Tutorial: Build a Java Spring Boot web app with Azure App Service on Linux and Azure Cosmos DB
Note
For Spring applications, we recommend using Azure Spring Apps. However, you can still use Azure App Service as a destination. See Java Workload Destination Guidance for advice.
This tutorial walks you through the process of building, configuring, deploying, and scaling Java web apps on Azure. When you are finished, you will have a Spring Boot application storing data in Azure Cosmos DB running on Azure App Service on Linux.

In this tutorial, you learn how to:
- Create an Azure Cosmos DB database.
- Connect a sample app to the database and test it locally
- Deploy the sample app to Azure
- Stream diagnostic logs from App Service
- Add additional instances to scale out the sample app
If you don't have an Azure subscription, create an Azure free account before you begin.
Prerequisites
Clone the sample TODO app and prepare the repo
This tutorial uses a sample TODO list app with a web UI that calls a Spring REST API backed by Spring Data for Azure Cosmos DB. The code for the app is available on GitHub. To learn more about writing Java apps using Spring and Azure Cosmos DB, see the Spring Boot Starter with the Azure Cosmos DB for NoSQL tutorial and the Spring Data for Azure Cosmos DB quick start.
Run the following commands in your terminal to clone the sample repo and set up the sample app environment.
git clone --recurse-submodules https://github.com/Azure-Samples/e2e-java-experience-in-app-service-linux-part-2.git
cd e2e-java-experience-in-app-service-linux-part-2
yes | cp -rf .prep/* .
Create an Azure Cosmos DB
Follow these steps to create an Azure Cosmos DB database in your subscription. The TODO list app will connect to this database and store its data when running, persisting the application state no matter where you run the application.
Login to your Azure CLI, and optionally set your subscription if you have more than one connected to your login credentials.
az login az account set -s <your-subscription-id>Create an Azure Resource Group, noting the resource group name.
az group create -n <your-azure-group-name> \ -l <your-resource-group-region>Create Azure Cosmos DB with the
GlobalDocumentDBkind. The name of the Azure Cosmos DB instance must use only lower case letters. Note down thedocumentEndpointfield in the response from the command.az cosmosdb create --kind GlobalDocumentDB \ -g <your-azure-group-name> \ -n <your-azure-COSMOS-DB-name-in-lower-case-letters>Get your Azure Cosmos DB key to connect to the app. Keep the
primaryMasterKey,documentEndpointnearby as you'll need them in the next step.az cosmosdb keys list -g <your-azure-group-name> -n <your-azure-COSMOSDB-name>
Configure the TODO app properties
Open a terminal on your computer. Copy the sample script file in the cloned repo so you can customize it for the Azure Cosmos DB database you just created.
cd initial/spring-todo-app
cp set-env-variables-template.sh .scripts/set-env-variables.sh
Edit .scripts/set-env-variables.sh in your favorite editor and supply Azure Cosmos DB connection info. For the App Service Linux configuration, use the same region as before (your-resource-group-region) and resource group (your-azure-group-name) used when creating the Azure Cosmos DB database. Choose a WEBAPP_NAME that is unique since it cannot duplicate any web app name in any Azure deployment.
export COSMOSDB_URI=<put-your-COSMOS-DB-documentEndpoint-URI-here>
export COSMOSDB_KEY=<put-your-COSMOS-DB-primaryMasterKey-here>
export COSMOSDB_DBNAME=<put-your-COSMOS-DB-name-here>
# App Service Linux Configuration
export RESOURCEGROUP_NAME=<put-your-resource-group-name-here>
export WEBAPP_NAME=<put-your-Webapp-name-here>
export REGION=<put-your-REGION-here>
Then run the script:
source .scripts/set-env-variables.sh
These environment variables are used in application.properties in the TODO list app. The fields in the properties file set up a default repository configuration for Spring Data:
azure.cosmosdb.uri=${COSMOSDB_URI}
azure.cosmosdb.key=${COSMOSDB_KEY}
azure.cosmosdb.database=${COSMOSDB_DBNAME}
@Repository
public interface TodoItemRepository extends DocumentDbRepository<TodoItem, String> {
}
Then the sample app uses the @Document annotation imported from com.microsoft.azure.spring.data.cosmosdb.core.mapping.Document to set up an entity type to be stored and managed by Azure Cosmos DB:
@Document
public class TodoItem {
private String id;
private String description;
private String owner;
private boolean finished;
Run the sample app
Use Maven to run the sample.
mvn package spring-boot:run
The output should look like the following.
bash-3.2$ mvn package spring-boot:run
[INFO] Scanning for projects...
