Tutorial: Install applications in Virtual Machine Scale Sets with the Azure CLI
To run applications on virtual machine (VM) instances in a scale set, you first need to install the application components and required files. In a previous tutorial, you learned how to create and use a custom VM image to deploy your VM instances. This custom image included manual application installs and configurations. You can also automate the install of applications to a scale set after each VM instance is deployed, or update an application that already runs on a scale set. In this tutorial you learn how to:
- Automatically install applications to your scale set
- Use the Azure Custom Script Extension
- Update a running application on a scale set
If you don't have an Azure subscription, create an Azure free account before you begin.
Prerequisites
Use the Bash environment in Azure Cloud Shell. For more information, see Quickstart for Bash in Azure Cloud Shell.
If you prefer to run CLI reference commands locally, install the Azure CLI. If you're running on Windows or macOS, consider running Azure CLI in a Docker container. For more information, see How to run the Azure CLI in a Docker container.
If you're using a local installation, sign in to the Azure CLI by using the az login command. To finish the authentication process, follow the steps displayed in your terminal. For other sign-in options, see Sign in with the Azure CLI.
When you're prompted, install the Azure CLI extension on first use. For more information about extensions, see Use extensions with the Azure CLI.
Run az version to find the version and dependent libraries that are installed. To upgrade to the latest version, run az upgrade.
- This article requires version 2.0.29 or later of the Azure CLI. If using Azure Cloud Shell, the latest version is already installed.
What is the Azure Custom Script Extension?
The Custom Script Extension downloads and executes scripts on Azure VMs. This extension is useful for post deployment configuration, software installation, or any other configuration / management task. Scripts can be downloaded from Azure storage or GitHub, or provided to the Azure portal at extension run-time.
The Custom Script extension integrates with Azure Resource Manager templates, and can also be used with the Azure CLI, Azure PowerShell, Azure portal, or the REST API. For more information, see the Custom Script Extension overview.
To use the Custom Script Extension with the Azure CLI, you create a JSON file that defines what files to obtain and commands to execute. These JSON definitions can be reused across scale set deployments to apply consistent application installs.
Create Custom Script Extension definition
To see the Custom Script Extension in action, let's create a scale set that installs the NGINX web server and outputs the hostname of the scale set VM instance. The following Custom Script Extension definition downloads a sample script from GitHub, installs the required packages, then writes the VM instance hostname to a basic HTML page.
In your current shell, create a file named customConfig.json and paste the following configuration. For example, create the file in the Cloud Shell not on your local machine. You can use any editor you wish. In this tutorial we will use Vi. Entervi in the Cloud Shell. Paste the below JSON into the editor and type :w customConfig.json.
{
"fileUris": ["https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/compute-automation-configurations/master/automate_nginx.sh"],
"commandToExecute": './automate_nginx.sh'
}
Note
You may need to invert the use of the single (') and double quotes (") within the JSON block if you decide to reference the JSON directly (instead of referencing the customConfig.json file) in the --settings parameter below.
Create a scale set
Important
Starting November 2023, VM scale sets created using PowerShell and Azure CLI will default to Flexible Orchestration Mode if no orchestration mode is specified. For more information about this change and what actions you should take, go to Breaking Change for VMSS PowerShell/CLI Customers - Microsoft Community Hub
Create a resource group with az group create. The following example creates a resource group named myResourceGroup in the eastus location:
az group create --name myResourceGroup --location eastus
Now create a Virtual Machine Scale Set with az vmss create. The following example creates a scale set named myScaleSet, and generates SSH keys if they do not exist:
az vmss create \
--resource-group myResourceGroup \
--name myScaleSet \
--image Ubuntu2204 \
--orchestration-mode Flexible \
--admin-username azureuser \
--generate-ssh-keys
It takes a few minutes to create and configure all the scale set resources and VMs.
Apply the Custom Script Extension
Apply the Custom Script Extension configuration to the VM instances in your scale set with az vmss extension set. The following example applies the customConfig.json configuration to the myScaleSet VM instances in the resource group named myResourceGroup:
az vmss extension set \
--publisher Microsoft.Azure.Extensions \
--version 2.0 \
--name CustomScript \
--resource-group myResourceGroup \
--vmss-name myScaleSet \
--settings customConfig.json
Caution
File names are case sensitive. Use the exact file name stated in these instructions to avoid failure.
Apply the extension to the existing scale set instances
Upgrade all the instances to apply the custom script. The upgrade may take a couple of minutes.
az vmss update-instances --resource-group myResourceGroup --name myScaleSet --instance-ids "*"
Allow traffic to port 80
To allow traffic to flow through the load balancer to the virtual machines the default network security group needs to be updated.
az network nsg rule create --name AllowHTTP --resource-group myResourceGroup --nsg-name myScaleSetNSG --access Allow --priority 1010 --destination-port-ranges 80
Test your scale set
To see your web server in action, obtain the public IP address of your load balancer with az network public-ip show. The following example obtains the IP address for myScaleSetLBPublicIP created as part of the scale set:
az network public-ip show \
--resource-group myResourceGroup \
--name myScaleSetLBPublicIP \
--query [ipAddress] \
--output tsv
Enter the public IP address of the load balancer in to a web browser. The load balancer distributes traffic to one of your VM instances, as shown in the following example:
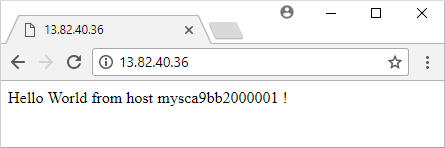
Leave the web browser open so that you can see an updated version in the next step.
Change the upgrade policy
In the previous section, in order to apply the updated application to all the scale set instances, a manual upgrade was needed. To enable updates to be applied automatically to all existing scale set instances, update the upgrade policy from manual to automatic. For more information on upgrade policies, see Upgrade policies for Virtual Machine Scale Sets.
az vmss update \
--name myScaleSet \
--resource-group myResourceGroup \
--set upgradePolicy.mode=automatic
Update app deployment
In your current shell, create a file named customConfigv2.json and paste the following configuration. This definition runs an updated v2 version of the application install script:
{
"fileUris": ["https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/compute-automation-configurations/master/automate_nginx_v2.sh"],
"commandToExecute": "./automate_nginx_v2.sh"
}
Apply the Custom Script Extension configuration to the your scale set again with az vmss extension set. The customConfigv2.json is used to apply the updated version of the application:
az vmss extension set \
--publisher Microsoft.Azure.Extensions \
--version 2.0 \
--name CustomScript \
--resource-group myResourceGroup \
--vmss-name myScaleSet \
--settings @customConfigv2.json
Because the scale set is now using an automatic upgrade policy, the updated application will automatically be applied to existing scale set instances. Refresh your web browser to see the updated application.
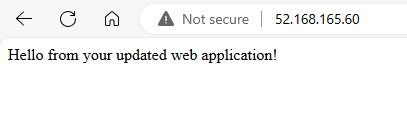
Clean up resources
To remove your scale set and additional resources, delete the resource group and all its resources with az group delete. The --no-wait parameter returns control to the prompt without waiting for the operation to complete. The --yes parameter confirms that you wish to delete the resources without an additional prompt to do so.
az group delete --name myResourceGroup --no-wait --yes
Next steps
In this tutorial, you learned how to automatically install and update applications on your scale set with the Azure CLI:
- Automatically install applications to your scale set
- Use the Azure Custom Script Extension
- Update a running application on a scale set
Advance to the next tutorial to learn how to automatically scale your scale set.
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for
