Tutorial: Use the REST API to manage an Azure IoT Central application
This tutorial shows you how to use the Azure IoT Central REST API to create and interact with an IoT Central application. This tutorial uses the REST API to complete many of the steps you completed by using the Web UI in the quickstarts. These steps include using an app on your smartphone as an IoT device that connects to IoT Central.
In this tutorial, you learn how to:
- Authorize the REST API.
- Create an IoT Central application.
- Add a device to your application.
- Query and control the device.
- Set up data export.
- Delete an application.
Prerequisites
To complete the steps in this tutorial, you need:
An active Azure subscription. If you don't have an Azure subscription, create a free account before you begin.
An Android or iOS smartphone on which you're able to install a free app from one of the official app stores.
Azure CLI
You use the Azure CLI to generate the bearer tokens that some of the REST APIs use for authorization.
Use the Bash environment in Azure Cloud Shell. For more information, see Quickstart for Bash in Azure Cloud Shell.
If you prefer to run CLI reference commands locally, install the Azure CLI. If you're running on Windows or macOS, consider running Azure CLI in a Docker container. For more information, see How to run the Azure CLI in a Docker container.
If you're using a local installation, sign in to the Azure CLI by using the az login command. To finish the authentication process, follow the steps displayed in your terminal. For other sign-in options, see Sign in with the Azure CLI.
When you're prompted, install the Azure CLI extension on first use. For more information about extensions, see Use extensions with the Azure CLI.
Run az version to find the version and dependent libraries that are installed. To upgrade to the latest version, run az upgrade.
Postman
In this tutorial, you use Postman to make the REST API calls. If you prefer not to download and install Postman, you can use the online version. You can complete all the steps in the tutorial by using the free version of Postman.
The tutorial uses a predefined Postman collection that includes some scripts to help you complete the steps.
Import the Postman collection
To import the collection, open Postman and select Import. In the Import dialog, select Link and paste in the following URL, select Continue.
Your workspace now contains the IoT Central REST tutorial collection. This collection includes all the APIs you use in the tutorial.
The collection uses variables to parameterize the REST API calls. To see the variables, select the ... next to IoT Central REST tutorial and select Edit. Then select Variables. Many of the variables are either set automatically as you make the API calls or have preset values.
Authorize the REST API
Before you can use the REST API, you must configure the authorization. The REST API calls in this tutorial use one of three authorization types:
- A bearer token that authorizes access to
https://management.azure.com. You use this bearer token when you create and delete and IoT Central application. An IoT Central application is an Azure resource. - A bearer token that authorizes access to
https://apps.azureiotcentral.com. You use this bearer token to create the API tokens in the IoT Central application. - Administrator and operator API tokens that authorize access to capabilities in your IoT Central application. You use these tokens for most the API calls in this tutorial. These tokens only authorize access to one specific IoT Central application.
Assign values to the following variables in the Postman collection:
bearerToken: Run the following Azure CLI commands to generate a bearer token that authorizes access to
https://management.azure.com:az login az account get-access-token --resource https://management.azure.comTip
You may need to run
az logineven if you're using the Cloud Shell.Copy the
accessTokenvalue into the Current value column for bearerToken in the collection variables.bearerTokenApp: Run the following Azure CLI commands to generate a bearer token that authorizes access to
https://apps.azureiotcentral.com:az account get-access-token --resource https://apps.azureiotcentral.comTip
If you started a new instance of your shell, run
az loginagain.Copy the
accessTokenvalue into the Current value column for bearerTokenApp in the collection variables.subscriptionId: Your subscription ID was included in the output from the two previous commands. Copy the
subscriptionvalue into the Current value column for subscriptionId in the collection variables.
