Why choose Microsoft Dataverse?
Data is at the center of everything a business does today and powers the insights that can drive what it should do tomorrow. To thrive and grow, businesses need to capture, analyze, predict, present, and report data and do it all with a high level of agility.
Building out the data infrastructure to enable business insight can be both time consuming and expensive. The data originates from a variety of devices, applications, systems, services, and software as a service (SaaS). This large and growing number of sources often consists of multiple data technologies that store different types of data, expose different APIs, and use a mixture of security models. The developers needed to create these technologies can be expensive and hard to find. Developers often must have a deep understanding of how to deploy, configure, manage, and integrate these different data technologies.
Dataverse addresses these concerns with an easy to use, easy to manage, compliant, secure, scalable, and globally available SaaS data service. Dataverse empowers organizations to work with any type of data and any type of app, and use the data within it to gain insights and drive business action.
As part of Microsoft Power Platform, Dataverse requires no or little code to be written, so it can easily be used by everyone from knowledge workers to professional developers.
Knowing that it's built on Azure, organizations choosing Dataverse can be confident that it's globally available, compliant, scalable, and secure.
Work with any type of data
Dataverse is designed to work with any type of data and incorporates all the major categories of data technologies that your organization needs—relational, non-relational, file, image, search, and data lake.
Dataverse includes a set of visual designers to create, edit, and interact with data. This makes it easy to quickly define the tables, relationships, business rules, forms, and workflows that represent your business.
With the easy-to-configure integration features built into Dataverse, deep integration with Microsoft's cloud services such as Azure, Dynamics 365, and Microsoft 365—plus access to many connectors in Power Automate and Azure Logic Apps—Dataverse can connect to the devices, apps, systems, services, and popular SaaS offerings that contain the data for your business.
As a result, a wide range of enterprise integration scenarios—from retrieving data sent in a spreadsheet as an email attachment to emerging scenarios like using Dataverse data in a blockchain network—can be achieved with ease and with little to no code required. Integration efforts that previously were measured in days and weeks can now often be measured in hours and minutes.
In addition to providing the ability to create data or import it from other systems, Dataverse also supports virtual tables. Virtual tables map data in an external data source so that it appears to exist in Dataverse. This enables Dataverse to execute real-time data operations against the external data source. More information: Create and edit virtual tables that contain data from an external data source
Work with any type of app
When an organization wants to create a new app, it can realize additional productivity gains by using Dataverse with Power Apps. Power Apps understands the rich metadata included in Dataverse and uses it in multiple ways to help you rapidly build great-looking apps that are secure and scalable, and make them available across desktop, web, mobile, and Microsoft Teams.
Organizations that use Power Apps can quickly develop mobile apps for iOS and Android. You can also take advantage of Dataverse mobile offline functionality, which enables apps to collect, query, and interact with data when offline.
For organizations that want to integrate Dataverse data into existing apps or write new apps by using custom code, Dataverse provides a powerful REST-based API, a developer SDK, and a growing list of samples for common scenarios.
You can also use Dataverse in bot-based apps that deliver intuitive, interactive dialogues with employees, partners, and customers. Whether they're embedded within Power Apps or custom code, bots can be built quickly by using Microsoft Copilot Studio and powered by Dataverse data.
The goal of Dataverse working with any app means it should also work with the tools that knowledge workers and professional developers use. To help them be even more productive, Dataverse is integrated into popular tools such as Excel, Outlook, Dynamics 365 customer engagement apps, Power BI Desktop, Power Query, Azure Data Factory, Data Export Service, and SQL Server Management Studio. More information: Work with any type of app
Analytics and reporting
Dataverse can be used to gain insights and drive business action using analytics and reporting. Dataverse also includes a variety of ways to deliver data and insight to key decision makers.
Dataverse includes the ability to create lightweight charts and paginated reports. The data in Dataverse can also be used with Power BI to create rich, interactive reports and dashboards.
