Translator v3.0
What's new?
Version 3.0 of the Translator provides a modern JSON-based Web API. It improves usability and performance by consolidating existing features into fewer operations and it provides new features.
- Transliteration to convert text in one language from one script to another script.
- Translation to multiple languages in one request.
- Language detection, translation, and transliteration in one request.
- Dictionary to look up alternative translations of a term, to find back-translations and examples showing terms used in context.
- More informative language detection results.
Base URLs
Requests to Translator are, in most cases, handled by the datacenter that is closest to where the request originated. If there's a datacenter failure when using the global endpoint, the request may be routed outside of the geography.
To force the request to be handled within a specific geography, use the desired geographical endpoint. All requests are processed among the datacenters within the geography.
✔️ Feature: Translator Text
| Service endpoint | Request processing data center |
|---|---|
Global (recommended):api.cognitive.microsofttranslator.com |
Closest available data center. |
Americas:api-nam.cognitive.microsofttranslator.com |
East US 2 • West US 2 |
Asia Pacific:api-apc.cognitive.microsofttranslator.com |
Japan East • Southeast Asia |
Europe (except Switzerland):api-eur.cognitive.microsofttranslator.com |
France Central • West Europe |
| Switzerland: For more information, see Switzerland service endpoints. |
Switzerland North • Switzerland West |
Switzerland service endpoints
Customers with a resource located in Switzerland North or Switzerland West can ensure that their Text API requests are served within Switzerland. To ensure that requests are handled in Switzerland, create the Translator resource in the Resource region Switzerland North or Switzerland West, then use the resource's custom endpoint in your API requests.
For example: If you create a Translator resource in Azure portal with Resource region as Switzerland North and your resource name is my-swiss-n, then your custom endpoint is https​://my-swiss-n.cognitiveservices.azure.com. And a sample request to translate is:
// Pass secret key and region using headers to a custom endpoint
curl -X POST "https://my-swiss-n.cognitiveservices.azure.com/translator/text/v3.0/translate?to=fr" \
-H "Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key: xxx" \
-H "Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Region: switzerlandnorth" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d "[{'Text':'Hello'}]" -v
Custom Translator isn't currently available in Switzerland.
Authentication
Subscribe to Translator or multi-service in Azure AI services, and use your key (available in the Azure portal) to authenticate.
There are three headers that you can use to authenticate your subscription. This table describes how each is used:
| Headers | Description |
|---|---|
| Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key | Use with Azure AI services subscription if you're passing your secret key. The value is the Azure secret key for your subscription to Translator. |
| Authorization | Use with Azure AI services subscription if you're passing an authentication token. The value is the Bearer token: Bearer <token>. |
| Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Region | Use with multi-service and regional translator resource. The value is the region of the multi-service or regional translator resource. This value is optional when using a global translator resource. |
Secret key
The first option is to authenticate using the Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key header. Add the Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key: <YOUR_SECRET_KEY> header to your request.
Authenticating with a global resource
When you use a global translator resource, you need to include one header to call the Translator.
| Headers | Description |
|---|---|
| Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key | The value is the Azure secret key for your subscription to Translator. |
Here's an example request to call the Translator using the global translator resource
// Pass secret key using headers
curl -X POST "https://api.cognitive.microsofttranslator.com/translate?api-version=3.0&to=es" \
-H "Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key:<your-key>" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d "[{'Text':'Hello, what is your name?'}]"
Authenticating with a regional resource
When you use a regional translator resource, there are two headers that you need to call the Translator.
| Headers | Description |
|---|---|
| Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key | The value is the Azure secret key for your subscription to Translator. |
| Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Region | The value is the region of the translator resource. |
Here's an example request to call the Translator using the regional translator resource
// Pass secret key and region using headers
curl -X POST "https://api.cognitive.microsofttranslator.com/translate?api-version=3.0&to=es" \
-H "Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key:<your-key>" \
-H "Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Region:<your-region>" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d "[{'Text':'Hello, what is your name?'}]"
Authenticating with a Multi-service resource
A multi-service resource allows you to use a single API key to authenticate requests for multiple services.