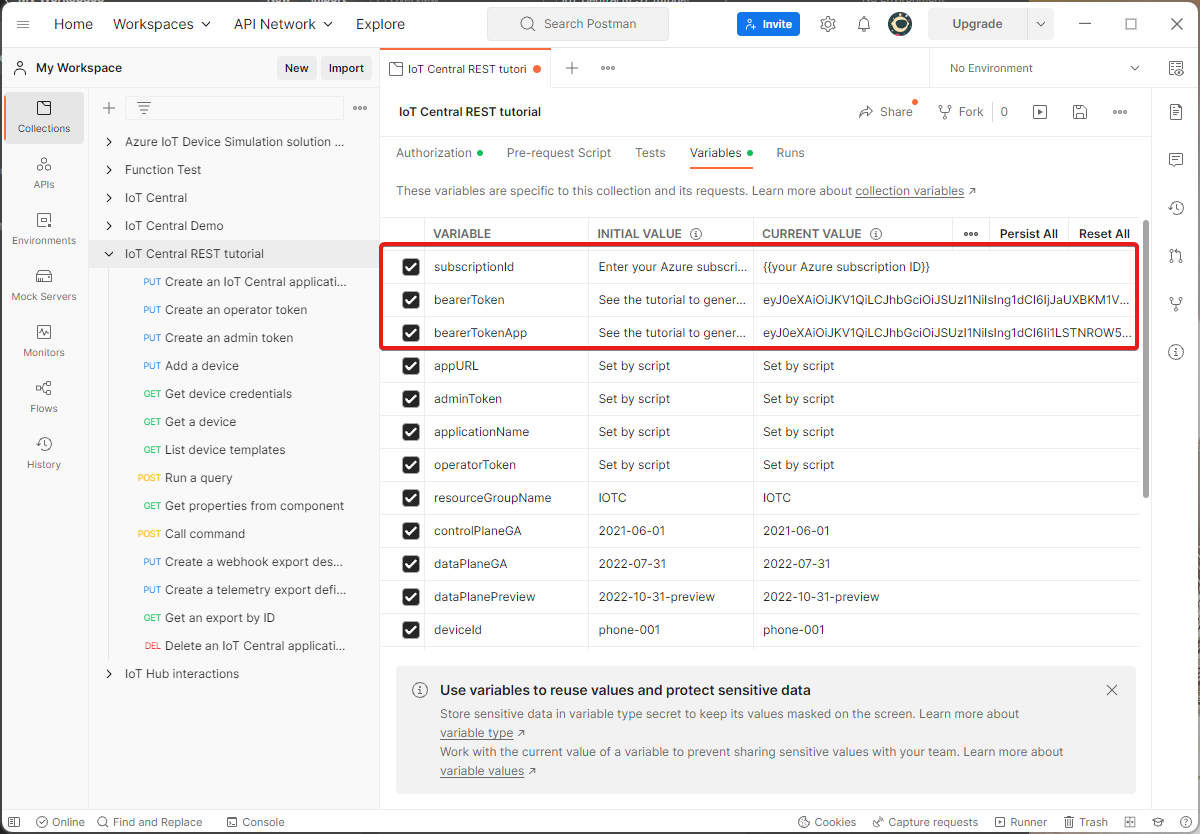
Be sure to save the changes to the Postman collection.
Note
Bearer tokens expire after an hour.
Create an application
Use the control plane requests to create and manage IoT central applications. Use the following PUT request to create the application that you use in this tutorial. The request uses a bearer token to authorize and generates a random application name.
- In Postman, open the IoT Central REST tutorial collection, and select the Create an IoT central application request.
- Select Send.
- Check the request succeeds. If it fails, verify that you entered the bearerToken and subscriptionId variable values in the Postman collection.
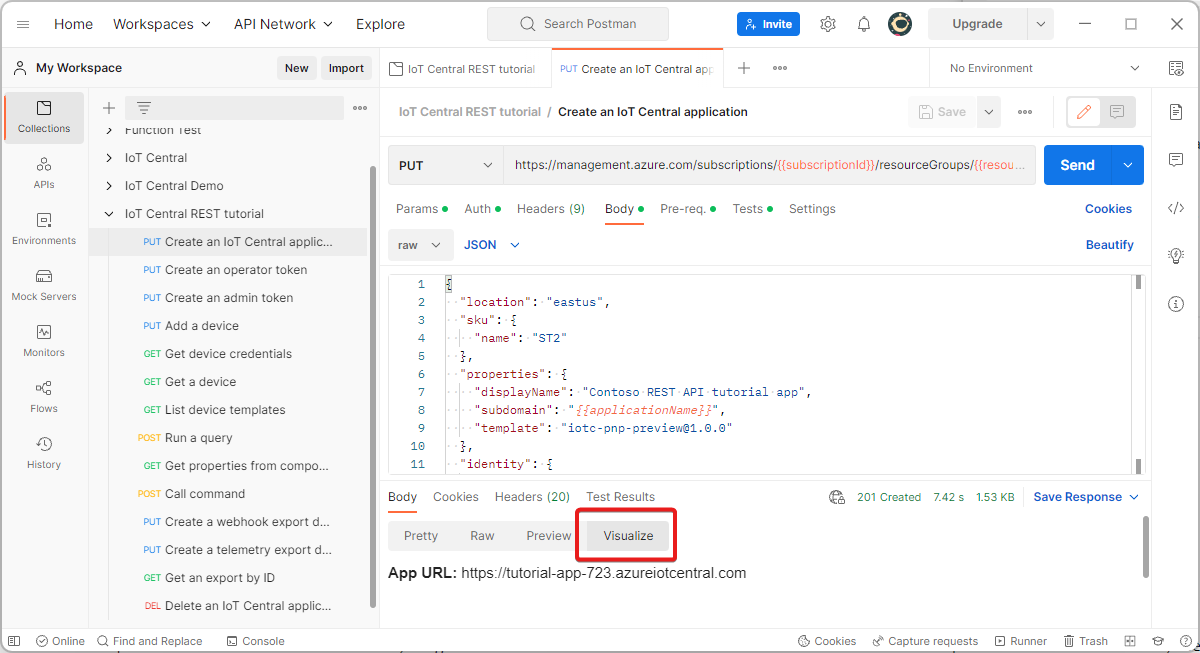
- Select Visualize to see the URL of your new IoT Central application. Make a note of this URL, you need it later in this tutorial.
