Troubleshoot Azure Stream Analytics by using resource logs
Occasionally, an Azure Stream Analytics job unexpectedly stops processing. It's important to be able to troubleshoot this kind of event. Failures can be caused by an unexpected query result, by connectivity to devices, or by an unexpected service outage. The resource logs in Stream Analytics can help you identify the cause of issues when they occur and reduce recovery time.
It's highly recommended to enable resource logs for all jobs as it will greatly help with debugging and monitoring.
Log types
Stream Analytics offers two types of logs:
Activity logs (always on), which give insights into operations performed on jobs.
Resource logs (configurable), which provide richer insights into everything that happens with a job. Resource logs start when the job is created and end when the job is deleted. They cover events when the job is updated and while it’s running.
Note
You can use services like Azure Storage, Azure Event Hubs, and Azure Monitor logs to analyze nonconforming data. You are charged based on the pricing model for those services.
Note
This article was recently updated to use the term Azure Monitor logs instead of Log Analytics. Log data is still stored in a Log Analytics workspace and is still collected and analyzed by the same Log Analytics service. We are updating the terminology to better reflect the role of logs in Azure Monitor. See Azure Monitor terminology changes for details.
Debugging using activity logs
Activity logs are on by default and give high-level insights into operations performed by your Stream Analytics job. Information present in activity logs may help find the root cause of the issues impacting your job. Do the following steps to use activity logs in Stream Analytics:
Sign in to the Azure portal and select Activity log under Overview.
You can see a list of operations that have been performed. Any operation that caused your job to fail has a red info bubble.
Select an operation to see its summary view. Information here's often limited. To learn more details about the operation, select JSON.

Scroll down to the Properties section of the JSON, which provides details of the error that caused the failed operation. In this example, the failure was due to a runtime error from out of bound latitude values. Discrepancy in the data that is processed by a Stream Analytics job causes a data error. You can learn about different input and output data errors and why they occur.
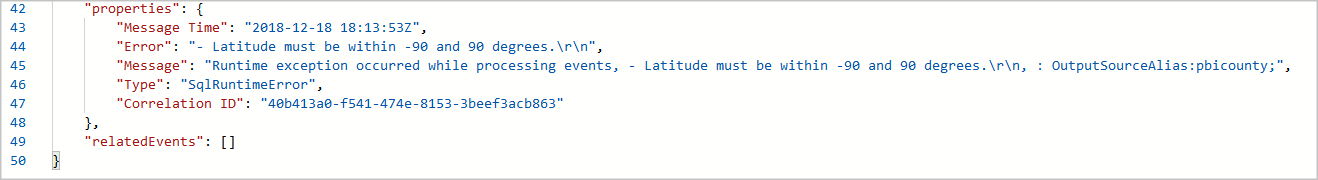
You can take corrective actions based on the error message in JSON. In this example, checks to ensure latitude value is between -90 degrees and 90 degrees need to be added to the query.
If the error message in the Activity logs isn’t helpful in identifying root cause, enable resource logs and use Azure Monitor logs.
Send diagnostics to Azure Monitor logs
Turning on resource logs and sending them to Azure Monitor logs is highly recommended. They're off by default. To turn them on, complete these steps:
Create a Log Analytics workspace if you don't already have one. It's recommended to have your Log Analytics workspace in the same region as your Stream Analytics job.
Sign in to the Azure portal, and navigate to your Stream Analytics job. Under Monitoring, select Diagnostics logs. Then select Turn on diagnostics.