When you use a multi-service secret key, you must include two authentication headers with your request. There are two headers that you need to call the Translator.
| Headers | Description |
|---|---|
| Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key | The value is the Azure secret key for your multi-service resource. |
| Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Region | The value is the region of the multi-service resource. |
Region is required for the multi-service Text API subscription. The region you select is the only region that you can use for text translation when using the multi-service key. It must be the same region you selected when you signed up for your multi-service subscription through the Azure portal.
If you pass the secret key in the query string with the parameter Subscription-Key, then you must specify the region with query parameter Subscription-Region.
Authenticating with an access token
Alternatively, you can exchange your secret key for an access token. This token is included with each request as the Authorization header. To obtain an authorization token, make a POST request to the following URL:
| Resource type | Authentication service URL |
|---|---|
| Global | https://api.cognitive.microsoft.com/sts/v1.0/issueToken |
| Regional or Multi-Service | https://<your-region>.api.cognitive.microsoft.com/sts/v1.0/issueToken |
Here are example requests to obtain a token given a secret key for a global resource:
// Pass secret key using header
curl --header 'Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key: <your-key>' --data "" 'https://api.cognitive.microsoft.com/sts/v1.0/issueToken'
// Pass secret key using query string parameter
curl --data "" 'https://api.cognitive.microsoft.com/sts/v1.0/issueToken?Subscription-Key=<your-key>'
And here are example requests to obtain a token given a secret key for a regional resource located in Central US:
// Pass secret key using header
curl --header "Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key: <your-key>" --data "" "https://centralus.api.cognitive.microsoft.com/sts/v1.0/issueToken"
// Pass secret key using query string parameter
curl --data "" "https://centralus.api.cognitive.microsoft.com/sts/v1.0/issueToken?Subscription-Key=<your-key>"
A successful request returns the encoded access token as plain text in the response body. The valid token is passed to the Translator service as a bearer token in the Authorization.
Authorization: Bearer <Base64-access_token>
An authentication token is valid for 10 minutes. The token should be reused when making multiple calls to the Translator. However, if your program makes requests to the Translator over an extended period of time, then your program must request a new access token at regular intervals (for example, every 8 minutes).
Authentication with Microsoft Entra ID
Translator v3.0 supports Microsoft Entra authentication, Microsoft's cloud-based identity and access management solution. Authorization headers enable the Translator service to validate that the requesting client is authorized to use the resource and to complete the request.
Prerequisites
A brief understanding of how to authenticate with Microsoft Entra ID.
A brief understanding of how to authorize access to managed identities.
Headers
| Header | Value |
|---|---|
| Authorization | The value is an access bearer token generated by Azure AD.
|
| Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Region | The value is the region of the translator resource.
|
| Ocp-Apim-ResourceId | The value is the Resource ID for your Translator resource instance.
|
Translator property page—Azure portal
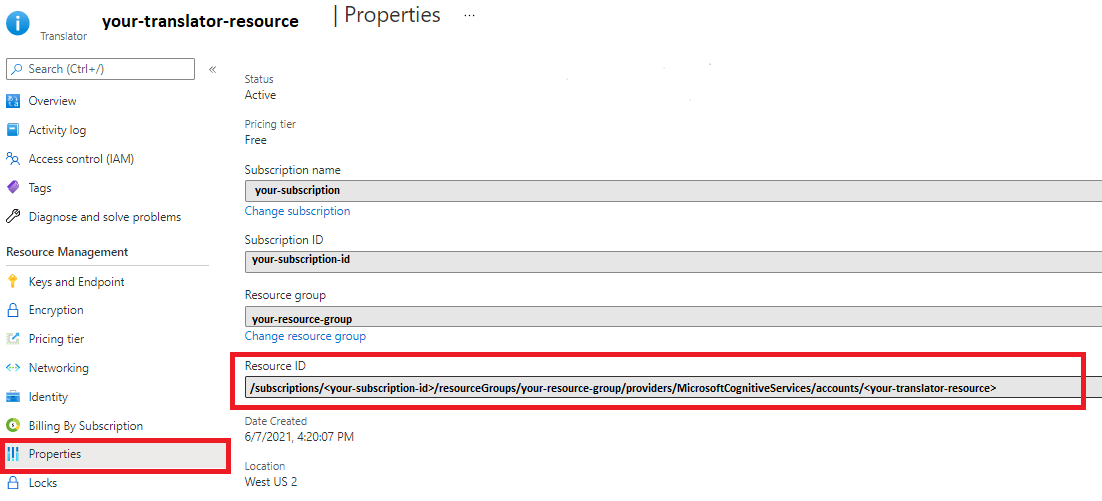
Examples
Using the global endpoint
// Using headers, pass a bearer token generated by Azure AD, resource ID, and the region.