Create the API tokens
Use the following data plane requests to create the application API tokens in your IoT Central application. Some of the requests in this tutorial require an API token with administrator permissions, but the majority can use operator permissions:
- In Postman, open the IoT Central REST tutorial collection, and select the Create an operator token request.
- Select Send.
- In Postman, open the IoT Central REST tutorial collection, and select the Create an admin token request.
- Select Send.
If you want to see these tokens in your IoT central application, open the application and navigate to Security > Permissions > API tokens.
Note
A script in Postman automatically adds these API tokens to the list of collection variables for you.
Register a device
You must register a device with IoT Central before it can connect. Use the following requests to register your device in your application and retrieve the device credentials. The first request creates a device with phone-001 as the device ID:
- In Postman, open the IoT Central REST tutorial collection, and select the Add a device request.
- Select Send. In the response, notice that the device isn't provisioned.
- In Postman, open the IoT Central REST tutorial collection, and select the Get device credentials request.
- Select Send.
- The Visualize tab shows the ID Scope and Primary key values that the device needs to able to connect.
Provision and connect a device
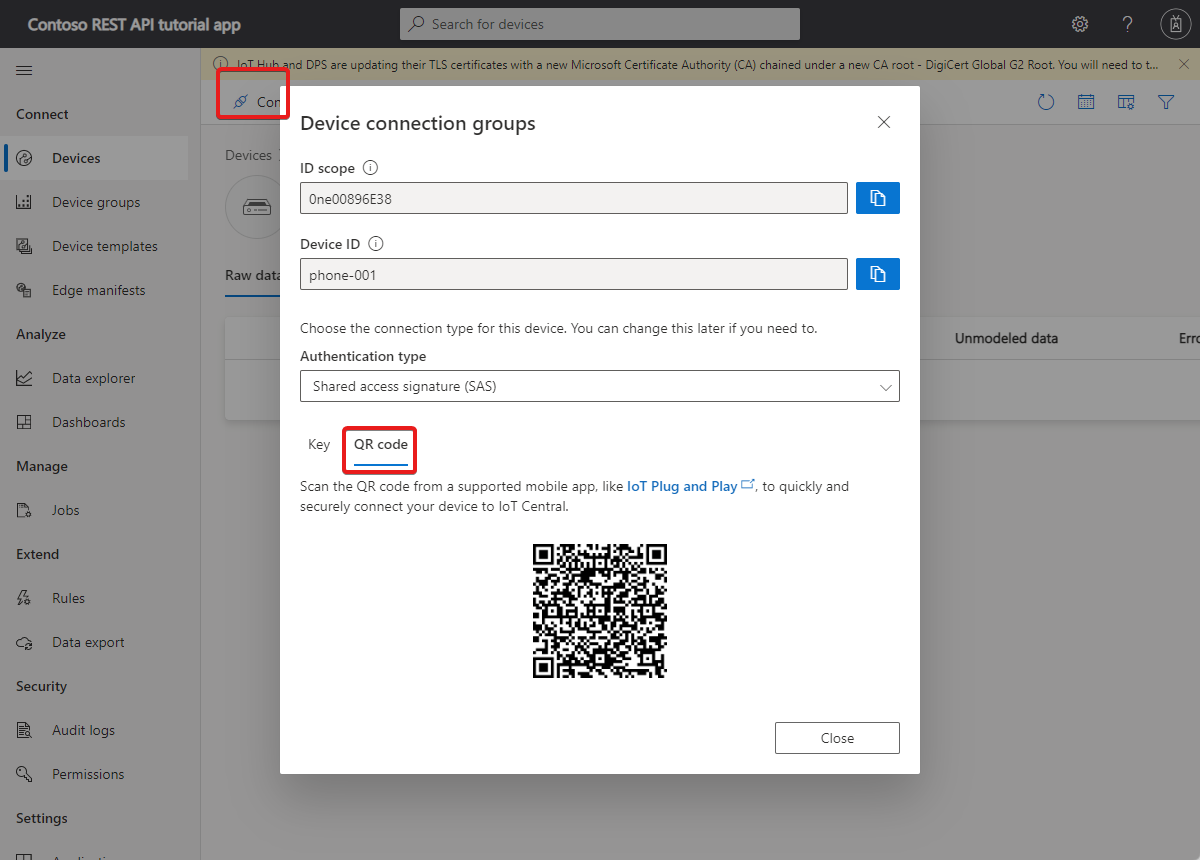
To avoid the need to enter the device credentials manually on your smartphone, you can use a QR code generated by IoT central. The QR code encodes the device ID, ID scope, primary key. To display the QR code:
- Open your IoT central application by using the application URL you made a note of previously.