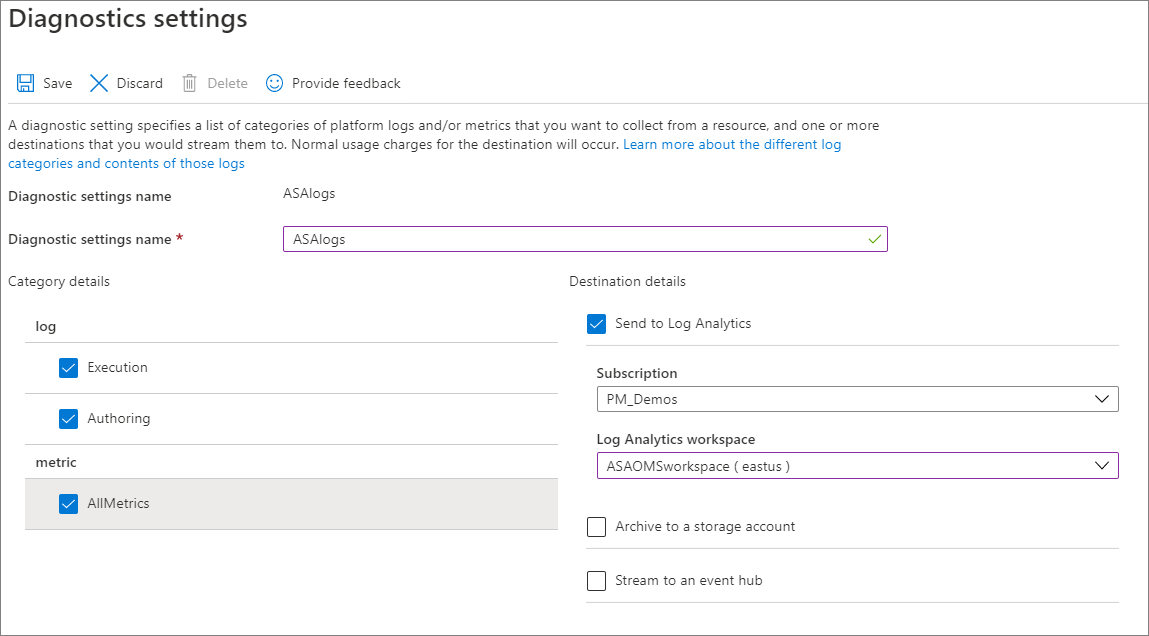
Provide a Name in Diagnostic settings name and check the boxes for Execution and Authoring under log, and AllMetrics under metric. Then select Send to Log Analytics and choose your workspace. Select Save.
When your Stream Analytics job starts, resource logs are routed to your Log Analytics workspace. To view resource logs for your job, select Logs under the Monitoring section.
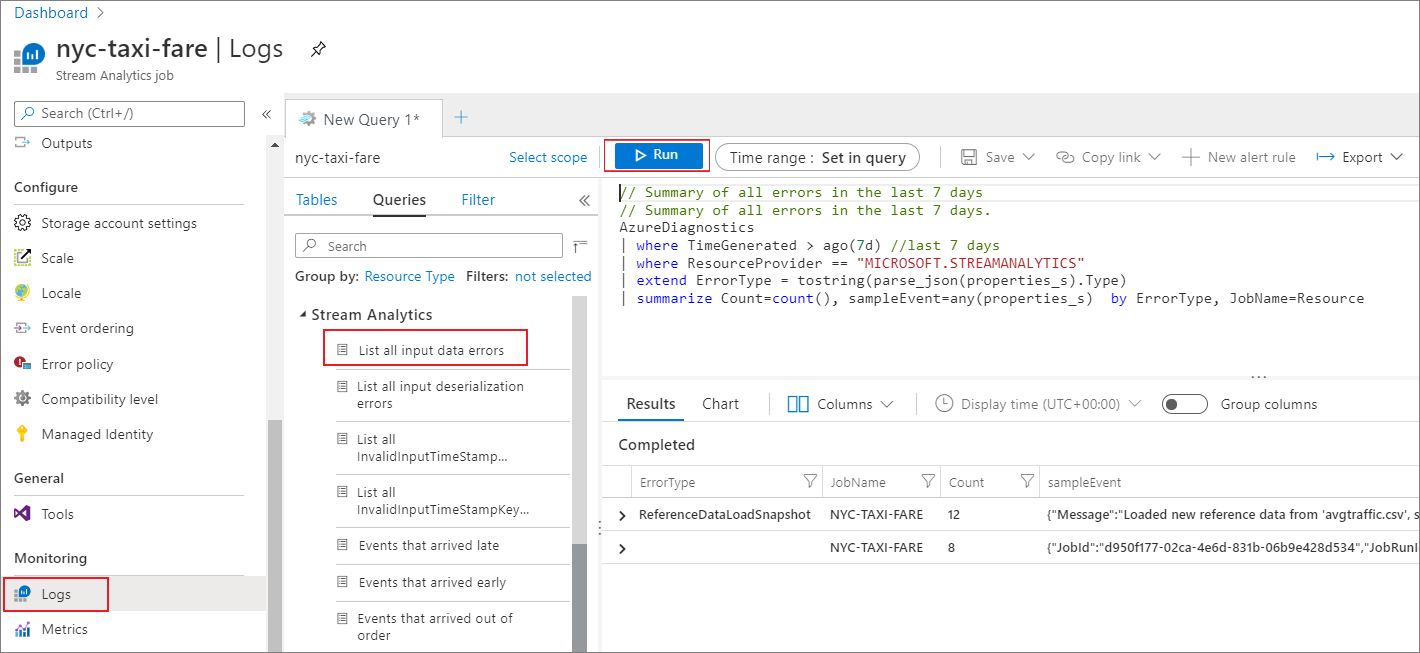
Stream Analytics provides predefined queries that allow you to easily search for the logs that you're interested in. You can select any predefined queries on the left pane and then select Run. You'll see the results of the query in the bottom pane.
