Tutorial: Get started with Windows Forms Designer
The Windows Forms Designer provides many tools for building Windows Forms applications. This article illustrates how to build an app by using the various tools provided by the designer, including the following tasks:
- Arrange controls by using snaplines.
- Accomplish designer tasks by using smart tags.
- Set margins and padding for controls.
- Arrange controls by using a TableLayoutPanel control.
- Partition your control’s layout by using a SplitContainer control.
- Navigate your layout with the Document Outline window.
- Position controls with the size and location information display.
- Set property values by using the Properties window.
When you're finished, you'll have a custom control that's been assembled by using many of the layout features available in the Windows Forms Designer. This control implements the user interface (UI) for a simple calculator. The following image shows the general layout of the calculator control:
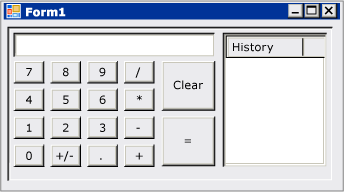
Tip
If you're a C++ developer and are looking for a tutorial to help you create a Windows app that includes forms and controls, see Creating a forms-based MFC application. For more generalized info, see Overview of Windows programming in C++.
Create the custom control project
The first step is to create the DemoCalculator control project.
Open Visual Studio and create a new Windows Forms Control Library project by using the .NET Framework template for either C# or Visual Basic. Name the project DemoCalculatorLib.
To rename the file, in Solution Explorer, right-click UserControl1.vb or UserControl1.cs, select Rename, and change the file name to DemoCalculator.vb or DemoCalculator.cs. Select Yes when you're asked if you want to rename all references to the code element "UserControl1".
The Windows Forms Designer shows the designer surface for the DemoCalculator control. In this view, you can graphically design the appearance of the control by selecting controls and components from Toolbox and placing them on the designer surface. For more information about custom controls, see Varieties of custom controls.
Design the control layout
The DemoCalculator control contains several Windows Forms controls. In this procedure, you'll arrange the controls by using the Windows Forms Designer.
In the Windows Forms Designer, change the DemoCalculator control to a larger size by selecting the sizing handle in the lower-right corner and dragging it down and to the right. In the lower-right corner of Visual Studio, find the size and location information for controls. Set the size of the control to width 500 and height 400 by watching the size information as you resize the control.
In Toolbox, select the Containers node to open it. Select the SplitContainer control and drag it onto the designer surface.
The
SplitContaineris placed on the DemoCalculator control's designer surface.Tip
The
SplitContainercontrol sizes itself to the fit the size of the DemoCalculator control. Look at the Properties window to see the property settings for theSplitContainercontrol. Find the Dock property. Its value is DockStyle.Fill, which means theSplitContainercontrol will always size itself to the boundaries of the DemoCalculator control. Resize the DemoCalculator control to verify this behavior.In the Properties window, change the value of the Dock property to
None.The
SplitContainercontrol shrinks to its default size and no longer follows the size of the DemoCalculator control.Select the smart tag glyph (
 ) on the upper-right corner of the
) on the upper-right corner of the SplitContainercontrol. Select Dock in Parent Container to set theDockproperty toFill.The
SplitContainercontrol docks to the DemoCalculator control's boundaries.Note
Several controls offer smart tags to facilitate design. For more information, see Walkthrough: Perform common tasks by using Smart Tags on Windows Forms controls.
Select the vertical border between the panels and drag it to the right, so that the left panel takes most of the space.
The
SplitContainerdivides the DemoCalculator control into two panels with a movable border separating them. The panel on the left holds the calculator buttons and display, and the panel on the right shows a record of the arithmetic operations performed by the user.In the Properties window, change the value of the
BorderStyleproperty toFixed3D.In Toolbox, select the Common Controls node to open it. Select the
ListViewcontrol and drag it into the right panel of theSplitContainercontrol.Select the
ListViewcontrol's smart tag glyph. In the smart tag panel, change theViewsetting toDetails.In the smart tag panel, select Edit Columns.
The ColumnHeader Collection Editor dialog box opens.