- In your IoT Central application, navigate to Devices > My phone app > Connect > QR code. Keep this page open until the device is connected.
To simplify the setup, this article uses the IoT Plug and Play smartphone app as an IoT device. The app sends telemetry collected from the smartphone's sensors, responds to commands invoked from IoT Central, and reports property values to IoT Central.
Install the app on your smartphone from one of the app stores:
To connect the IoT Plug and Play app to your Iot Central application:
Open the IoT PnP app on your smartphone.
On the welcome page, select Scan QR code. Point the smartphone's camera at the QR code. Then wait for a few seconds while the connection is established.
On the telemetry page in the app, you can see the data the app is sending to IoT Central. On the logs page, you can see the device connecting and several initialization messages.
To verify the device is now provisioned, you can use the REST API:
- In Postman, open the IoT Central REST tutorial collection, and select the Get a device request.
- Select Send. In the response, notice that the device is now provisioned. IoT Central also assigned a device template to the device based on the model ID sent by the device.
You can use the REST API to manage device templates in the application. For example, to view the device templates in the application:
- In Postman, open the IoT Central REST tutorial collection, and select the List device templates request.
- Select Send.
Query and control the device
You can use the REST API to query telemetry from your devices. The following request returns the accelerometer data from all devices that share a specific device template ID:
- In Postman, open the IoT Central REST tutorial collection, and select the Run a query request.
- Select Send.
You can use the REST API to read and set device properties. The following request returns all the property values from the Device Info component that the device implements:
- In Postman, open the IoT Central REST tutorial collection, and select the Get properties from a component request.
- Select Send.
You can use the REST API to call device commands. The following request calls a command that switches on your smartphone light on twice for three seconds. For the command to run, your smartphone screen must be on with the IoT Plug and Play app visible:
- In Postman, open the IoT Central REST tutorial collection, and select the Call command request.
- Select Send.
Export telemetry
You can use the REST API to configure and manage your IoT Central application. The following steps show you how to configure data export to send telemetry values to a webhook. To simplify the setup, this article uses a RequestBin webhook as the destination. RequestBin is a non-Microsoft service.
To create your test endpoint for the data export destination:
- Navigate to RequestBin.
- Select Create a RequestBin.
- Sign in with one of the available methods.
- Copy the URL of your RequestBin endpoint.
- In Postman, open the IoT Central REST tutorial collection and navigate to the collection variables.
- Paste the URL of your RequestBin endpoint into the Current value column for webHookURL in the collection variables.
- Save the changes.
To configure the export destination in your IoT Central application by using the REST API:
- In Postman, open the IoT Central REST tutorial collection, and select the Create a webhook export destination request.
- Select Send.
To configure the export definition in your IoT Central application by using the REST API:
- In Postman, open the IoT Central REST tutorial collection, and select the Create a telemetry export definition request.
- Select Send. Notice that the status is Not started.
It might take a couple of minutes for the export to start. To check the status of the export by using the REST API:
- In Postman, open the IoT Central REST tutorial collection, and select the Get an export by ID request.
- Select Send. When the status is healthy, IoT Central is sending telemetry to your webhook.
The app on your smartphone doesn't send telemetry unless the screen is on and the IoT Plug and Play app is visible.
When your smartphone app is sending telemetry, navigate to your RequestBin to view the exported telemetry.
Clean up resources
If you've finished with the IoT Central application you used in this tutorial, you can use the REST API to delete it:
- In Postman, open the IoT Central REST tutorial collection, and select the Delete an IoT central application request.
- Select Send.
Tip
This request uses a bearer token that you generated at the start of the tutorial. Bearer tokens expire after hour. You may need to generate a new bearer token that authorizes access to https://apps.azureiotcentral.com.
Next steps
If you'd prefer to continue through the set of IoT Central tutorials and learn more about building an IoT Central solution, see:
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for