curl -X POST "https://api.cognitive.microsofttranslator.com/translate?api-version=3.0&to=es" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer <Base64-access_token>"\
-H "Ocp-Apim-ResourceId: <Resource ID>" \
-H "Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Region: <your-region>" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-data-raw "[{'Text':'Hello, friend.'}]"
Using your custom endpoint
// Using headers, pass a bearer token generated by Azure AD.
curl -X POST https://<your-custom-domain>.cognitiveservices.azure.com/translator/text/v3.0/translate?api-version=3.0&to=es \
-H "Authorization: Bearer <Base64-access_token>"\
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-data-raw "[{'Text':'Hello, friend.'}]"
Examples using managed identities
Translator v3.0 also supports authorizing access to managed identities. If a managed identity is enabled for a translator resource, you can pass the bearer token generated by managed identity in the request header.
With the global endpoint
// Using headers, pass a bearer token generated either by Azure AD or Managed Identities, resource ID, and the region.
curl -X POST https://api.cognitive.microsofttranslator.com/translate?api-version=3.0&to=es \
-H "Authorization: Bearer <Base64-access_token>"\
-H "Ocp-Apim-ResourceId: <Resource ID>" \
-H "Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Region: <your-region>" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-data-raw "[{'Text':'Hello, friend.'}]"
With your custom endpoint
//Using headers, pass a bearer token generated by Managed Identities.
curl -X POST https://<your-custom-domain>.cognitiveservices.azure.com/translator/text/v3.0/translate?api-version=3.0&to=es \
-H "Authorization: Bearer <Base64-access_token>"\
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-data-raw "[{'Text':'Hello, friend.'}]"
Virtual Network support
The Translator service is now available with Virtual Network (VNET) capabilities in all regions of the Azure public cloud. To enable Virtual Network, See Configuring Azure AI services virtual networks.