In the ColumnHeader Collection Editor dialog box, select Add to add a column to the
ListViewcontrol. Change the value of the column'sTextproperty to History. Select OK to create the column.In the smart tag panel, select Dock in Parent Container, and then select the smart tag glyph to close the smart tag panel.
From the Containers node Toolbox, drag a
TableLayoutPanelcontrol into the left panel of theSplitContainercontrol.The
TableLayoutPanelcontrol appears on the designer surface with its smart tag panel open. TheTableLayoutPanelcontrol arranges its child controls in a grid. TheTableLayoutPanelcontrol holds the DemoCalculator control's display and buttons. For more information, see Walkthrough: Arrange controls by using a TableLayoutPanel.Select Edit Rows and Columns on the smart tag panel.
The Column and Row Styles dialog box opens.
Select the Add button until five columns are displayed. Select all five columns, and then select Percent in the Size Type box. Set the Percent value to 20. This action sets each column to the same width.
Under Show, select Rows.
Select Add until five rows are displayed. Select all five rows, and the select Percent in the Size Type box. Set the Percent value to 20. This action sets each row to the same height.
Select OK to accept your changes, and then select the smart tag glyph to close the smart tag panel.
In the Properties window, change the value of the
Dockproperty toFill.
Populate the control
Now that the layout of the control is set up, you can populate the DemoCalculator control with buttons and a display.
In Toolbox, select the
TextBoxcontrol icon.A
TextBoxcontrol is placed in the first cell of theTableLayoutPanelcontrol.In the Properties window, change the value of the
TextBoxcontrol's ColumnSpan property to 5.The
TextBoxcontrol moves to a position that is centered in its row.Change the value of the
TextBoxcontrol'sAnchorproperty toLeft,Right.The
TextBoxcontrol expands horizontally to span all five columns.Change the value of the
TextBoxcontrol'sTextAlignproperty toRight.In the Properties window, expand the
Fontproperty node. SetSizeto 14, and setBoldto true for theTextBoxcontrol.Select the
TableLayoutPanelcontrol.In Toolbox, select the
Buttonicon.A
Buttoncontrol is placed in the next open cell of theTableLayoutPanelcontrol.In Toolbox, select the
Buttonicon four more times to populate the second row of theTableLayoutPanelcontrol.Select all five
Buttoncontrols by selecting them while holding down the Shift key. Press Ctrl+C to copy theButtoncontrols to the clipboard.Press Ctrl+V three times to paste copies of the
Buttoncontrols into the remaining rows of theTableLayoutPanelcontrol.Select all 20
Buttoncontrols by selecting them while holding down the Shift key.In the Properties window, change the value of the
Dockproperty toFill.All the
Buttoncontrols dock to fill their containing cells.In the Properties window, expand the
Marginproperty node. Set the value ofAllto 5.All the
Buttoncontrols are sized smaller to create a larger margin between them.Select button10 and button20, and then press Delete to remove them from the layout.
Select button5 and button15, and then change the value of their
RowSpanproperty to 2. These buttons represent the Clear and = buttons for the DemoCalculator control.
Use the Document Outline window
When your control or form is populated with several controls, you may find it easier to navigate your layout with the Document Outline window.
On the menu bar, choose View > Other Windows > Document Outline.
The Document Outline window shows a tree view of the DemoCalculator control and its constituent controls. Container controls like the
SplitContainershow their child controls as subnodes in the tree. You can also rename controls in place by using the Document Outline window.In the Document Outline window, right-click button1, and then select Rename. Change its name to sevenButton.