For organizations that are interested in employing AI to analyze their data, AI Builder can give everyone in the organization—regardless of their technical expertise—the ability to add AI capabilities to the business process flows they create and use. Delivered as part of Microsoft Power Platform, AI Builder includes six pre-built AI models that can be used in Power Automate and Power Apps, and to evaluate data within Dataverse.
To support advanced analytics and machine learning, Dataverse includes a managed data lake. Data within the lake can be used to run Power BI reporting, machine learning, data warehousing, and other downstream data processing.
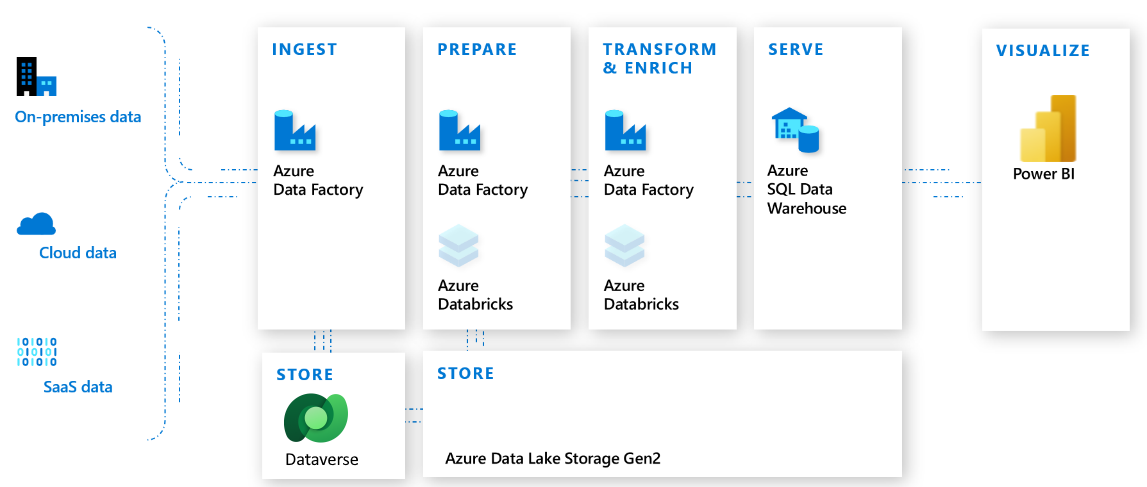
One of the benefits of the data being in Azure Data Lake is that organizations can take advantage of Azure Synapse Analytics. This service can deliver added productivity by bringing together enterprise data warehousing, data exploration, code-free data orchestration, deeply integrated Apache Spark and SQL engines, and integrated AI and BI.
Security
Dataverse uses Microsoft Entra identity and access management mechanisms to help ensure that only authorized users can access the environment, data, and reports.
Dataverse uses role-based security to group together a collection of privileges. These security roles can be associated directly with users, or they can be associated with Dataverse teams and business units.
In Dataverse, individual rows can be shared on a one-by-one basis with another user. Because row-level control of access isn't adequate for some business scenarios, Dataverse has a column-level security feature to allow more granular control of security at the column level.
Dataverse also includes two security models that can be used for hierarchies: the manager hierarchy and the position hierarchy. With the manager hierarchy, a manager must be within the same business unit as the report, or in the parent business unit of the report's business unit, to have access to the report's data. The position hierarchy allows data access across business units.
Because Dataverse is built on Azure, it benefits from the Azure platform's powerful security technologies. Encryption of data, at rest and in transit, preserves confidentiality.
Dataverse is governed by the Microsoft Online Services Terms and the Microsoft Privacy Statement.
More information: Security concepts in Dataverse
Compliance
Compliance is a key concern for organizations. Microsoft regularly engages with dozens of regulators around the world, so organizations can be assured that the data placed in Dataverse is held in accordance with stringent industry safeguards. Dataverse complies with numerous standards, and compliance is verified by third-party audits and certifications.
The list of currently supported standards can be found at the Microsoft Trust Center website.