Once you turn on this capability, you must use the custom endpoint to call the Translator. You can't use the global translator endpoint ("api.cognitive.microsofttranslator.com") and you can't authenticate with an access token.
You can find the custom endpoint after you create a translator resource and allow access from selected networks and private endpoints.
Navigate to your Translator resource in the Azure portal.
Select Networking from the Resource Management section.
Under the Firewalls and virtual networks tab, choose Selected Networks and Private Endpoints.
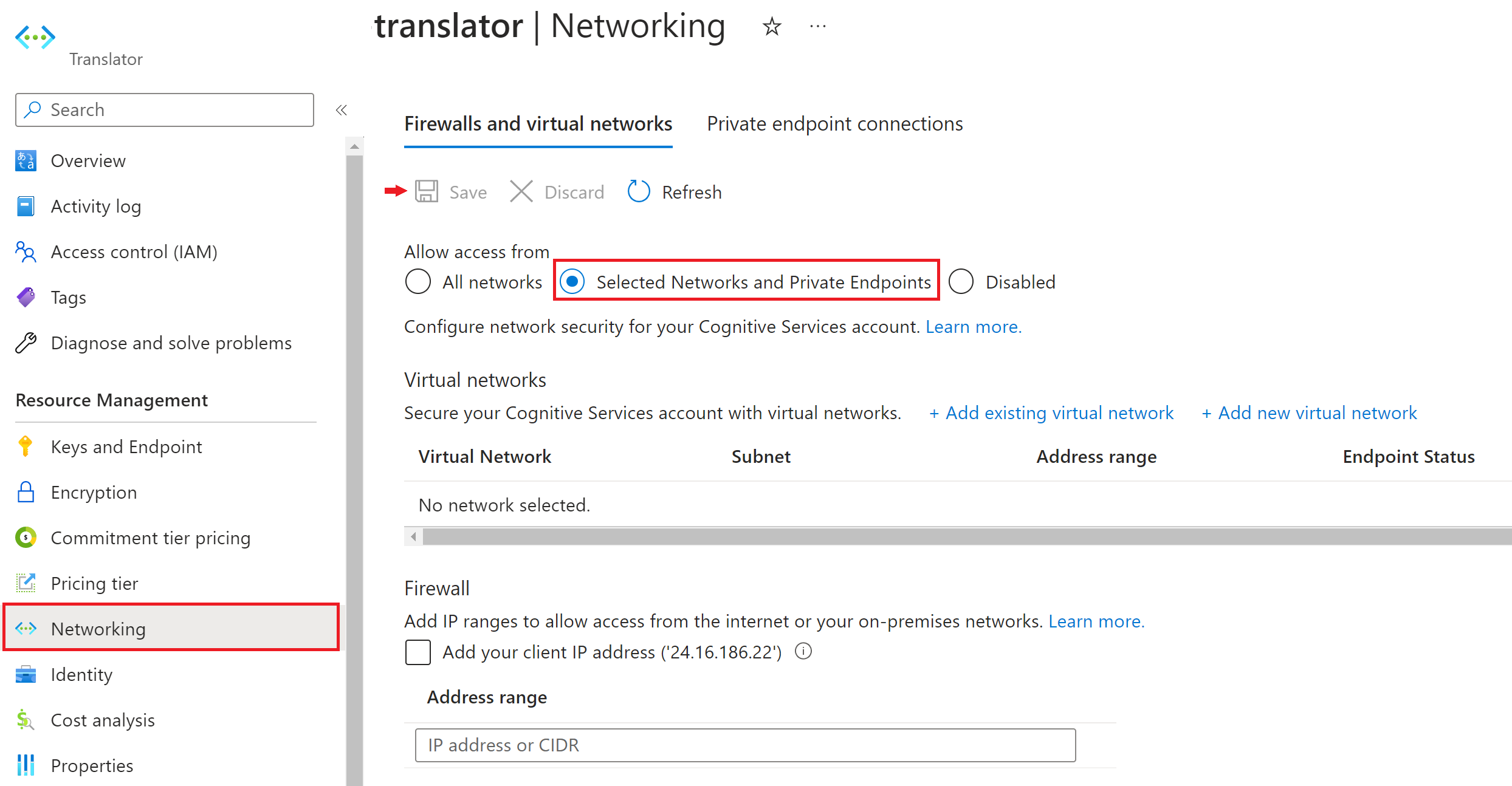
Select Save to apply your changes.
Select Keys and Endpoint from the Resource Management section.
Select the Virtual Network tab.
Listed there are the endpoints for Text Translation and Document Translation.
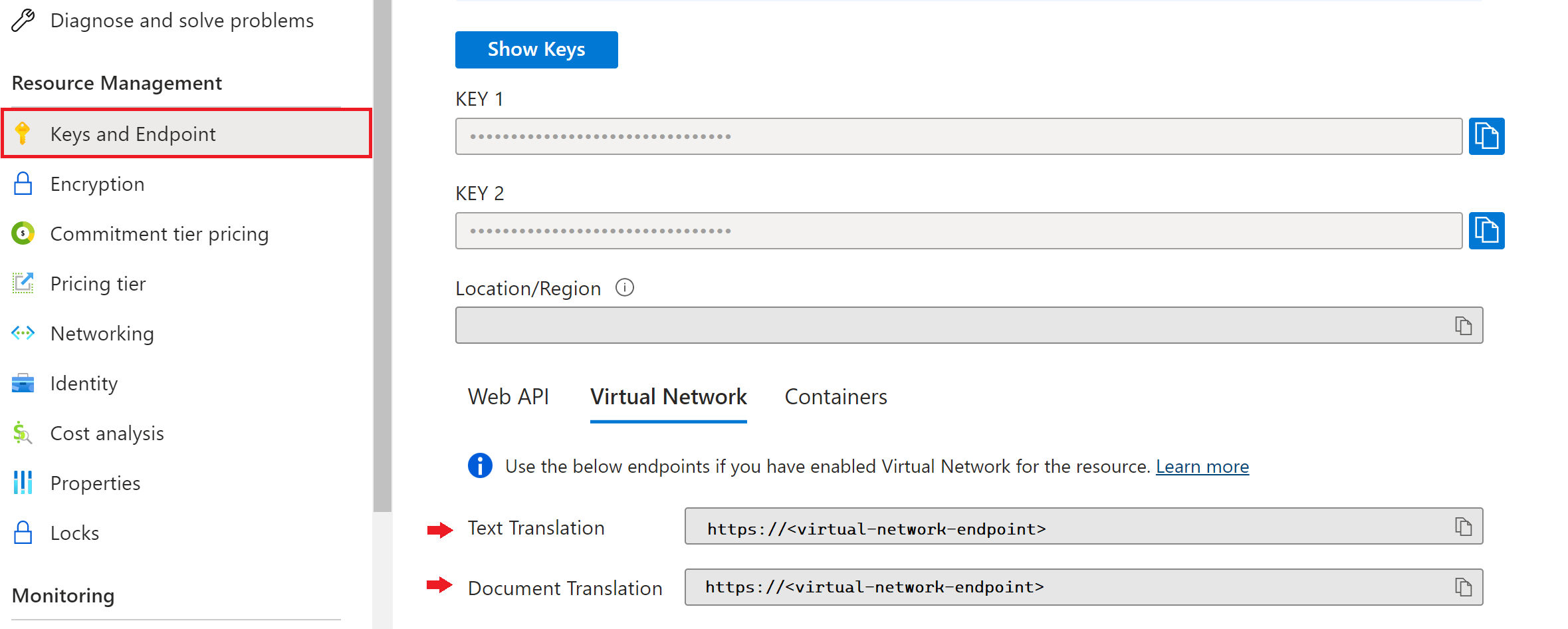
| Headers | Description |
|---|---|
| Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key | The value is the Azure secret key for your subscription to Translator. |
| Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Region | The value is the region of the translator resource. This value is optional if the resource is global |
Here's an example request to call the Translator using the custom endpoint
// Pass secret key and region using headers
curl -X POST "https://<your-custom-domain>.cognitiveservices.azure.com/translator/text/v3.0/translate?api-version=3.0&to=es" \
-H "Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key:<your-key>" \
-H "Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Region:<your-region>" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d "[{'Text':'Hello, what is your name?'}]"
Errors
A standard error response is a JSON object with name/value pair named error. The value is also a JSON object with properties:
code: A server-defined error code.message: A string giving a human-readable representation of the error.
For example, a customer with a free trial subscription would receive the following error once the free quota is exhausted:
{
"error": {
"code":403001,
"message":"The operation isn't allowed because the subscription has exceeded its free quota."
}
}
The error code is a 6-digit number combining the 3-digit HTTP status code followed by a 3-digit number to further categorize the error. Common error codes are:
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
| 400000 | One of the request inputs isn't valid. |
| 400001 | The "scope" parameter is invalid. |
| 400002 | The "category" parameter is invalid. |
| 400003 | A language specifier is missing or invalid. |
| 400004 | A target script specifier ("To script") is missing or invalid. |
| 400005 | An input text is missing or invalid. |
| 400006 | The combination of language and script isn't valid. |
| 400018 | A source script specifier ("From script") is missing or invalid. |
| 400019 | One of the specified languages isn't supported. |
| 400020 | One of the elements in the array of input text isn't valid. |
| 400021 | The API version parameter is missing or invalid. |
| 400023 | One of the specified language pair isn't valid. |
| 400035 | The source language ("From" field) isn't valid. |
| 400036 | The target language ("To" field) is missing or invalid. |
| 400042 | One of the options specified ("Options" field) isn't valid. |
| 400043 | The client trace ID (ClientTraceId field or X-ClientTranceId header) is missing or invalid. |
| 400050 | The input text is too long. View request limits. |
| 400064 | The "translation" parameter is missing or invalid. |
| 400070 | The number of target scripts (ToScript parameter) doesn't match the number of target languages (To parameter). |
| 400071 | The value isn't valid for TextType. |
| 400072 | The array of input text has too many elements. |
| 400073 | The script parameter isn't valid. |
| 400074 | The body of the request isn't valid JSON. |
| 400075 | The language pair and category combination isn't valid. |
| 400077 | The maximum request size has been exceeded. View request limits. |
| 400079 | The custom system requested for translation between from and to language doesn't exist. |
| 400080 | Transliteration isn't supported for the language or script. |
| 401000 | The request isn't authorized because credentials are missing or invalid. |
| 401015 | "The credentials provided are for the Speech API. This request requires credentials for the Text API. Use a subscription to Translator." |
