Tutorial: Create an alias record to refer to an Azure public IP address
You can create an alias record to reference an Azure resource. An example is an alias record that references an Azure public IP resource.
In this tutorial, you learn how to:
- Create a virtual network and a subnet.
- Create a web server virtual machine with a public IP.
- Create an alias record that points to the public IP.
- Test the alias record.
If you don’t have an Azure subscription, create a free account before you begin.
Prerequisites
- An Azure account with an active subscription.
- A domain name hosted in Azure DNS. If you don't have an Azure DNS zone, you can create a DNS zone, then delegate your domain to Azure DNS.
Note
In this tutorial, contoso.com is used as an example domain name. Replace contoso.com with your own domain name.
Sign in to Azure
Sign in to the Azure portal.
Create the network infrastructure
Create a virtual network and a subnet to place your web server in.
In the Azure portal, enter virtual network in the search box at the top of the portal, and then select Virtual networks from the search results.
In Virtual networks, select + Create.
In Create virtual network, enter or select the following information in the Basics tab:
Setting Value Project Details Subscription Select your Azure subscription. Resource Group Select Create new.
In Name, enter PIPResourceGroup.
Select OK.Instance details Name Enter myPIPVNet. Region Select your region. Select the IP Addresses tab or select the Next: IP Addresses button at the bottom of the page.
In the IP Addresses tab, enter the following information:
Setting Value IPv4 address space Enter 10.10.0.0/16. Select + Add subnet, and enter this information in the Add subnet:
Setting Value Subnet name Enter WebSubnet. Subnet address range Enter 10.10.0.0/24. Select Add.
Select the Review + create tab or select the Review + create button.
Select Create.
Create a web server virtual machine
Create a Windows Server virtual machine and then install IIS web server on it.
Create the virtual machine
Create a Windows Server 2019 virtual machine.
In the Azure portal, enter virtual machine in the search box at the top of the portal, and then select Virtual machines from the search results.
In Virtual machines, select + Create and then select Azure virtual machine.
In Create a virtual machine, enter or select the following information in the Basics tab:
Setting Value Project Details Subscription Select your Azure subscription. Resource Group Select PIPResourceGroup. Instance details Virtual machine name Enter Web-01. Region Select (US) East US. Availability options Select No infrastructure redundancy required. Security type Select Standard. Image Select Windows Server 2019 Datacenter - Gen2. Size Select your VM size. Administrator account Username Enter a username. Password Enter a password. Confirm password Reenter the password. Inbound port rules Public inbound ports Select None. Select the Networking tab, or select Next: Disks, then Next: Networking.
In the Networking tab, enter or select the following information:
Setting Value Network interface Virtual network Select myPIPVNet. Subnet Select WebSubnet. Public IP Take the default public IP. NIC network security group Select Basic. Public inbound ports Select Allow selected ports. Select inbound ports Select HTTP (80), HTTPS (443) and RDP (3389). Select Review + create.
Review the settings, and then select Create.
This deployment may take a few minutes to complete.
Note
Web-01 virtual machine has an attached NIC with a basic dynamic public IP that changes every time the virtual machine is restarted.
Install IIS web server
Install IIS web server on Web-01.
In the Overview page of Web-01, select Connect and then RDP.
In the RDP page, select Download RDP File.
Open Web-01.rdp, and select Connect.
Enter the username and password entered during virtual machine creation.
On the Server Manager dashboard, select Manage then Add Roles and Features.
Select Server Roles or select Next three times. On the Server Roles screen, select Web Server (IIS).
Select Add Features, and then select Next.