Availability and scalability
Dataverse is designed to meet enterprise-level scalability needs and offers a service level agreement of 99.9% uptime.
To help ensure service levels, availability, and quality, entitlement limits to the number of requests users can make each day are governed by licenses. Service protection limits have also been put in place against malicious behavior that would otherwise disrupt service for all customers.
Microsoft Power Platform requests
Microsoft Power Platform requests consist of actions that users perform across various products.
At a high level, the following constitute Microsoft Power Platform requests:
Connectors: All API requests to connectors from Power Apps or Power Automate.
Power Automate: All Power Automate step actions.
Dataverse: All create, update, delete (CRUD) operations, in addition to special operations like "share" or "assign." These can come from any client or app, using any SOAP or REST endpoint. These include—but aren't limited to—plug-ins, asynchronous workflows, and custom controls making the abovementioned operations.
The specific number of allowed requests that a user can make in a 24-hour period is governed by the user's license.
Entitlement limits
Entitlement limits represent the number of requests users are entitled to make each day. The allocated limit depends on the type of license assigned to each user.
For information about these entitlement limits, see Microsoft Power Platform requests allocations based on licenses.
For information about viewing and allocating capacity add-ons, see Capacity add-ons.
For information about purchasing individual capacity add-ons, see the Power Apps and Power Automate licensing guide.
Service protection limits
Service protection limits exist to protect the health of the service for everyone. These limits provide a level of protection against random and unexpected surges in request volumes that threaten the availability and performance characteristics of the Dataverse platform.
The service limits the number of concurrent connections per user account, the number of API requests per connection, and the amount of execution time that can be used for each connection. These are evaluated within a five-minute sliding window. When one of these limits is exceeded, an exception is returned by the platform.
Service limits aren't expected to negatively affect normal usage of Dataverse.
For information about current service protection limits for each service, see:
Dataverse API request limits: Applicable to Dynamics 365 customer engagement apps, such as Dynamics 365 Sales and Dynamics 365 Customer Service, in addition to connections from Power Apps and Power Automate to Dataverse.
Microsoft Power Automate limits: Applicable for Power Automate.
Limits in connectors: Applicable for Power Automate and Power Apps.
Capacity add-ons
The specific number of allowed Microsoft Power Platform requests that a user can make in a 24-hour period is governed by the user's license. For scenarios where additional capacity is required, a Power Apps and Power Automate capacity add-on allows customers to purchase additional requests.
Each capacity add-on provides an additional 10,000 requests every 24 hours, which can be assigned to any user. Multiple capacity add-ons can also be assigned to the same user.
Dataverse has entitlement limits that will evaluate the number of requests made against the number allowed by their current license.
Backups
Dataverse provides two types of backups: automatic backups, referred to as system backups, and manual backups.
System backups
System backups back up all environments. They take place automatically and continuously. The underlying technology used is Azure SQL Database. For more information about Azure SQL automated backups, see Automated backups.
System backups for production environments that have been created with a database and have one or more Dynamics 365 applications installed are retained for 28 days. System backups for production environments that don't have Dynamics 365 applications deployed in them are retained for seven days. System backups for sandbox environments are retained for seven days.
Manual backups
Manual backups are user-initiated, typically done before making a significant customization change or applying a version update.
Both sandbox and production environments can be manually backed up. Sandbox backups are retained for seven days. Manual backups for production environments that have been created with a database and have one or more Dynamics 365 applications installed are retained for 28 days. Manual backups for production environments that don't have Dynamics 365 applications deployed in them are retained for seven days.
There's no limit to the number of manual backups that can be made, and manual backups don't count against storage limits.
Note
Both system and manual backups may only be restored to an environment in the same region in which it was backed up.
More information: Back up and restore environments
Datacenter regions
As many organizations do business globally, their data needs are also global in nature. With Dataverse deployed and supported in regions across the world, organizations can have confidence that Dataverse is available when and where they need it.
For the current list of datacenter regions, see Datacenter regions.
See also
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for