Resource log categories
Azure Stream Analytics captures two categories of resource logs:
Authoring: Captures log events that are related to job authoring operations, such as job creation, adding and deleting inputs and outputs, adding and updating the query, and starting or stopping the job.
Execution: Captures events that occur during job execution.
- Connectivity errors
- Data processing errors, including:
- Events that don’t conform to the query definition (mismatched field types and values, missing fields, and so on)
- Expression evaluation errors
- Other events and errors
Resource logs schema
All logs are stored in JSON format. Each entry has the following common string fields:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| time | Timestamp (in UTC) of the log. |
| resourceId | ID of the resource that the operation took place on, in upper case. It includes the subscription ID, the resource group, and the job name. For example, /SUBSCRIPTIONS/6503D296-DAC1-4449-9B03-609A1F4A1C87/RESOURCEGROUPS/MY-RESOURCE-GROUP/PROVIDERS/MICROSOFT.STREAMANALYTICS/STREAMINGJOBS/MYSTREAMINGJOB. |
| category | Log category, either Execution or Authoring. |
| operationName | Name of the operation that is logged. For example, Send Events: SQL Output write failure to mysqloutput. |
| status | Status of the operation. For example, Failed or Succeeded. |
| level | Log level. For example, Error, Warning, or Informational. |
| properties | Log entry-specific detail, serialized as a JSON string. For more information, see the following sections in this article. |
Execution log properties schema
Execution logs have information about events that happened during Stream Analytics job execution. The schema of properties varies depending on whether the event is a data error or a generic event.
Data errors
Any error that occurs while the job is processing data is in this category of logs. These logs most often are created during data read, serialization, and write operations. These logs don't include connectivity errors. Connectivity errors are treated as generic events. You can learn more about the cause of various different input and output data errors.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Source | Name of the job input or output where the error occurred. |
| Message | Message associated with the error. |
| Type | Type of error. For example, DataConversionError, CsvParserError, or ServiceBusPropertyColumnMissingError. |
| Data | Contains data that is useful to accurately locate the source of the error. Subject to truncation, depending on size. |
Depending on the operationName value, data errors have the following schema:
Serialize events occur during event read operations. They occur when the data at the input doesn't satisfy the query schema for one of these reasons:
Type mismatch during event serialization/deserialization: Identifies the field that's causing the error.
Can't read an event, invalid serialization: Lists information about the location in the input data where the error occurred. Includes blob name for blob input, offset, and a sample of the data.
Send events occur during write operations. They identify the streaming event that caused the error.
Generic events
Generic events cover everything else.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Error | (optional) Error information. Usually, it's the exception information if it's available. |
| Message | Log message. |
| Type | Type of message. Maps to internal categorization of errors. For example, JobValidationError or BlobOutputAdapterInitializationFailure. |
| Correlation ID | GUID that uniquely identifies the job execution. All execution log entries from the time the job starts until the job stops have the same Correlation ID value. |
For reference, see a list of all resource logs category types supported in Azure Monitor or all the resource log category types collected for Azure Stream Analytics.
Next steps
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for