Using the Document Outline window, rename the
Buttoncontrols from the designer-generated name to the production name according to the following list:button1 to sevenButton
button2 to eightButton
button3 to nineButton
button4 to divisionButton
button5 to clearButton
button6 to fourButton
button7 to fiveButton
button8 to sixButton
button9 to multiplicationButton
button11 to oneButton
button12 to twoButton
button13 to threeButton
button14 to subtractionButton
button15 to equalsButton
button16 to zeroButton
button17 to changeSignButton
button18 to decimalButton
button19 to additionButton
Using the Document Outline and Properties windows, change the
Textproperty value for eachButtoncontrol name according to the following list:Change the sevenButton control text property to 7
Change the eightButton control text property to 8
Change the nineButton control text property to 9
Change the divisionButton control text property to / (forward slash)
Change the clearButton control text property to Clear
Change the fourButton control text property to 4
Change the fiveButton control text property to 5
Change the sixButton control text property to 6
Change the multiplicationButton control text property to * (asterisk)
Change the oneButton control text property to 1
Change the twoButton control text property to 2
Change the threeButton control text property to 3
Change the subtractionButton control text property to - (hyphen)
Change the equalsButton control text property to = (equals sign)
Change the zeroButton control text property to 0
Change the changeSignButton control text property to +/-
Change the decimalButton control text property to . (period)
Change the additionButton control text property to + (plus sign)
On the designer surface, select all the
Buttoncontrols by selecting them while holding down the Shift key.In the Properties window, expand the
Fontproperty node. SetSizeto 14, and setBoldto true for all theButtoncontrols.
This set of instructions completes the design of the DemoCalculator control. All that remains is to provide the calculator logic.
Implement event handlers
The buttons on the DemoCalculator control have event handlers that can be used to implement much of the calculator logic. The Windows Forms Designer enables you to implement the stubs of all the event handlers for all the buttons with one selection.
On the designer surface, select all the
Buttoncontrols by selecting them while holding down the Shift key.Select one of the
Buttoncontrols.The Code Editor opens to the event handlers generated by the designer.
Test the control
Because the DemoCalculator control inherits from the UserControl class, you can test its behavior with the UserControl Test Container. For more information, see How to: Test the run-time behavior of a UserControl.
Press F5 to build and run the DemoCalculator control in the UserControl Test Container.
Select the border between the
SplitContainerpanels and drag it left and right. TheTableLayoutPaneland all its child controls resize themselves to fit in the available space.When you're finished testing the control, select Close.
Use the control on a form
The DemoCalculator control can be used in other composite controls or on a form. The following procedure describes how to use it.
Create the project
The first step is to create the application project. You'll use this project to build the application that shows your custom control.
Create a new Windows Forms Application project and name it DemoCalculatorTest.
In Solution Explorer, right-click the DemoCalculatorTest project, and then select Add > Project Reference to open the Reference Manager dialog box.
Go to the Projects tab, and then select the DemoCalculatorLib project to add the reference to the test project.
In Solution Explorer, right-click DemoCalculatorTest, and then select Set as StartUp Project.
In the Windows Forms Designer, increase the size of the form to about 700 x 500.
Use the control in the form's layout
To use the DemoCalculator control in an application, you need to place it on a form.
In Toolbox, expand the DemoCalculatorLib Components node.
Drag the DemoCalculator control from Toolbox onto your form. Move the control to the upper-left corner of the form. When the control is close to the form's borders, snaplines appears. Snaplines indicate the distance of the form's
Paddingproperty and the control'sMarginproperty. Position the control at the location indicated by the snaplines.For more information, see Walkthrough: Arrange controls by using snaplines.
Drag a
Buttoncontrol from Toolbox and drop it onto the form.Move the
Buttoncontrol around the DemoCalculator control and observe where the snaplines appear. You can align your controls precisely and easily by using this feature. Delete theButtoncontrol when you're finished.Right-click the DemoCalculator control, and then select Properties.
Change the value of the
Dockproperty toFill.Select the form, and then expand the
Paddingproperty node. Change the value of All to 20.The size of the DemoCalculator control is reduced to accommodate the new
Paddingvalue of the form.Resize the form by dragging the various sizing handles to different positions. Observe how the DemoCalculator control is resized to fit.
Next steps
This article has demonstrated how to construct the user interface for a simple calculator. To continue, you can extend its functionality by implementing the calculator logic, then publish the app by using ClickOnce. Or, continue on to a different tutorial where you create a picture viewer by using Windows Forms.
See also
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for