:
- architecture: arm64
- os: linux
Get help
For further assistance, try the Microsoft Q&A question page for Azure Stream Analytics.
Next steps
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for