[INFO]
[INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------------
[INFO] Building spring-todo-app 2.0-SNAPSHOT
[INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------------
[INFO]
[INFO] SimpleUrlHandlerMapping - Mapped URL path [/webjars/**] onto handler of type [class org.springframework.web.servlet.resource.ResourceHttpRequestHandler]
[INFO] SimpleUrlHandlerMapping - Mapped URL path [/**] onto handler of type [class org.springframework.web.servlet.resource.ResourceHttpRequestHandler]
[INFO] WelcomePageHandlerMapping - Adding welcome page: class path resource [static/index.html]
2018-10-28 15:04:32.101 INFO 7673 --- [ main] c.m.azure.documentdb.DocumentClient : Initializing DocumentClient with serviceEndpoint [https://sample-cosmos-db-westus.documents.azure.com:443/], ConnectionPolicy [ConnectionPolicy [requestTimeout=60, mediaRequestTimeout=300, connectionMode=Gateway, mediaReadMode=Buffered, maxPoolSize=800, idleConnectionTimeout=60, userAgentSuffix=;spring-data/2.0.6;098063be661ab767976bd5a2ec350e978faba99348207e8627375e8033277cb2, retryOptions=com.microsoft.azure.documentdb.RetryOptions@6b9fb84d, enableEndpointDiscovery=true, preferredLocations=null]], ConsistencyLevel [null]
[INFO] AnnotationMBeanExporter - Registering beans for JMX exposure on startup
[INFO] TomcatWebServer - Tomcat started on port(s): 8080 (http) with context path ''
[INFO] TodoApplication - Started TodoApplication in 45.573 seconds (JVM running for 76.534)
You can access Spring TODO App locally using this link once the app is started: http://localhost:8080/.

If you see exceptions instead of the "Started TodoApplication" message, check that the bash script in the previous step exported the environment variables properly and that the values are correct for the Azure Cosmos DB database you created.
Configure Azure deployment
Open the pom.xml file in the initial/spring-boot-todo directory and add the following Azure Web App Plugin for Maven configuration.
<plugins>
<!--*************************************************-->
<!-- Deploy to Java SE in App Service Linux -->
<!--*************************************************-->
<plugin>
<groupId>com.microsoft.azure</groupId>
<artifactId>azure-webapp-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.5.0</version>
<configuration>
<schemaVersion>v2</schemaVersion>
<!-- Web App information -->
<resourceGroup>${RESOURCEGROUP_NAME}</resourceGroup>
<appName>${WEBAPP_NAME}</appName>
<region>${REGION}</region>
<pricingTier>P1v2</pricingTier>
<!-- Java Runtime Stack for Web App on Linux-->
<runtime>
<os>linux</os>
<javaVersion>Java 8</javaVersion>
<webContainer>Java SE</webContainer>
</runtime>
<deployment>
<resources>
<resource>
<directory>${project.basedir}/target</directory>
<includes>
<include>*.jar</include>
</includes>
</resource>
</resources>
</deployment>
<appSettings>
<property>
<name>COSMOSDB_URI</name>
<value>${COSMOSDB_URI}</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>COSMOSDB_KEY</name>
<value>${COSMOSDB_KEY}</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>COSMOSDB_DBNAME</name>
<value>${COSMOSDB_DBNAME}</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>JAVA_OPTS</name>
<value>-Dserver.port=80</value>
</property>
</appSettings>
</configuration>
</plugin>
...
</plugins>
Deploy to App Service on Linux
Use the mvn azure-webapp:deploy Maven goal to deploy the TODO app to Azure App Service on Linux.
# Deploy
bash-3.2$ mvn azure-webapp:deploy
[INFO] Scanning for projects...
[INFO]
[INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------------
[INFO] Building spring-todo-app 2.0-SNAPSHOT
[INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------------
[INFO]
[INFO] --- azure-webapp-maven-plugin:2.5.0:deploy (default-cli) @ spring-todo-app ---
Auth Type: AZURE_CLI
Default subscription: xxxxxxxxx
Username: xxxxxxxxx
[INFO] Subscription: xxxxxxxxx
[INFO] Creating App Service Plan 'ServicePlanb6ba8178-5bbb-49e7'...
[INFO] Successfully created App Service Plan.
[INFO] Creating web App spring-todo-app...
[INFO] Successfully created Web App spring-todo-app.
[INFO] Trying to deploy artifact to spring-todo-app...