| 403000 | The operation isn't allowed. |
| 403001 | The operation isn't allowed because the subscription has exceeded its free quota. |
| 405000 | The request method isn't supported for the requested resource. |
| 408001 | The translation system requested is being prepared. Retry in a few minutes. |
| 408002 | Request timed out waiting on incoming stream. The client didn't produce a request within the time that the server was prepared to wait. The client may repeat the request without modifications at any later time. |
| 415000 | The Content-Type header is missing or invalid. |
| 429000, 429001, 429002 | The server rejected the request because the client has exceeded request limits. |
| 500000 | An unexpected error occurred. If the error persists, report it with date/time of error, request identifier from response header X-RequestId, and client identifier from request header X-ClientTraceId. |
| 503000 | Service is temporarily unavailable. Retry. If the error persists, report it with date/time of error, request identifier from response header X-RequestId, and client identifier from request header X-ClientTraceId. |
Metrics
Metrics allow you to view the translator usage and availability information in Azure portal, under metrics section as shown in the below screenshot. For more information, see Data and platform metrics.
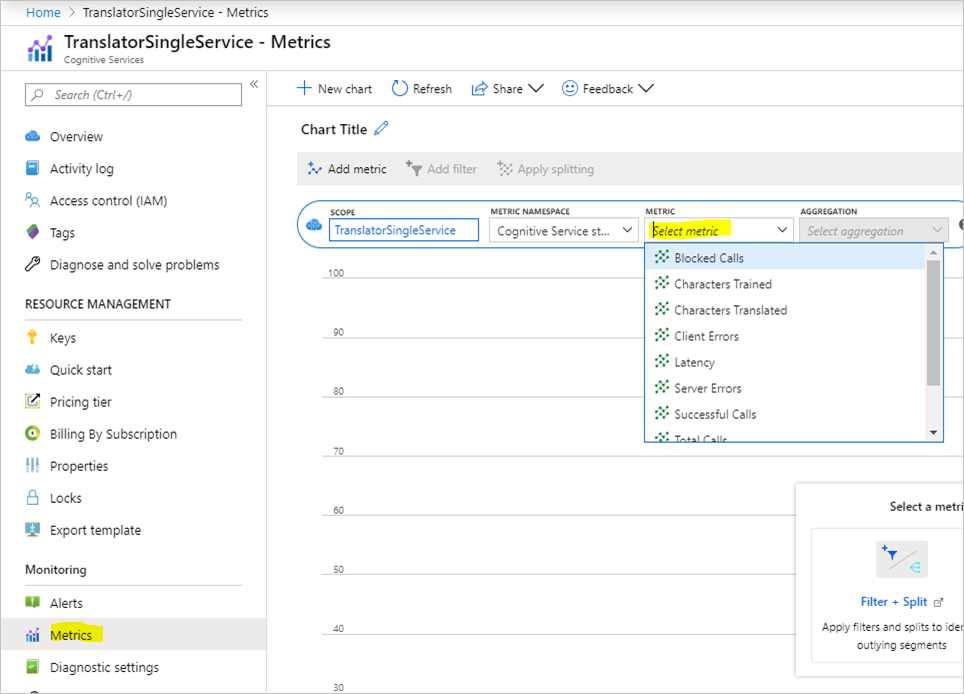
This table lists available metrics with description of how they're used to monitor translation API calls.
| Metrics | Description |
|---|---|
| TotalCalls | Total number of API calls. |
| TotalTokenCalls | Total number of API calls via token service using authentication token. |
| SuccessfulCalls | Number of successful calls. |
| TotalErrors | Number of calls with error response. |
| BlockedCalls | Number of calls that exceeded rate or quota limit. |
| ServerErrors | Number of calls with server internal error(5XX). |
| ClientErrors | Number of calls with client-side error(4XX). |
| Latency | Duration to complete request in milliseconds. |
| CharactersTranslated | Total number of characters in incoming text request. |
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for