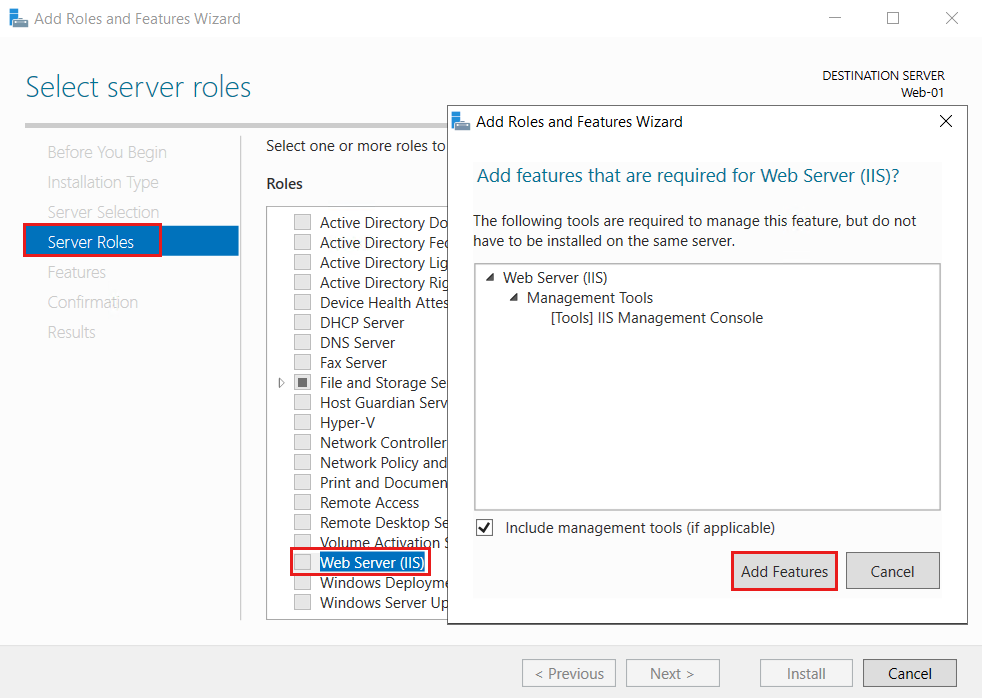
Select Confirmation or select Next three times, and then select Install. The installation process takes a few minutes to finish.
After the installation finishes, select Close.
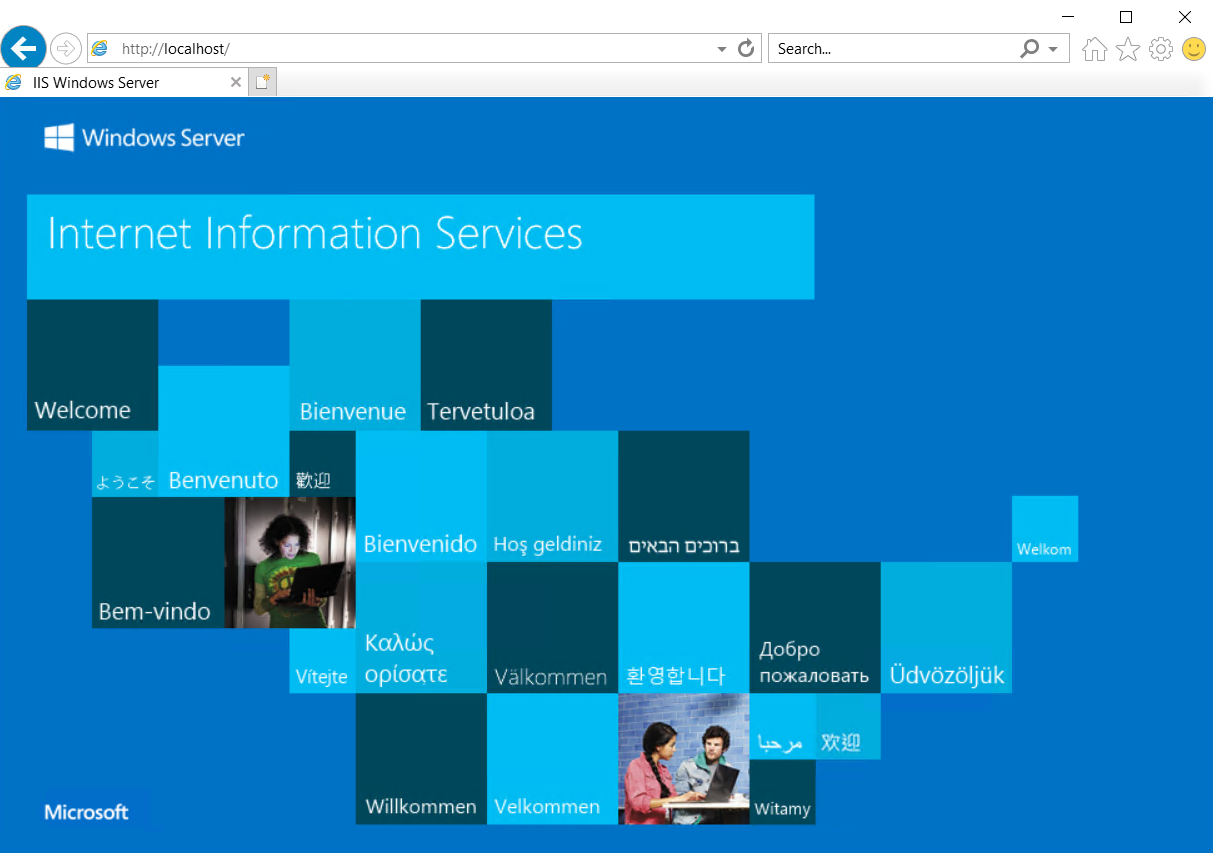
Open a web browser. Browse to localhost to verify that the default IIS web page appears.
Create an alias record
Create an alias record that points to the public IP address.
In the Azure portal, enter contoso.com in the search box at the top of the portal, and then select contoso.com DNS zone from the search results.
In the Overview page, select the + Record set button.
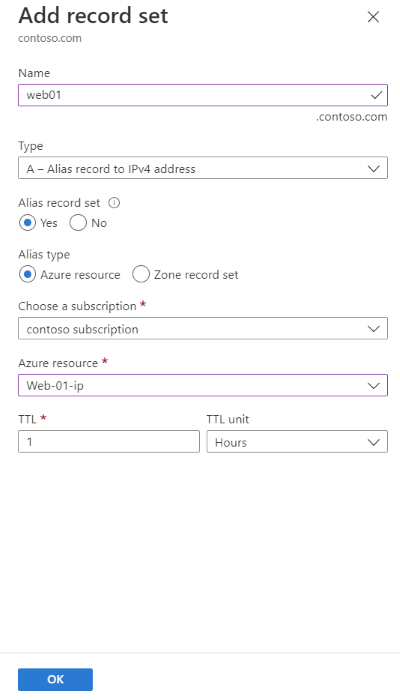
In the Add record set, enter web01 in the Name.
Select A for the Type.
Select Yes for the Alias record set, and then select the Azure Resource for the Alias type.
Select the Web-01-ip public IP address for the Azure resource.
Select OK.
Test the alias record
- In the Azure portal, enter virtual machine in the search box at the top of the portal, and then select Virtual machines from the search results.
- Select the Web-01 virtual machine. Note the public IP address in the Overview page.
- From a web browser, browse to
web01.contoso.com, which is the fully qualified domain name of the Web-01 virtual machine. You now see the IIS default web page. - Close the web browser.
- Stop the Web-01 virtual machine, and then restart it.
- After the virtual machine restarts, note the new public IP address for the virtual machine.
- From a web browser, browse again to
web01.contoso.com.
This procedure succeeds because you used an alias record to point to the public IP resource instead of a standard A record that points to the public IP address, not the resource.
Clean up resources
When no longer needed, you can delete all resources created in this tutorial by following these steps:
- On the Azure portal menu, select Resource groups.
- Select the PIPResourceGroup resource group.
- On the Overview page, select Delete resource group.
- Enter PIPResourceGroup and select Delete.
- On the Azure portal menu, select All resources.
- Select contoso.com DNS zone.
- On the Overview page, select the web01 record created in this tutorial.
- Select Delete and then Yes.
Next steps
In this tutorial, you learned how to create an alias record to refer to an Azure public IP address resource. To learn how to create an alias record to support an apex domain name with Traffic Manager, continue with the next tutorial:
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for