[INFO] Successfully deployed the artifact to https://spring-todo-app.azurewebsites.net
[INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------------
[INFO] BUILD SUCCESS
[INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------------
[INFO] Total time: 02:19 min
[INFO] Finished at: 2019-11-06T15:32:03-07:00
[INFO] Final Memory: 50M/574M
[INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------------
The output contains the URL to your deployed application (in this example, https://spring-todo-app.azurewebsites.net). You can copy this URL into your web browser or run the following command in your Terminal window to load your app.
explorer https://spring-todo-app.azurewebsites.net
You should see the app running with the remote URL in the address bar:
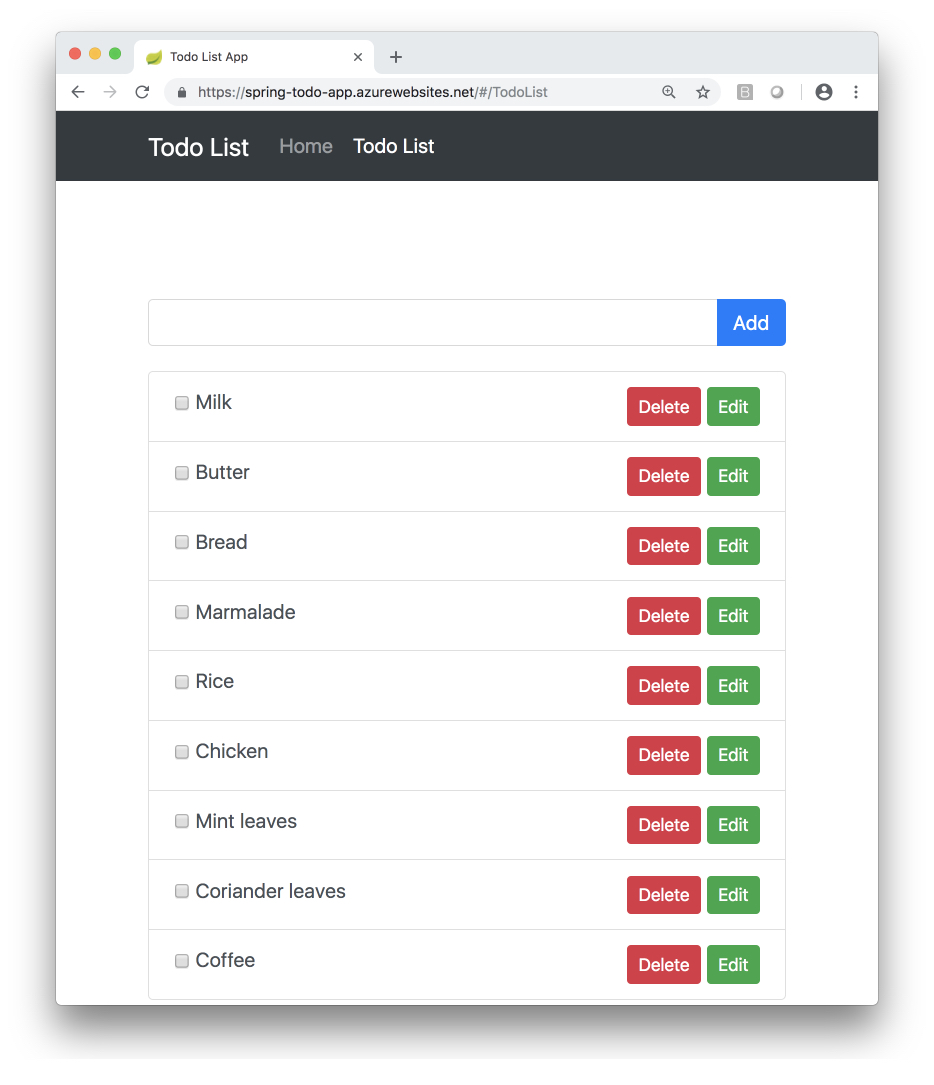
Stream diagnostic logs
To access the console logs generated from inside your application code in App Service, turn on diagnostics logging by running the following command in the Cloud Shell:
az webapp log config --resource-group <resource-group-name> --name <app-name> --docker-container-logging filesystem --level Verbose
Possible values for --level are: Error, Warning, Info, and Verbose. Each subsequent level includes the previous level. For example: Error includes only error messages, and Verbose includes all messages.
Once diagnostic logging is turned on, run the following command to see the log stream:
az webapp log tail --resource-group <resource-group-name> --name <app-name>
If you don't see console logs immediately, check again in 30 seconds.
Note
You can also inspect the log files from the browser at https://<app-name>.scm.azurewebsites.net/api/logs/docker.
To stop log streaming at any time, type Ctrl+C.
Scale out the TODO App
Scale out the application by adding another worker:
az appservice plan update --number-of-workers 2 \
--name ${WEBAPP_PLAN_NAME} \
--resource-group <your-azure-group-name>
Clean up resources
If you don't need these resources for another tutorial (see Next steps), you can delete them by running the following command in the Cloud Shell:
az group delete --name <your-azure-group-name> --yes
Next steps
Azure for Java Developers Spring Boot, Spring Data for Azure Cosmos DB, Azure Cosmos DB and App Service Linux.
Learn more about running Java apps on App Service on Linux in the developer guide.
Learn how to secure your app with a custom domain and certificate.
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for